Medicines Design Flashcards
What are soft-drugs?
Drugs that are deactivated by metabolism (opposite of pro-drugs)
Why do we use soft-drugs?
Reduce the duration of action of drugs
Reduce side effects by restricting their avaliability outside of the target area
They often have a predicatable metabolic route, which produces no active metabolites

What are the 3 main groups that are added to drugs to make them into soft-drugs?
Esters
Carbamates
Quaternary Nitrogens
What is an isotere?
A molecule that has a different structure to the lead, but shares equal steric and electronic effects
A good example is changing an amide to an ester

Define Context Sensitive Half-Life
The time required to achieve a 50% decrease in concentration after stopping an infusion targeted to steady state
What is retrometabolic drug design?
Starting from the end point
For soft-drugs this means starting from the inactive metabolite, ensuring that no active metabolites are made from the final drug.
How would you make this B-blocker into a soft drug?
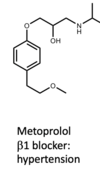
Replace the ether with an ester (with R groups)
Makes the inactive metabolite more likely to be formed

How do local anaesthetics work?
Reversible binding, and inactivation, of open sodium channels
They have a very high affinity for the open state of the sodium channel
Why is creating an effective local anaesthetic a chemical balancing act?
As non-protonated molecules have the fastest method of action
Protonated molecules bind to the receptor
So we need a mix of these so that the we can bind to the receptor, but we have a quick onset of action also
What local anasthetic will have a quicker onset of action?

Cocaine –> as it contains an ester
How do general anaesthetics work?
And what are the 3 things that they should ideally be?
Enhance the inhibitory effect of GABA(A) receptors
Should be….
Fast onset and recovery
Few side effects (wide therapeutic window)
Aqueous solubility

Why is Propofol not the perfect general anaesthetic?
Very lipophillic (only one hydrogen bond acceptor/donator)
Therefore administered as an emulsion

How can we improve Propofol?

Add phosphate groups to it, which are protonated at physiological pH….and so make it water soluble

How was Etomidate improved to MOC-Etomidate?
But why was this drug still problematic? And what was the solution?
The ester was altered to enable more rapid metabolism and prevent accumulation. However there was accumulation problems with the metabolite still!
CPPM has a space linker which causes the drug to be more potent and be metabolised more slowly. It also doesnt have accumulation of metabolites, which makes it a much safer drug.
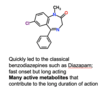
What is the main problem with Diazepam?
Very long acting due to many active metabolites.