Pneumonia, Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis Flashcards
Gram positive cocci are observed under a microscope. They are catalase negative. What type of cocci are they?
Streptococci
A streptococcus was identified and hemolytic classification was performed. The blood agar is shown below. The bug is alpha hemolytic and bile sensitive. What is the bug?

Streptococcus pneumoniae
What are the virulence factors of S. pneumoniae?
Capsule and Leukocidin
Is there a vaccine available for pneumococcus? Who is it generally administered to? What does it contain?
Yes; Children and elderly; Polysaccharide capsule in polyvalent vaccine.
What is the traditional Tx for pneumonia? Alternate? What is an important test to perform in determining Tx?
Penicillin/Erythromycin; Vancomycin; AB sensitivity/resistance testing
What are other important pathogens that cause pneumonia?
- Group B streptococci (S. agalactiae)
- Klebsiella
- S. aureus
- HACEK group of gram negative rods (Haemophilus, Actinobacillus actiomcetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella species)
What strains of bug cause Rheumatic Fever?
- Group A streptococci (S. pyogenes) - M3, M5, M13 strains
What are the clinical features of Rheumatic Fever?
- Fever
- Polyarthris
- Endocarditis
- Myocarditis (Murmur)
A patient presents with rheumatic fever. A heart biopsy is performed and the following morphology is found. What is this?
Aschoff body
How is rheumatic fever Dx?
- IgM anti-Streptolysin O Ab
- Lesions/joints are sterile
What are serious complications of Rheumatic fever? What can these complications predispose a patient to?
Fibrosis/calcification of endocardium, permanent valve distortion; Life-long risk of endocarditis
What is the Tx for rheumatic fever?
Aspirin/steroids to treat Syx
What are preventative measures for those who have Hx of RF?
Aggressive AB Tx (Penicillin/Erythromycin)
Blood is taken from a patient with endocarditis and cultured. The bug is alpha hemolytic and bile resistant. What is the bug? Where
Streptococcus viridans
What bug is expected to cause endocarditis in patients with IV lines or drug abusers?
S. aureus
What are the typical lesions found in endocarditis? What is a major problem with treatment of endocarditis?
Vegetations; ABs don’t penetrate vegetation well
A patient with endocarditis shows the following lesions. What are they?
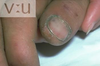
Splinter hemorrhages caused by fragments of septic vegetations
What are the preventative measures undergone by patients at risk for endocarditis?
Prophylactic ABs at the time of dental Tx, Catheterization
What type of organisms are catalase positive? How effective is the Pneumovax vaccine against these organisms?
Staphylococcus; Not at all. Pneumovax only protects patients from pneumococcus (catalase negative)
Why is bacterial pneumonia more common in the winter?
Viral coughs and colds predispose patients to pneumonia and are more common in the winter
What is the value of penicillin in the management of Rheumatic Fever?
Can prevent a recurrent attack in a patient with a history of the condition.
In which of the following conditions is the bug likely to be found in the blood?
- Streptococcal phryngitis
- Pneumococcal pneumonia
- Bacterial Endocarditis
- Rheumatic Fever
Penumococcal pneumonia and Bacterial endocarditis
Which of the following conditions is the anti-streptolysin Ab assist the Dx?
- Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Pneumococcal pneumonia
- Bacterial endocarditis
- Rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever


