Pharyngitis Flashcards
____________
Sore throat: common chief complaint
Majority are non-bacterial/viral: part of the influenza
and common cold syndrome
Uncommon in children < 1 yr
Peak: 4-7 yrs
May continue throughout childhood and into adult life
Pharyngitis
What is the peak age of pharyngitis?
4-7 yo
Response to antibiotics
Complications of streptococcal infection (Number 1
most dreaded etiology)
_______________
Acute streptococcal pharyngitis: warrants accurate
diagnosis and therapy to prevent suppurative and nonsuppurative
complications.
The life threatening infectious complications of
oropharyngeal infections warrant some discussion.
Rheumatic fever
glomerolonephritis
Tonsillitis/Epiglottitis
Uvulitis
Peritonsillar abscess __________-
Retropharyngeal abscess ____________
Ludwig angina___________-
Vincent angina__________________
(Quinsy)
(prevertebral)
(submandibular)
(mixed anaerobic bacteria)
What are the etiology of pharyngitis?
Infection
Bacterial/Viral/Fungal
Tonsillitis/Epiglottitis
Uvulitis
Peritonsillar abscess (Quinsy)
Retropharyngeal abscess (prevertebral)
Ludwig angina (submandibular)
Vincent angina (mixed anaerobic bacteria)
2. Irritation
Cigarette smoke/smog
Inhaled irritants
Reflux esophagitis
Chemical toxins
Dry hot air
Hot foods, liquids
3. Others
Tumors
Granulomatosis
Foreign body
What are the viral etiologies?
Viral Etiology
Parainfluenza (types1-4)
Influenza
Rhinovirus
Coronavirus
RSV
Adenovirus
Herpes simplex 1&2
Epstein-Barr virus
Adenovirus (types 2,4,7,14,21,others)
Coxsackie A & B
CMV
HIV
Human Herpesvirus6
Measles
Varicella
Rubella
What are the bacterial etiology?
Bacterial Etiology
S. pyogenes (lives in throat, ↑ if stressed)
Grp A-β hemolytic strep (GABHS)
Grp C & G - β hemolytic strep
Mixed aerobic/anaerobic organisms
Neisseria gonorrheae
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Yersinia enterocolitis
Chlamydia pneumonia atypical pneumonia &
Mycoplasma pneumonia pharyngitis
Arcanobacterium hemolyticum
Francisella tularensis
___________________ (lives in throat, ↑ if stressed)
S. pyogenes
Inflammatory mediators generated by viruses
Bradykinin & Lysylbradykinin
Stimulate pain nerve endings
Direct invasion and colonization of the pharyngeal
mucosa
Elaboration of virulence factors: exotoxins, hemolysins,
streptokinase, deoxyribonucleases, proteinases,
hyaluronidase – confer resistance to phagocytosis and
destruction.
Pharygitis pathophysio
What are the pathological changes in viral infection?
Viral pharyngitis
Edema, hyperemia ( increase blood flow) of tonsils and pharyngeal mucous
membrane
Nasopharyngeal hyperplasia
Vesiculation and mucosal ulceration
Herpes simplex & Coxsackie A
Inflammatory exudate
Adenovirus & Epstein-Barr virus
__________
Intense inflammatory response : marked erythema (**redness of the skin)
Edema of fauces and uvula
Grayish yellow tonsillar exudate
Streptococcal
__________ –drumstick appearance
Fibrous pseudomembrane with necrotic epithelium,
leucocytes, bacterial colonies
Dislodgement of pseudomembrane provokes bleeding and
aspiration
Bull Neck ➡ due to swelling
Diphtheria
This is a clinical feature of : ______________
Mild to moderate pharyngeal discomfort
Soreness, scratchiness, irritation
Rhinorrhea and post nasal discharge
Low to moderate temperature elevation (38.5C)
Pharynx may appear normal or with mild edema and
erythema
NO pharyngeal/tonsillar exudates
Complaints subside over 3-4 days
Pharyngitis with the common cold
This is a clinical feature of: ___________
Sorethroat: major complaint
Myalgia, headache, cough
Coryzal (acute inflammation of the mucousmembrane of the nasal cavities; cold in the head.) symptoms and cough
Fever - uncommon, if present:early defervescence ( abatement of fever)
Edema/erythema of pharynx – mild
NO exudates, NO painful cervical adenopathy
Pharyngitis with Influenza
Pharyngoconjunctival Fever : _________________
Marked sore throat with cough, malaise, myalgia,
headache, chills, dizziness
High grade fever : 5-6 day duration
Conjunctivitis: follicular type, bilateral
Pharyngeal erythema, some exudates
Cervical adenitis
Adenoviruses
____________
-marked sore throat, erythematous pharynx, fever, rash
- red peritonsilar area
- Posterior pharynx ➡ Petechiae
** hand foot mouth disease— vesicles not seen in the mucosa
Pharyngitis due to Coxsackie Viruses
What are the two syndromes of pharingitis of coxsackie?
2 syndromes:
1 Herpangina
2 HandFootMouth disease(
1_______________: discrete(1-2mm across) painful graywhite
papulovesicular lesionson thesoft palate,uvula,
ant. tonsillar pillars x 7 days; lesions rupture - ulcerate
** Herpangina**
____________): painful
vesicles in the oropharynx, ulcerative vesicles in the palms
and soles,trunk; not toxic looking; < 7days
2 HandFootMouth disease(CoxsackieA16
_______________
_______________– oral infections common during childhood and
adolescence
high fever, gingivostomatitis which become ulcers -
anterior portion of mouth and lips, tongue, palate,
tonsils, pharynx; tender lymphadenopathy; Drooling,
refusal to eat/drink
Resolves in 7-14 days, even if untreated
Pharyngitis and the Herpes simplex virus
HSV1
________________
“kissing disease”
Epstein-Barr virus found in the oropharynx, spread by
person to person contact/blood transfusion
Common among adolescents
With hepatomegaly and splenomegaly ➡ avoid contact
sports
Incubation: 4-7wks
Prodome: 2-5 days: chills, sweats,feverishness, malaise
Triad: Severe sore throat, high grade fever,
Lymphadenopathy– cervical,axillary,inguinal
Tonsillitis in 70-90%; Tonsillar exudates in 30%
Hepatomegaly in 10-15%;
Splenomegaly in 50%
Leucocytosis in 60-70%; lymphocytosis
10% - atypical lymphocytes by 2nd wk of illness
Self-limited, resolves in 3 wks
Diagnosis:
- Heterophil antibody test: IgM
85% of older children and adults are positive
2nd wk to illness – 6months
- atypical lymphocytes (periph smears) on 2nd wk of
illness
- specific antibody tests
- viral culture
- DNA PCR
Management: No need for antiviral drugs
- Avoid contact sports until pt is fully recovered and
spleen is not anymore palpable
- Do not give Ampicillin/Amoxicillin: may cause the
appearance of morbilliform rash
- Steroids only for those with airway obstruction,
massive splenomegaly, myocarditis, hemolytic anemia
Viral Pharyngitis
Symptomatic Treatment
Relieve pharyngeal discomfort
Warm saline gargle
Anesthetic sprays and lozenges (benzocaine)
Rest, liquids
Paracetamol/ibuprofen
CLINICAL FEATURE
MANAGEMENT
Infectious
Infectious Mononucleosis – Glandular Fever
What is the triad in infectious mononucleosis?
Severe sorethroat
High grade fever
lymphadenopathy
What is the mgt for viral pharyngitis?
Viral Pharyngitis
Symptomatic Treatment
Relieve pharyngeal discomfort
Warm saline gargle
Anesthetic sprays and lozenges (benzocaine)
Rest, liquids
Paracetamol/ibuprofen
15% of all episodes of pharyngitis
Prevention of sequelae : (acute rheumatic fever & acute
glomerulonephritis)depends on the timely diagnosis of
Strep pharyngitis and prompt antibiotic tx
Incubation: 2-5 days; contact with respiratory
secretions of a person with strep pharyngitis
Most common among school-aged & adolescent
Associated with crowding, close contact in
school/military installations
Grp A Streptococcal pharyngitis
Colonization of the pharynx : results in asymptomatic
carrier state
What is the major virulence factor of Group A strep?
Acute infection
Major virulence factor: M protein – resistance to
phagocytosis by PMNs
Type specific immunity to specific M serotype develops
after infection
Scarlet fever – GABHS erythrogenic exotoxin (A,B,C)
Grp A Streptococcal pharyngitis
Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no cough
Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea, vomiting (in
contrast to viral:cough, rhinorrhea, conjunctivitis,
stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
Marked pharyngeal erythema
Petechiae on palate(donut lesion), enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged cervical lymph
nodes
Group A Strep
___________: Scarlet fever
- Not everybody gets scarlet fever!
Pharyngitis with fine diffuse red “sand paper” rash
that blanches with pressure; desquamation follows
after 1 wk
Circumoral pallor: red face with pallor around the
mouth
Pastia’s lines: accentuated erythema over flexor creases
especially on the antecubital
**Strep pharyngitis
_____________
Signs
Tonsillar & pharyngeal
erythema and
exudates
Donut lesions – soft
palate
Beefy red and swollen
uvula
Anterior cervical
adenitis
Scalatiniform rash
Symptoms
Sudden onset sore
throat
Pain on swallowing
Fever
Headache
Abdominal pain
Nausea
Vomiting
GAS infection
signs
Conjunctivitis
Stomatitis
Discrete ulcerative
lesions
symptoms
Coryza
Hoarseness
Cough
Diarrhea
Not GAS infection
Diagnosis
Gold standard Group A strep: _________-
throat culture
NOTE : Gram stain- more practical (gm + in chain/pair)
Lab confirmation of GrpA Strep (GAS) pharyngitis
recommended – because it is not possible to clinically
differentiate viral vs GAS pharyngitis
Swab of tonsil and post pharynx for C/S
– cannot distinguish carrier vs true infection
What is being detected in rapid diagnostic test for group A strep?
Rapid test: detect grp A carbohydrate Ag on the cell wall of
GAS – latex agglutination test/ optical immunoassay/
chemiluminescent DNA probes
__________________
– Valid for determining past infections
Strep Antibody Tests: (wks after onset)
–Tool for evaluating possible post-strep illnesses
_______________________
ASO – antistreptolysin O
antiDNAse B
antihyaluronidase
When to start treatment in Group A strep pharyngitis?
________________
Antibiotics should be started within 9th day of onset of Strep
pharyngitis…
NOTE: to prevent acute rheumatic fever
To prevent the suppurative sequelae: i.e. peritonsillar
abscess
To produce a rapid resolution of the signs and symptoms
and to terminate contagiousness within 24 hrs (reduce
transmission)
To shorten the clinical course of the disease
What are the complications of Group A strep pharyngitis?
Complications
Otitis media
Sinusitis
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Rheumatic Fever
Abscess Formation:
-peritonsillar abscess
-retropharyngeal abscess
(both will require intensive antibiotic tx and drainage of
the abscess)
Etiologic agent: GAS/anaerobes
Occurs in the potential space between the superior
constrictor muscles and the tonsil
Clinical manifestations:
preceded by acute pharyngitis with fever
severe throat pain, trismus (lock jaw), difficulty
swallowing or speaking, hot potato voice,
torticollis ( also known as wry neck or loxia, is a dystonic condition defined by an abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position), swollen inflammed tonsils,
displaced uvula
Treatment:
- Antibiotic therapy effective vs GABHS
- Surgical drainage
- Needle aspiration
- Incision and drainage
- Tonsillectomy
Peritonsillar Abscess
Involves the space between the posterior pharyngeal
walland theprevertebral fascia:has many lymph nodes
which become infected and progress to suppuration.
Clinical manifestations: abrupt onset of high fever,
difficulty feeding, severe distress with throat pain,
hyperextension of head, noisy gurgling respiration,
stridor, drooling, bulge on the posterior pharyngeal
wall,cervical lymphadenopathy
Differential dx: epiglottitis/foreign body aspiration,
meningitis, lymphoma, hematoma, vertebral
osteomyelitis
Diagnosis: I&D with culture of abscessed node
Soft tissue neck films/CT scan
Most often polymicrobial: GABHS, oropharyngeal
anaerobes, Staph aureus, H.flu, Klebsiella
Retropharyngeal Abscess
Treatment
- IV antibiotics with or without surgical drainage
- Surgical drainage: for patients in respiratory distress
or unresponsive to IV antibiotics
Retropharyngeal Abscess
What are the red flags associated with sore throat
___________________________
Fever of > 2 wks
Duration of sore throat >2wks
Trismus, drooling, cyanosis
Hemorrhage
Assymetric tonsillar swelling
Respiratory distress (airway obstruction/pneumonia)
Apnea
Severe unremitting pain
What is the DOC for sorethroat with red flags?
Drug of choice Child Adol
Pen V BID/TID x10d PO 250mg 500MG
Pen G OD IM 600,000 U 1.2M U
<25kg >25kg
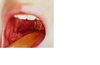
Pseudomembrane of Diphteria

Bull neck: Diptheria

Herpangina: discrete(1-‐‑2mm across) painful gray-‐‑
white papulovesicular lesions on the soft palate,
uvula, ant. tonsillar pillars x 7 days; lesions rupture
-‐‑ ulcerate

HFMD

Pharyngitis and the Herpes simplex virus
• HSV1 – oral infections common during
childhood and adolescence
• high fever, gingivostomatitis which become
ulcers -‐‑ anterior portion of mouth and lips,
tongue, palate, tonsils, pharynx; tender
lymphadenopathy;Drooling, refusal to eat/
drink
• Resolves in 7-‐‑14 days, even if untreated

Infectious Mononucleosis – Glandular
Fever
• Epstein-‐‑Barr virus found in the
oropharynx, spread by person to person
contact/blood transfusion
• Common among adolescents
• Incubation: 4-‐‑7wks
• Prodome: 2-‐‑5 days: chills,
sweats,feverishness, malaise

Strep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesStrep Pharyngitis: Clinical Features
• Sudden onset of fever and sore throat, no
cough
• Headache, malaise, abdom pain, nausea,
vomiting (in contrast to viral: cough, rhinorrhea,
conjunctivitis, stridor, diarrhea, hoarseness)
• Marked pharyngeal erythema
• Petechiae on palate, enlarged tonsils with
exudates, strawberry tongue, enlarged
cervical lymph nodesv

Peritonsillar Abscess

Retropharyngeal Abscess


