Pharmacology and Therapeutics - Carie Martin Flashcards
What is CKD?
A progressive and irreversible condition
Known as an eGFR of <60ml/min/1.73m2 and/or kidney damage that is present for 3 or more months
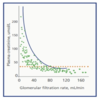
What molecule is used to measure glomerular filtration rate?
And why?
Creatinine –> A waste product from muscle
It is generated at a relatively constant rate
Mostly removed via filtration
However…. Affected by age, race and weight, and it has a non-linear realtionship with true GFR
What equation is used to calculate renal function in order to figure out dosing adjustments?
And what are the downsides of this?
Cockcroft and Gault (CrCl)
Not accurate when the CrCl is less than 20ml/min
Also problematic in those with large body weight/muscle

What are some of the causes of CKD?
Diabetes –> Number 1 cause
Hypertension
Previous AKIs
Nephrotoxic drugs
Glomerulonephritis
Reflux neuropathy
What are some of the complications of CKD?
Itching –> Due to build up of toxins
Oedema
Nausea
Restless legs and cramps
Electrolyte imbalances

Can ACEi be used in CKD?
YES
They are protective in low doses
Contraindicated in AKIs!
How do we manage Renal Anaemia in CKD?
Give Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents (ESAs) and iron (eg, Darbepoetin)
Aim for a Hb level of 10-12g/dL
How does Renal Bone Disease occur?
And how is treated?
A reduction in Vit D hydroxylation causes hypocalcemia. This increases parathyroid stimulation, which causes more calcium and phosphate to be released from our bones
Use alfacalcidol 250ng three times week (already hydroxylated vitamin D)
Phosphate binders are also used (eg, calcium carbonate/acetate)
What can Uremia cause?
Displacement of drugs from protein binding sites
Eg, phenytoin/diazepam/digoxin/sodium valproate/warfarin
What is the effect on insulin in CKD?
Insulin cannot be cleared, so its half-life is increased
So dose requirements are decreased
Which types of drugs will have problematic elimination in CKD?
Those that have over 25% excretion (unchanged) in the kidneys

Define Frailty
A syndrome of physiological decline in late life, characterised by marked vunerability to adverse health outcomes
People arent always old!!….but more likely
What’s the difference between compliance and adherence?
Compliance –> The extent to which the patients behaviour matches the prescriber’s recommendations
Adherence –> The extent to which the patients behaviour matches agreed recommendations from the prescriber
Give some examples of intentional and unintentional non-adherance
Unintentional –> Difficulty swallowing large tablets, Memory Problems, Complicated polypharmacy
Intentional –> Lack of confidence in drugs/prescriber, concerns of side effects, lack of information
What 5 things are assessed in a NOMAD assessment?
Knowledge
Visual Issues
Manual Dexterity
Cognition
Supply



