Peripheral blood flim Flashcards
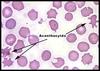
Acanthocytes (spur/spike cells) - describe, underlying path (2)
- RBCs show many spicules
- Abetalipoproteinamiae, liver disease, hyposplenism
So either due to alteration in membrane lipids or severe liver disease
Basophilic RBC stippling: description, underlying path (3)
Accellerated erythopoeisis OR defective HB synthesis - see small dots at the periphery (rRNA)
- megaloblastic anaemia
- thalassemia
- lead poisoning
- liver disease
- myelodysplasia

Burr cells (Echinocyte) - describe, causes (3)
Irregularly shaped cells
- uraemia
- GI bleeding
- stomach cancer

Heinz bodies - descibe, cause
Inclusions within RBCs of denatured Hb
- G6PD def, also liver disease

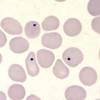
Howell jolly bodies - describe, causes (3)
Basophilic nuclear remnants (purple) in RBCs (normally should be expelled - indicate spleen damage)
- Post-splenectomy/ hyposplenism e.g. SCD, coeliac, amyloid
- megaloblastic anaemia
- hereditary spherocytosis
Leucoerythroblastic anaemia: describe, casue (1)
RBCs with nuclei + primitive WBCs enter the blood - due to marrow infiltration e.g. malignancy, myelofibrosis
Pelger Huet Cells - descibre, causes (2)
hyposegmented neutrophil
- congenital - lamin B receptor mutation
- acquired - myelogenous leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome
Polychromasia (sign of reticulocytosis) - describe, cause
RBCs of different shades - blue/grey; due to varying amounts of HB; this is a result of premature/inappropriate release from BM
Reticulocytes - describe, when are they increased? decreased?
Immature RBCs - increased in haemolytic anaemias, decreased in aplastic anaemia
Ribosomal RNA becomes visible wth methylene blue
Right shift - describe, cause
hypermature WBCs - hypersegmented neutrophils
- megaloblastic anaemia
- uraemia, liver disease
Schistocytes - describe, causes (3)
fragmented parts of RBCs
- microangiopathic anaemia e.g. DIC, HUS, TTP
Spherocytes - describe, cause (2)
Sphere shaped RBC
- hereditary spherocytosis
- Autoimmune haemolytic anemia
Stomatocytes - describe, causes (2)
Central pallor is curved/ rodshaped, RBCs appear as ‘smiling faces’ or ‘fish mouth’
Causes
- hereditary stomatocytosis - membrane defect causing K+ and Na+ leakage
- high alcohol & liver disease

Target cells (codocyte) - describe, causes (3)
Bull’s eye appearance in central pallor
- IDA
- thalassemia
- hyposplenism
- liver disease
Auer rods
clumps of granular material seen in cytoplasm of luekemic blasts

