Perineum 1 & 2 Flashcards
The perineum is the region of the trunk below the pelvic diaphragm and bounded by the pelvic outlet. It is subdivided by a line connecting the ischial tuberosities into 2 triangles that do not communicate. They are:
–anterior urogenital triangle(horizontal)
–posterior anal triangle (almost vertical)

What is the innervation and nerve supply of the perineum?
- Main innervation: pudendal nerve
- Main blood supply: internal pudendal artery & internal pudendal vein
The urogenital triangle consists of what 5 things?
- Skin
- Superficial fascia
- Superficial perineal pouch
- Perineal membrane
- Deep perineal pouch

The Superficial fascia of the urogenital triangle consists of 2 layers, a fatty layer and a membranous layer known as……………….
Colle’s fascia
The superficial perenial pouch is located between the colles’s fascia and the perineal membrane. It does what?
anchors external genitalia

The deep perineal pouch is located between the pelvic diaphragm and the perineal membrane. It includes what important structure?
external urethral sphincter
What 3 things make up the anal triangle?
- Skin
- Superficial fascia (fatty layer that extends into the ischio-anal fossa)
- Anal canal surrounded by the external anal sphincter

The pudendal nerve & internal pudendal vessels are the main nerve & blood supply of the perineum. The pudendal nerve leaves the pelvis through the…………. and enters the perineum through the………………
greater sciatic foramen
lesser sciatic foramen

Inferior to the………………., the pudendal nerve enters the…………………. canal formed from the obturator internus fascia (below pelvic diaphragm) to travel in lateral wall of ischioanal fossa. It is accompanied by the internal pudendal artery and vein.
ischial spine
pudendal

What kind of nerve is the pudendal nerve?
a mixed somatic nerve
What are the parts that make up the pudendal nerve (which is a mixed somatic nerve)?
- Inferior rectal nerve to the external anal sphincter and levator ani (GSE) and perianal skin (GSA)
- Perineal nerve
- Dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris, which is sensory (specially to glans) (GSA)

The perineal nerve (a part of the pudendal nerve) divides into what 2 nerves?
- Cutaneous posterior scrotal or labial branches (GSA) which goes to posterior scrotum or labia.
- Deep perineal nerve (GSE) which goes to skeletal muscles of the superficial and deep perineal pouches, including the external urethral sphincter/skin of vestibule, and mucosa of lower vagina (GSA)
Visceral innervation of the perineum comes from what?
- Branches of the pudendal nerve (SYMPATHETIC)
- Inferior hypogastric plexus (SYMPATHETIC AND PARASYMPATHETIC)
Branches of the pudendal nerve are sympathetic fibers (L1-2) which go to what?
- Skin of perineum (vessels, sweat glands, hair erector muscle)
- Vessels of skeletal muscles of perineum & mucosa of lower anal canal
- Erectile tissues of penis & clitoris
The Inferior hypogastric plexus has sympatheic and parasympathetic fibers that supply what?
- Sympathetic fibers (L1-2) to blood vessels of upper anal canal, internal anal sphincter, membranous urethra
- Parasympathetic fibers (S2-4) to blood vessels of upper anal canal, internal anal sphincter, membranous urethra, glands of reproductive system/erectile tissues of penis & clitoris (cavernous nerves)
- GVA fibers with parasympathetic fibers (S2-4)
What are the Internal Pudendal Artery Branches?
- Inferior rectal artery (Anal canal & sphincters)
- Perineal artery
- branches to Posterior scrotal or labial arteries.
• Terminal branches
- Artery to the bulb of the penis or vestibule
- Deep artery of the penis or clitoris
- Dorsal artery of the penis or clitoris

Which artery is essential for erection?
Deep artery of the penis!
* The deep artery of the penis or clitoris each enters a crus (corpora cavernosa).

What are the Internal Pudendal Vein tributaries?
- Inferior rectal vein
- Posterior scrotal or labial vein
- Vein to the bulb of the penis or vestibule

What are the exceptions to the tributaries of the Internal Pudendal Vein (meaning the veins that dont feed into the internal pudendal vein)?
- Deep dorsal vein of penis or clitoris: drains glans & corpora cavernosa; drains in prostatic plexus (male) or vesical plexus (female) of veins.
- Superficial dorsal vein of the penis or clitoris: drains corpus spongiosum, urethra, fascia & skin of penis in external pudendal vein (femoral vein)

Lymph Drainage from the Perineum is mainly to the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes, with important exceptions:
- The testis drains to lateral aortic nodes in the abdomen.
- Some lymph vessels follow the round ligament of the uterus from the uterus to the labium majus, which then drains to superficial inguinal nodes.
The Ischio anal fossa is filled with fat & loose connective tissue. It is bordered by skin, gluteus maximus, obturator internus and fascia, levator ani and fascia, and external anal sphincter.
On the lateral wall is the…………… containing the…………….
Pudendal canal
pudendal nerve & vessels

Crossing the ischioanal fossa are the…………………..
inferior rectal nerves and vessels (branch from pudendal n. and internal pudendal a. and v. at the sciatic notch)

What is important to note clinically about the Ischioanal fossae?
It is a common site for abscess formation. An infection in one ischioanal fossa may spread behind the anal canal into the other ischioanal fossa.

The anal canal is surrounded by what 3 things?
- Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle)
- External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle)
- Fat of the ischioanal fossa
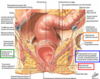
The pectinate line divides the anal canal into what?
• Superior Half:
- Anal columns joined by anal valves: terminal branch of superior rectal vessels
- Anal sinuses: exude mucus during defecation
• Inferior Half:
- Anal pecten (transition mucosa>skin) ending at anocutaneous (white) line

The internal anal sphincter is smooth muscle which is continuous with musculature of the rectum. It has………………. innervation from what plexus?
sympathetic & parasympathetic, GVE
inferior hypogastric plexus

What type of muscle is the external anal sphincter?
The external anal sphincter fuses with the……………….. (inferior rectal nerves, GSE)
Skeletal muscle
puborectalis

Above the pectinate line receives blood from the……………. artery
superior rectal

Above the pectinate line, the blood is drained from the internal rectal venous plexus through the superior rectal vein into the portal venous system. Lymph is drained to the………….. lymph nodes
internal iliac

Regarding the pectinate line, above the line is GVA fibers
from the inferior hypogastric plexus (………….), while below the line is GSA fibers from the inferior rectal nerves (……………………)
painless
painful!
Below the pectinate line receives blood from the………………… artery.
Blood is drained from the external rectal venous plexus through the inferior rectal vein to the cava venous system
Lymph to……………….. lymph nodes
inferior rectal
superficial inguinal
Hemorrhoids are enlarged submucosal rectal veins that are portocaval anastamoses between superior, middle & inferior rectal veins. They are due to portal hypertension, and straining or compression of abdominal veins during pregnancy.
Internal hemorrhoids are dilated tributaries of sup. rectal veins located…………………
External hemorrhoids are dilated tributaries of inf. rectal veins located
above the pectinate line (They tend to bleed but are painless due to GVA fibers)
below the pectinate line (They are painful due to GSA fibers)
Progression of feces through the anal canal with opening of internal anal sphincter is under……………… control (GVE)
parasympathetic
Opening of the external anal sphincter is VOLUNTARY (GSE) and under control of the……………. nerve (which is a branch of the pudendal n.). Fecal continence depends on that sphincter working appropriately!
inferior rectal nerve

What are the superficial parts of the urogenital triangle in a male?
Scrotum, raphe
–Homologue to labia majora in females
–Contains testes
Penis: Root, body, glans & corona
–Glans normally covered by skin (prepuce)
–Prepuce removed in circumcision

The scrotum has a septum (dividing it into 2 internal compartments). The scrotum also has 2 layers. What are they?
- Pigmented skin layer
- Dartosmuscle /fascia
- Continuous with Scarpa fascia
- Fat-free
- Smooth muscles fibers (assist cremasterm)
- Adjacent to external spermatic fascia

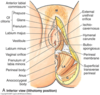
What are the superficial parts of the urogenital triangle in a female?
•Genitalia: pudendum or vulva
•Mons pubis (M in the picture)
•Labia majora
•Labia minora
•Clitoris
–Prepuce
–Glans
•Vestibule
•External urethral orifice
•Vaginal opening
Superficial Fascia of the urogenital triangle consists of:
• Fatty layer
- Just below skin
- Continuous with Camper’s fascia
- Abundant in labia majora & monspubis, none in scrotum
•Colles’ fascia (superficial perineal)
Colles fascia attaches to the perineal membrane and covers the urogenital triangle. Is it in the anal triangle?
No!
Colles’ fascia lines the scrotum (dartos fascia) or labia. It extends around the penis (superficial penile fascia), and is continuous with Scarpa’s fascia of the anterior abdominal wall. It attaches to the fascia lata of thigh just distal to inguinal ligament. Is there continuation with the lower limb?
NO!!!

Extravasation of urine can occur after rupture of the spongy urethra in the bulb of the penis. Where does the fluid go?
Urine passes into the superficial perineal space, under dartos fascia of scrotum around penis, and can spread upward into the anterior abdominal wall under the scarpa’s fascia!
Infection or fluids can also move from the superficial pouch to the abdomen!
* DOES NOT GO INTO THE LOWER LIMB, ANAL TRIANGLE, PELVIC OR ABDOMINAL CAVITY.

The perineal membrane separates the……………… from the……………….. It is a site of attachment for external genitalia, and offers support for pelvic structures.
the deep perineal pouch from the superficial perineal pouch

What is the perineal body?
A fibromuscular mass located between the anal canal and the perineal membrane.

The perineal membrane is an attachment point for many muscles and fascial structures of the pelvis and perineum, including what?
- perineal membrane
- bulbospongiosus
- deep & superficial transverse muscles
- external anal sphincter
- the levator ani

The perineal body Is larger in females and helps to provide support for pelvic viscera. If overstretched or torn during childbirth, the uterus, bladder, or rectum may sag into the vagina (which is called………….). This may be surgically incised during childbirth (via an episiotomy) to prevent jagged tears.
prolapse
What are the contents of the Superficial Perineal Pouch in males?
- Root of the penis (bulb & crura)
- Proximal (bulbar) portion of the spongy urethra
- Bulbospongiosus, Ischiocavernosus, Superficial transverse perineal muscle
- Deep perineal branches of internal pudendal vessels & pudendal nerve

What are the contents of the Superficial Perineal Pouch in females?
– Crura of the clitoris & bulb of vestibule
– Distal part of the urethra & lower vagina
– Bulbospongiosus, Ischiocavernosus, Superficial transverse perineal muscle
– Deep perineal branches of internal pudendal vessels & pudendal nerve
– Greater vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands) & Skene’s glands

The Superficial Pouch in Males contains the Erectile Tissues. These are innervated by…………….. fibers of……………….. nerves
Parasympathetic GVE
cavernous
What makes up the bulb of the penis?
corpus spongiosum (contains spongy urethra) that extends in body of the penis and glans
* purple in pic.

What makes up the Crura of the penis?
2 corpora cavernosa (90% blood during erection) that extends in body of penis
* Pink in pic

* Body of the penis is a free part suspended from the pubic symphysis, and terminates with the glans.
What are the muscles of the Superficial Perineal Pouch?
Skeletal muscles innervated by deep perineal nerve (GSE):
– Ischiocavernosus muscles covering the crura of the penis.
– Bulbospongiosus muscle covering the bulb of the penis and proximal corpus spongiosum.
–Superficial transverse perineal muscles which stabilize the perineal body and support viscera.

Both the Ischiocavernosus muscles and Bulbospongiosus muscle move blood from the root to body of penis, and compress outflow veins during erection (90% of blood is in the corpora…………….) and support the erect penis.
cavernosa

The penis has a covering of skin, superficial fascia, and deep (Buck’s) fascia. When it comes to blood supply of the penis, there is a……………. vein of the penis in the superficial fascia.
There is a…………….. vein, dorsal artery, and dorsal nerve (GSA) deep to the deep fascia of the penis.
superficial dorsal
deep dorsal

Each corpus cavernosum contains a central…………… artery of the penis responsible for erection!
deep

* Order of Sex:
- Erection (male and female)
- Emission (male)/ lubrication (female)
- Ejaculation (male)
- Remission (male)/ resolution (female)
During erection (male & female), there is dilation of the corpora cavernosa arteries by cavernous nerves to increase blood flow (………………….., GVE). Reduced………….. tone contributes to tumescence.
parasympathetic
sympathetic
In erection, contraction of bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles increases engorgement by pumping blood and compressing venous return (via………… nerve, GSE)
pudendal
Afferents in dorsal nerve of penis/clitoris (via…………… nerve, GSA) provide tactile sensory information involved in arousal.
pudendal
Emission (male)/ lubrication (female) set the stage for ejaculation. It involves:
- Transport of sperm / semen (…………….., GVE)
- Closure of internal urethral sphincter (…………….., GVE) to prevent sperm reflux in bladder
- Gland secretion (………………., GVE)
sympathetic
sympathetic
parasympathetic
Ejaculation is under control of…………………
somatic spinal reflex
* Ejaculation is under control of somatic spinal reflex. Afferents in branches of pudendal nerve (GSA) provide sensory information from semen entering the bulbous urethra. Contraction of ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscle (pudendal nerve, GSE) as well as pelvic diaphragm (GSE) contribute the force of seminal expulsion. This is also associated with orgasm in the female!
Remission (male)/ resolution (female) is associated with constriction of what muscles and relaxation of what muscles?
- Constriction of arterial smooth muscles in corpora (sympathetic, GVE)
- Relaxation of bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus to allow venous drainage
A lesion of the prostatic plexus or cavernous nerves (containing…………………… fibers responsible for increasing blood flow in the erectile tissue of the penis) can cause impotence.
parasympathetic

Erectile dysfunction can happen in the absence of an autonomic nerve lesion. What can cause ED?
Compression of the pudendal nerve (numbness, neuralgia: GSA) or artery, hypothalamic or endocrine disorders, failure of autonomic stimulation or arteriosclerosis.
The Female Superficial Pouch also contains Erectile Tissues! Erectile tissues that fill with blood during erection (parasympathetic GVE fibers of cavernous nerves) include what?
–Bulb of the vestibule: which is a fixed part of corpus spongiosum, and DOES NOT CONTINUE IN BODY OF CLITORIS!
–Glans clitoris: attached to bulb by thin bands of erectile tissue, tip of body of clitoris
–Crura of clitoris: corpora cavernosa that continues into the body of clitoris
* Bulb & crura are attached to the perineal membrane.

What are the glands associated with female erectile tissues?
- Greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) glands: which produce secretions during sexual arousal. located near the vaginal opening, and can be a site of infection with inflammation (Bartholinitis).
- Skene’s (lesser vestibular) glands: produce secretions during sexual arousal, near urethral opening.

What are the muscles of the Female Superficial Perineal Pouch?
- Skeletal muscles innervated by deep perineal nerve
- Ischiocavernosus muscles covering the crura of the clitoris
- Bulbospongiosus muscle covering the bulb of the vestibule
- Superficial transverse perineal muscles

Ischiocavernosus muscles and Bulbospongiosus muscle both move blood from the root to body of clitoris & bulb of vestibule to glans, and compress outflow veins during sexual arousal.
………………. muscle also helps to compress the vagina.
Bulbospongiosus
Contents of the deep perineal pouch in males:
– Membranous portion of the urethra.
– Urogenital diaphragm.
– Deep perineal nerve & branches of perineal artery and vein.
– Dorsal neurovascular structures of the penis that pass through.
– Bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands.
Contents of the deep perineal pouch in females:
– Proximal part of the urethra and lower vagina.
– Urogenital diaphragm: external urethral sphincter, deep transverse perineal muscle, sphincter urethrovaginalis and compressor urethrae.
– Deep perineal nerve & branches of perineal artery and vein.
– Dorsal neurovascular structures of the clitoris passing through.
The external urethral sphincter is under what control?
voluntary
What muscles are in the deep perineal pouch?
- skeletal muscles
- external urethral sphincter
- Deep transverse perineal muscles
- a few more in females only.

What are the muscles of the deep perineal pouch that are ONLY in females?
- Sphincter urethrovaginalis (surrounds urethra and vagina as a unit)
- Compressor urethrae
* Both act with the external urethral sphincter to close the urethra & compress the vagina!

The membranous urethra is innervated by what fibers?
GVE (sympathetic & parasympathetic) & GVA fibers!

Bulbourethral glands are ONLY in MALES! They produce mucoid secretions that lubricate the urethra prior to ejaculation. What control is it under?
parasympathetic control

Bulbourethral glands in men are an Analog of the…………….. glands that are located in the superficial pouch in females.
Bartholin’s


