Pharynx and Esophageal anatomy Flashcards
CORE Radiology Radiology Assistant
What causes indentation of the anterior esophageal wall?
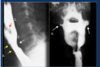
Submucosal venous plexus over cricoid cartilage (=post cricoid impression)


Curved arrow: obliquely coursing pharyngoepiglottic fold
V: vallecular pouches
open arrows: median glossoepiglottic fold
Straight solid arrow: free margin of the epiglottis
P: piriform sinus
open arrowheads: post cricoid line (bulk of larynx pressing on the anterior pharynx)
white arrow: aryepiglottic fold
a: arytenoid cartilage
PV: prevertebral soft tissues
H: hyoid bone
bot: base of tongue

How many muscular layers in the esophagus?
Two layers of muscle:
Inner: Circular
Outer: Longitudinal and Broken down into thirds
- upper 1/3: striated muscle
- middle 1/3: striated and smooth
- lower 1/3: smooth
Where is the cricopharyngeus muscle located?
Cricopharyngeus is along the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage around C5-C6.
It is the upper esophageal sphincter and demarcates the start of the cervical esophagus
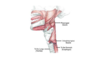
What is the “Z line”?
Z line = Interdigitation of the stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus with the columnar epithelium of the stomach. Also know as the squamocolumnar junction.
B-line and Z line are interchangable


What type of cells line the mucosa of the esophagus?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
This is why SCC happens in the mid-esophagus. If you see an apple core lesion in the middle of the esophagus, likely SCC.
Name the rings of the esophagus
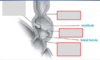
A ring: muscular ring
B ring: mucosal ring (squamocolumnar junction/z-line)
C ring: diaphragmatic impression
Schatzki ring: Pathologic narrowing of the B ring

What causes lateral pharyngeal pouches?

Protrusion of the lateral pharyngeal wall through the thyrohyoid membrane
https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.1148/rg.337125153
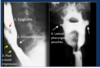
What causes the lateral pharyngeal pouches?
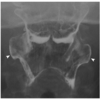
Protrusion of the lateral pharyngeal wall through the thyrohyoid membrane
“Lateral protrusion of the lateral hypopharyngeal walls. Anteroposterior image from an air-contrast barium study of the pharynx demonstrates lateral protrusion of the superior one-third of the lateral walls of the piriform sinuses (arrowheads). This phenomenon is more commonly seen in elderly patients, in whom the supporting thyrohyoid membrane is weakened, and becomes more pronounced with increased pharyngeal pressure during performance of a modified Valsalva maneuver.” https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.1148/rg.337125153
Is there a serosal layer in the esophagus?
No serosal layer in the esophagus, which means direct invasion from carcinomas
What is the vestibule?
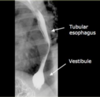
“Bulbous distention of the distal esophagus is called the vestibule and corresponds to the manometrically-defined lower esophageal sphincter. This distention is best demonstrated by breath holding in inspiration or a Valsalva maneuver.”
Do not mistake this for a hiatal hernia. https://radiologyassistant.nl/chest/esophagus/esophagus-i-anatomy-rings-inflammation
Describe what a normal esophagus should look like on an esophagram:
Esophagus mucosa: normal thin, parallel, uniform mucosal folds


At what diameter of narrowing of the esophagus do patients become symptomatic?
<13 mm


