Peds GU Flashcards
Unilateral Renal Agenesis Associations
Females- Genital anomalies
- Unicornuate uterus
- Rudimentary horn
Male genital anomalies
- missing epipdidymis and vas deferens on the side of missing kidney
- may also have seminal vesicle cyst on that side
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome
Mullerian duct anomalies
- absence or atresia of uterus or unicornuate uterus
- Unilateral renal agenesis
70% of females with unilateral agenesis have genital anomalies
Zinner Syndrome
Males
Unilateral renal agenesis
Seminal vesicle cyst on side missing kidney
Absent epididymis and vas deferens on side missing kidney
Bilateral Renal Agenesis
Potter Sequence
Insult in utero (ACE INHIBITOR)
Kidneys don’t form –> no urine
Oligohydramnios
Pulmonary Hypoplasia
PANCAKE ADRENAL SIGN on imaging
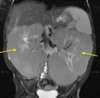
Horseshoe Kidney Associations
Increased risk of stones and infection
INcreased risk of cancer from chronic inflammation - Wilm’s, TCC< and Renal Carcinoid
Turner’s Syndrome
Vessel involved in Horseshoe Kidney
Lower poles fuse and get hung up on INFERIOR MESENTERIC ARTERY
Crossed-fused Renal Ectopia
One kidney crosses midline and fuses with other
Each kidney has its own ureter
the ECTOPIC kidney is INFERIOR
Left often crosses over to the Right
Complications: stones, infection, and hydronephrosis
Congenital UPJ Obstruction
Most common GU tract anomaly in neonates
Have to look for a crossing vessel before Tx (Pyeloplasty)
Intrinsic defect in the circular muscle bundle of the renal pelvis
Teen with flank pain after drinking lots of fluids
No hydro-ureter
May progress to multicystic dysplastic kidney
Whitaker Test
Urodynamic study combined with antegrade pyelogram
Differentiate between prominant extrarenal pelvis and congenital UPJ obstruction
NO HYDRO-URETER
AR Polycystic Kidney DIsease Associations
HTN
Renal Failure
Abnormal bile ducts
Liver fibrosis
Inverse relationship b/w kidney and liver disease (more severe kidney disease = less severe liver disease and vice versa)
US Findings in ARPKD
Smoothly marginated
Enlarged
Echogenic
Loss of corticomedullary differentiation
In utero - may not see urine in bladder

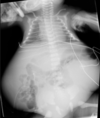
XR findings in ARPKD
Wide Abdomen
Bilateral flank “masses”
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Prune Belly/Eagle Barrett Syndrome
Males
Triad
- Lack of Abd muscles (partial or complete)
- Hydroureteronephrosis
- Cryptorchidism (bladder distension interferes with descent of testes)
Neonatal Renal Vein Thrombosis
Maternal DM
Usually UNILATERAL (Left)
Starts peripherally and progresses toward hilum
Renal Atrophy over time
Renal enlargement in acute phase
Neonatal Renal Artery Thrombosis
Often 2/2 UACs
Severe hypertension
No enlargement of kidney
Cryptorchidism Locations and Complications
Undescended testes - 72% in IC, 20% prescrotal, 8% intra-abdominal
- Malignant degeneration (even if fixed- still inc risk of testicular cancer even on UNAFFECTED side)
- Infertility
- Torsion
- Bowel incarceration 2/2 associated indirect inguinal henia
Primary Megaureter
Enlargement of ureter NOT related to obstruction
Causes
- distal adynamic segment (if no dilation of collecting system then it is NOT an obstruction)
- Reflux at UVJ
- Idiopathic
Retrocaval Ureter
Problem in development of the IVC – Ureter gets pinned behind IVC
Usually No Sx’s – but can get partial obstruction and recurrent UTIs
IV pyelogram –> reverse J aka fish-hook ureter

Ureterocele
ystic dilation of the intravesicular ureter 2/2 obstruction of the ureteral orifice
IVP or US - COBRA HEAD SIGN
Associated with duplicated collecting system (upper pole moiety)

Weigert Meyer Rule
Duplicated Collecting System
-
Upper Pole (vowels)
- Ectopic insertion - Inferior and Medial to lower pole insertion
- Tends to form Ureteroceles
- Tends to Obstruct
-
Lower Pole (consonants)
- Normal insertion Superior and Lateral
- Prone to Reflux

Ectopic Ureter
Normal collecting system
Ureter inserts ectopically
More common in females
results in incontinence when ureter connects distal to the external sphincter in the vestibule
Posterior Urethral Valves
Fold in the posterior urethra resulting in outflow obstruction and hydronephrosis with eventual renal failure
Most common cause of urethral obstruction in male infants
Forniceal rupture –> Peri-renal fluid collections (urinary ascites)
Actually a good prognostic indicator because pressure is relieved
(can happen in any obstructive pathology)
Posterior uretheral valve findings on VCUG and fetal MRI
VCUG - abrupt caliber change between dilated posterior urethra and normal caliber anterior urethra
Fetal MR - keyhole bladder

Vesicoureteral Reflux
Ureter insets horizontally/vertically (not oblique)
50% of children with UTIs
recurrent/2nd UTI–> get VCUG to eval for reflux
Urologist can inject material at UVJ to prevent reflux “DEFLUX”
Usually resolves by age 5-6
Chronically –> scarring –> HTN or renal failure

Grading of VUR
- Into non-dilated ureter
- Into pelvis and calyces - NO dilation
- Mild-Mod dilation of ureter, renal pelvis, and calyces– with minimal blunting of fornices
- Moderate ureteral tortuosity and dilation of pelvis and calyces
- Gross dilation of ureter, pelvic and calyces + loss of papillary impressions + ureteral tortuosity

Bladder Exstrophy
Herniation of urinary bladder through hole in anterior infra-umbilical abdominal wall
Increased risk of malignancy in extruded bladder
MANTA RAY SIGN
Manta Ray Sign
Unfused pubic bones on AP pelvic XR

Urachus
Umbilical attachment to the bladder
Starts off as the Allantois –> then urachus –> atrophies –> median umbilical ligament
Urachus can persist to form a canal, a sinus, a diverticulum, or a cyst –> often results in infection
2:1 M:F
Can turn into Adenocarcinoma from constant inflammation
Renal Mass DDx Age 0-3 yo
- Nephroblastomatosis
- Multicystic Dysplastic KIdney
- Mesoblastic Nephroma
Renal Masses Over age 3 (around age 4)
- Wilm’s
- Multilocular Cystic Nephroma
- Lymphoma
- Wilm’s Variants (actually under 2-3 yo)
- Clear Cell - Wilms + bone mets
- Rhabdoid (wilm’s + brain mets
- Wilms with mets to lungs