Pelvis and Pelvic Floor Flashcards
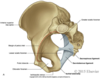
Name the bones of the pelvic girdle
- 1 sacrum
- 5 fused sacral vertebrae
- 2 os coxae
- ilium
- ischium
- pubis

Name the ligaments of the pelvis
- pubic symphysis
- connects 2 pubic bones
- Ant. sacroiliac lig.
- Post. sacroiliac lig.
- sacrotuberous lig.
- sacrospinuos lig.
- obturator membrane Interosseous lig.

Describe the differences between the female and male pelvis
- Oval pelvic brim in ♀ vs. heart-shaped in ♂
- shorter pubic symphysis in ♀
- much wider pubic arch in ♀
- more flared iliac wings (alae) in ♀
- ischial tuberosities farther apart in ♀
- sacrum shorter & less curved in ♀
Note: All for accommodation of childbirth
Describe the two triangles that make up the perineum
Urogenital Δ
- passage of urinary & genital systems
- deep trans. perineal mm. or UG diaphragm
Anal Δ
- passage of rectum & anus
- pelvic floor mm. or pelvic diaphragm

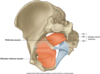
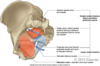
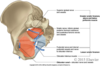
Describe the muscles and general features of the pelvic diaphragm
- Pelvic Floor = Pelvic Diaphragm
- 2 general mm
- Levator ani I
- liococcygeus
- Pubococcygeus
- Puborectalis
- Coccygeus
- Levator ani I
- assisted by piriformis & obturator internus mm.

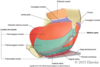
Describe the muscles and general features of the urogenital diaphragm
- Anterior/inferior to pelvic diaphragm
- Composed of deep transervse perineal mm.
- Extends between 2 pubic arches
- Attaches posteriorly to perineal body
- Blends with sphincter mm. of urethra and vagina(♀)

Describe the pelvic viscera common to both males and females
- Ureter
- Urethra
- Urinary Bladder
- Rectum
- Anal Canal
Describe the major components of the male pelvic viscera
- Ureter
- ductus deferens, crosses ureter
- Urethra four parts
- 1) preprostatic part
- 2) prostatic part
- 3)membranous part
- 4) spongy part
- Penis
- Testes
- Spermatic cord
- ductus (vas) deferens
- reproductive glands
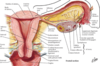
Describe the major components making up the female pelvic viscera
- Ureter
- uterine a. crosses ureter
- Urethra
- ~ 3.5 – 4 cm
- Pierces ant. portion of UG diaphragm
- between bladder and external urethral orifice
- Ovaries
- Uterine (Fallopian) tubes
- Uterus
- Uterine cervix
- vaginal fornix
Describe the peritoneal specializations and ligaments of the female
- Uterine ligaments
- Suspensory lig.
- peritoneum covering ovarian vessels & nn.
- Broad lig.
- peritoneum covering uterus and adnexa
- Ovarian lig.
- anchors ovary to uterus
- Round lig. of uterus
- continuation of ovarian lig.
- passes thru inguinal canal to fuse with labia majora
- Suspensory lig.

External organs & structures of the male pelvic viscera
- Penis
- Testes
- primary male reproductive organs
- housed in scrotum
- Spermatic cord
- fascial sheath derived from anterior abdominal wall
- from inguinal canal into scrotum
- surrounds ductus deferens, testicular vessels & nn.
- ductus (vas) deferens
- reproductive glands
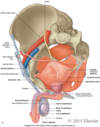
Describe the male reproductive glands
- seminal vesicles
- joins vas def, forms ejaculatory ducts, empty into prostatic urethra
- prostate gland
- walnut sized, btwn bladder & UG diaphragm
- bulbourethral (Cowper’s) gland
- 2 pea sized, within UG diaphragm, empty into penile urethra

Describe the ureter
- transport urine from kidneys to bladder
- cross ext. iliac vessels & descend into pelvis
- travel to posterolateral aspect of urinary bladder

Describe the urinary bladder
- stores urine prior to expulsion thru urethra
- consists of smooth m. = detrusor urinae
- covered by peritoneum & supported by pelvic floor
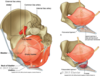
Describe the rectum
- located in true pelvis superior to pelvic floor
- normally constricted by puborectal sling
- U-shaped puborectalis m.