Phakomatosis - TSC Flashcards
another name for TSC
Bourneville-Pringle
multiple AMLs, rhabdomyoma, Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM)
TSC

TSC
subependymal nodules along the ventricular surface (black arrowheads).
and tubers ( white matter bright spots)
Note radial migration line appearing as a thin, straight band of hyperintensity extending from the juxtaventricular white matter to the cortex (black arrow), and white matter cyst-like lesion located in deep white matter near the atrium of the right lateral ventricle (white arrowhead).

TSC
Subependymal calcified tubers in a 9-month-old boy. Unenhanced CT clearly demonstrates multiple subependymal tubers with bilateral calcification along the walls of the lateral ventricles.
SGCAs are characterized by proliferation of what cells
astrocytes and giant cells
typical location of SGCAs
foramen of Monro –> leads to obstructive hydro



peak occurence of SGCAs
8-18 years
typical SCGA size
> 1cm
most common location of cardiac rhabdomyomas
vetnricular septum
treatment of rhabdomyomas
most regress and are asymptomatic, so follow up echocardiograms
surgical resection for symptomatic rhabdomyomas, aka refractory arrhythmias or hemodynamic compromise
LAM gender prediliction
women > men
two common complications of LAM
- pneumothorax
- chylous pleural effusion
29yoF

LAM, associated with TSC

37yoF

LAM in TSC patient

37yoF

LAM with pneumothorax
female pt with TSC



AML, angio

AML before and after embolization

AML on US
A shadowing echogenic renal mass is relatively specific for AML.

AML on US and CT
A shadowing echogenic renal mass is relatively specific for AML.

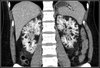
AML
when do you treat AMLs
size > 4cm

AML
AMLS have MACROSCOPIC fat so will not drop signal on OOP imaging. But they will demonstrate fat suppression