Pharmacology 1 Flashcards
What is pharmacology?
The study of drugs and their physiological effects
What is a drug?
Drug - An agent that interacts with specific target molecules within the body and produces a physiological effect.
What is a Ligand?
Ligand - substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose.
What is pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacodynamics - the mechanism by which drugs exert their effect on the body. “What drugs do to the body”
What is pharmokinetics?
Pharmacokinetics - what the body does to the drug (e.g. absorption, distribution, elimination)
What are the two main types of drugs?
-
Drugs with activity at high concentrations
- Little structural specificity
- Cause physical change
- e.g. general anaesthetics
-
Drugs acting at low concentration
- Structural specificity
- Act by chemical rather than physical interactions
- e.g. isoprenaline
What are Agonists?
Agonists – mimic endogenous ligands. They bind to a receptor and produce secondary effects
What are Antagonists?
Antagonists – binds to a receptor and prevents the action of an agonist
What are some key point about receptors?
- They are the site at which ligands (agonists or antagonists) can attach. Drugs can also target enzymes, carriers and ion channels.
- majority of drug receptors are proteins
- ligands may be neurotransmitters, hormones or local factors
- activation of receptors by an agonist produces a response
- Drugs have affinity and selectivity for receptors (i.e. drugs act preferentially with one receptor)
What are the types of receptors?
- Ligand-gated ion channels- Fast neurotransmitters
- G-protein coupled receptors - include adrenoreceptors and opioid receptors- Slow neurotransmitters
- Kinase-linked receptors - Include receptors for insulin, cytokines and growth factors
- Nuclear receptors – Include receptors for retinoic acids and vitamin D
Do you understand the following image on receptor action?
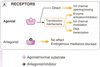
What are some common adrenogernic receptor sub-types?
- Beta 2 (lungs)
- Beta 1 (Heart)
- Alpha 1 (blood vessels)
THINK ASTHMA
Why has the development of drugs that interact with only one specific subtype revolutionised pharmacology?
It minimises side effects.
Why do side effects occur with drugs?
Side effects occur because:
- Receptors for a drug occur in several different tissue types, not just the target tissue.
- Non specificity of drugs
Why were drug regulations implemented, and when?
Regulations:
- Elixir of Sulfonamide tragedy in 1937 killed 107 children and led to the formation of regulations
- In the late 1950’s Thalidomide was used by pregnant women to treat morning sickness. Thalidomide was a teratogen (caused birth defects) so many children were born missing limbs
What are the assumptions of Drug-receptor interaction?
Assumed that the effect of a drug is proportional to the fraction of receptors occupied
Assumed that the maximal effect occurs when all receptors are occupied
These assumptions are not always true (e.g. some drugs can bind to more than 1 receptor subtype; some drugs are highly efficacious and do not need to bind to all receptors to achieve maximal effect)
What is the general drug-receptor equation?
Drug (D) + Receptor (R) ↔ DR → effect
What is Kd50 and Ed50 and what do they mean?
- KD is a binding constant and is numerically equal to the concentration of drug required to occupy 50% of the binding sites at equilibrium
- ED50 refers to the dose that produces 50% of maximum effect.
- Therefore KD=ED50 when effect is proportional to receptor occupancy and maximum effect occurs when all receptors are occupied.
ED50 is used to compare the potencies of different drugs:
Low ED50 means highly potent drug
High ED50 means a less potent drug
LOOK AT THE GRAPH IN CHANG’S NOTES :)
What happenes if a dose that yields more than the maximum effect is administered?
- • Max effect increases due to nonspecific effect; or
- • Max response decreases due to desensitization
What is potency?
Potency – a measure of the drug dosage needed to produce a particular therapeutic effect. It is determined by the strength of binding of a drug to a receptor or the receptor affinity for the drug
What is Efficacy?
Efficacy – a measure of the effectiveness of a drug in producing a maximum response. Antagonists have no efficacy (they stop responses rather than produce responses).
How do we measure dose-response?
Can use e.g. organ bath or blood pressure in live animal or some other variable.
Administering of a known dose of drug yields a measurable effect. Hence, a sigmoid dose-response curve can be plotted when maximum effectiveness has been established (two similar results in a row reach a platueu).


