Plasma Cell Dyscrasias Flashcards
Most patients start out with MGUS and then progress to ______ before developing _____
Most patients start out with MGUS and then progress to asymptomatic (smoldering) myeloma before developing symptomatic myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a monoclonal tumor of _____
plasma cells
Multiple myeloma is preceded by a premalignant tumor with which it shares genetic abnormalities, including dysregulation of the _____ pathway
cyclin D / retinoblastoma pathway
Malignant plasma cells interact with the bone marrow environment, leading to the activation of ____, suppression of ____, and thus development of ______.
Malignant plasma cells interact with the bone marrow environment, leading to the activation of osteoclasts, suppression of osteoblasts, and thus development of lytic bone disease.
The clinical and pathologic findings associated with multiple myeloma are in large part a consquence of: (2)
- tumor mass effect of the malignant plasma cells proliferating in the bone marrow, or
- abnormal secretory products from the malignant plasma cells including monoclonal immunoglobulins and cytokines
_____ is the presenting symptom of multiple myeloma in 70% of patients
bone pain
(pathologic fractures, associated neurological pain)
Commonly in vertebral column, ribs, skill
Findings associated with abnormal immunoglobulins and other factors secreted by malignant plasma cells:
Renal disease
Rouleaux
Amyloid
Hyperviscosity
Cryoglobulins
Coagulation abnormalities
What are CRAB symptoms associated with Multiple Myeloma?
hyperCalcemia
Renal disease
Anemia
Bone disease
How is Multiple myeloma diagnosed?
- Clonal bone marrow plasmacytosis of >10%
- Myeloma-defining event
- CRAB
- Biomarkers
- 60% or more clonal plasma cells in bone marrow
- MRI bone lesion of greater than 5mm
- FLC ratio of 100g/dl or greater (involved light chain of at least 100)
What is SPEP? What is it used for?
SPEP is Serum Protein ElectroPhoresis, and it is used in conjunction with Immunofixation to look at what immunoglobulins are present in serum.
In normal patients, should see a smear on SPEP and presence of various immunoglobulins composed of various chains.
In Multiple Myeloma, usually see either IgG or IgA, with one particular light chain associated - suggests monoclonality.

How is the Bence Jones protein detected via SPEP and Immunofixation? What does this indicate?
The Bence Jones protein is detected via urine SPEP/Immunofixation. Reveals the presence of ONLY a kappa light chain.
These proteins in the urine indicate the potential for renal failure development associated with Multiple Myeloma

What test is being run in this image? Are the results normal or abnormal?
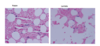
This is a bone marrow clonal plasmacytosis study staining for the presence of kappa and lambda.
This is a normal result - see blue staining confirming presence in each test.
(Abnormal result included here)

MGUS:
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
Characterized by high protein, but below 3
<10% clonal plasma cells in bone marrow
NO end organ damage (no CRAB symptoms)
Smoldering (Asymptomatic) Multiple Myeloma characteristics:
>3 g/dl serum monoclonal protein OR >10-60% bone marrow plasma cells OR urinary monoclonal protein
AND
NO myeloma defining events, i.e. no CRAB symptoms
Amyloidosis:
Clinical syndrome in which a precursor protein is secreted in a soluble state. The precursor becomes insoluble at some tissue site and compromises organ function.