Pharmacology and Therapeutics Flashcards
Explain the difference between pre and post ganglions
Preganglionic - The cell bodies are in the CNS
They are myelinated
The fibres release Ach –> which act on nicotinic receptors
Postganglionic - Cell body is in the autonomic ganglion
These are unmyelinated
The synapse is close to the target organ…..except for the adrenal medulla… which has no postganglionic fibre!!
Explain how ipratropium works
This is a muscarinic antagonist of both M2 and M3 receptors
This prevents the stimulations of M2 and M3, and in turn prevents the negative feedback loop that can occur when Ach builds up due to not binding to the M3 receptor

What is Wernicke-Korsakoff’s syndrome caused by?
Thiamine deficiency, normally caused by alcohol abuse
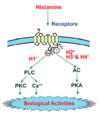
What will blocking H3 receptors do?
And what drug is used to exploit this?
This will increase the release of histamine
Ciproxifan is an inverse agonist, which will increase the histamine production, and increase wakefullness
Explain how Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhoea (AID) can occur
Broad spectrum antibiotics can disrupt the natural gut flora
Toxins produced from C.difficile can also cause an inflammatory response –> leading to diarrhoea

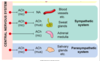
What are the 3 divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Enteric
How do you treat hepatic encephalopathy?
Reduce toxin production, and improve toxin excretion
Lactulose is good for reducing the nitrogen load in the gut (by binding to ammonia)
Antibiotics can be used to decrease ammonia forming bacteria
What is the mucus barrier used for in the stomach?
It is an alkaline barrier that protects the stomach lining from acid and pepsin
The mucus is secreted by surface mucous epithelial cells
This is all done under hormonal control
Where is histamine most commonly found?
Tissue mast granule cells
What are the key things to avoid when treating liver disease?
Drugs which cause…
Sedation –> as may worsen encephalopathy
GI Ulceration –> Due to possibility of bleeding as potentially a loss of clotting factors
Constipation –> As we need to get rid of toxins
Have a narrow therpeutic index
Are hepato/nephrotoxic
What makes up the enteric branch of the ANS?
And what neurotransmitters are used in it?
Myenteric and Submucosal plexuses
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Noradrenaline (NA)
Non-Adrenergic Non-Cholinergic (NANC)

What are the 4 different types of laxatives?
And how do they work?
Bulk Forming - These increase the size and fluid of the stools
Stool Softening - Reduce the surface tension, and increase the fluid content of the stools
Osmotic - Increases the volume and retention of intraluminal fluid
Stimulant - Increases peristalsis and water/electrolyte secretion by the mucosa
Muscarininc poisioning causes what kind of response?
Excessive parasympathetic responses
What is diarrhoea?
The abnormal passage of loose/liquid stools more than 3x daily….. or volume that is greater than 200g per day
Acute - Less than 14 days
Persistant - Longer than 14 days
Describe the 4 mechanisms of diarrhoea
Osmotic - Fluid and secondary ions are drawn into the lumen
Secretory - When fluid and electrolyte balance is unregulated
- This type will persist despite fasting
Inflammatory - Defective absorption of fluid and electrolytes
- Caused by the destruction of the mucosa….and associated with blood loss (dysentery)
Abnormal Motility - There is an increased motility, and so full absorption cannot take place