Pelvis 1 Flashcards
(58 cards)
What is the differene between the true pelvis and the false pelvis?
The pelvis Brim, or iliopectineal line, divide the pelvis into the pelvis major (false pelvis) and the pelvis minor (true pelvis)

- What is the true pelvis? What forms the inlet?
- What separates the true pelvis from the false pelvis?
1. The true pelvis is cylyndrical and has an inlet, a wall, and an outlet. The inlet is open, where as the outlet is closed by the pelvic diaphram.
Anterior: Pubic crest
Posterior: Prominatory
Lateral: Arcuate Line, Piriformis & Obturator internis muscle (above tendenous arch of levator ani)
Floor- Levator Ani and Coccygeal muscle.
- The arcuate line of the pelvis. Also called the terminal line.

What is the relationship of the peritoneum to the pelvis viscera?
What are the two very general things the peritoneum forms?
The peritoneum of the pelvis is continuous at the pelvic inlet with the peritoneum of the abdomen. In the pelvis the peritoneum drapes over the pelvic viscera in the midline.
*Forms pouches between adjacent viscera
*Forms folds and ligaments between viscera and pelvic walls.
Where is the pararectal fossae (male) ?
Formed by the lateral reflection of perineum over the superior third of the rectum
Is the rectovesicular pouch found in both males and females?
No, only in males.
Where is the vesicouterine and rectouterine fossae in the femail?
Vesicounerine pouch is located between the bladder and uterus.
Rectounerine Pouch is an invagination of peritoneum between the anus and uterus.
Differentiate among the median, medial, and lateral umbilical ligaments.
All are formed from folds in the peritoneum
Median- reminany of the urachis connects blatter to the umbilcus. If unclosed patient will pee from bellybutton.
Medial- Contains the umbilical artery
Lateral- Contains the inferior epigastric artery.
What composes the median umbilical ligament?
The Urachis. Connects umbilicus to the bladder
What composes the medial umbilical ligament?
Umbilical artery
What composes the lateral umbilical ligament?
Inferior Epigastric artery
What is the blood supply of the bladder?
The Blatter recieves blood from the Superior and Inferior Vesicle arteries ( and from the vaginal arteries in females)
The venous drainage via the Prostatic Plexus of veins which empty into the **internal iliac vein. **
- What is the position of the bladder?
- What is the smooth muscle that makes up the wall?
The Bladder is situated below the peritoneum and is slightly lower in the female than the male.
Expands into the pelvic brim as it fills, may reach as high as the umbilicus if fully distended.
- Detrusor Muscle
Discribe the major defining features of the bladder?
Learn Attached figure from lecture.

Describe the innervation of the bladder?
Sympathetic- (GVE) Lower Lumbar Splanchnics L1-2 **induces relaxation of the bladder wall (detrusor muscle) and constrict the internal sphincter, inhibiting emptying.
Parasympathetic- (GVE) **Pelvic splanchnics S2,3,4 (Inferior Hypogastric Plexus) **Induce a constriction of the detrussor muscles and relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter ** **
GVA Pelvic splanchnics S2-4, arise from stretch receptors in the bladder wall. Signal when bladder is full
GSE- Peudendal nerve- cause voluntary relaxation of the urethral sphincter and the bladder begins to void.
What is the location of the trigonal area of the bladder in relation to the ureters and urethra?
Smooth area of the posterior bladder in the nondistended state.
Superiorlateral borders are the openings of the ureters.
Inferior Border Is the neck and urethra.
Describe the sympathetic innervation of the bladder
Sympathetic GVE fibers induce relaxation of the bladder wall and constrict the internal sphincter.
Inhibits bladder emptying
May activate the detrussor to prevent semen reflux into bladder.
What is the position of the rectum and anal canal?
Sigmoid colon makes the turn into the pelvic basin at S3, S3, S3 (He said it 3x in lecture) and turns into the rectum. It is the most posterior portion of the true pelvis and is aganst the sacrum and coccyx.
Just posterior to the vaginal canal in girls.
Posterior to the prostate and mail genital structures in guys.
Describe the structure of the rectum and anal canal?
The rectum has curves, longitudinal rectal valves of Houston. Lead from the sigmoid colon to the ampula of the rectum. Distal to the ampula the rectum becomes the Anal Canal.
The anal canal has vertical structures called anal columns. These contain the internal venous plexus of the anal canal.
At the external anal opening you have the external venous plexus
What innervates the rectum and anal canal?
What structure differentiates between the superior and inferior rectum?
The anal canal is divided into the upper 2/3 (Visceral Portion) which is part of the intestine. and the lower 1/3 (Somatic Portion) which belongs to the perinem.
Demarcation between the two is the Pectinate Line
What muscles form the pelvis diaphram (2) ?
Relate each muscles position relative to the pelvis viscera?
How do they relate to the piriformis?
How do they relate to the obturator internis?
The Levator Ani and **Coccygeus Muscle **
Differentiate between parietal and visceral endopelvic facia in girls.
What structures are derived from each
Peritoneum drops to the pubis and flows over the superior dome of the bladder (vesicouterine Pouch). The peritoneum drapes over the Uturus and Forms the Broad ligament.
Pouch of Douglas is between the uterus and anus and is the most inferior point of peritoneum in females.
What is the blood supply of the vaginer?
Recieves blood from the vaginal branch of the uterine artery and the internal iliac artery
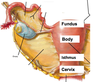
Describe the structure of the Vaginer?
Extends between the vestibule and the cervex of the uterus.
Fornex forms the recess between the cervex and the wal lof the vagina
Opening into the vestibule is partially colsed by membranous folds valled hymen.