Peds cardiology Flashcards
what is the most common congential heart defect?
ventricular septal defect
murmur associated with ventricular septal defect
holosystolic
large ventricular septal defect present with
- failure to thrive
- tachypnea
- hepatomegaly
- GERD
what is the most common heart defect in Trisomy 21 (down syndrome)
ventricular septal defect
ventricular septal defect is what type of shunt
L to R shunt
medication based treatment of ventricular septal defect
- diuretic
- ACE inhibitor
what is the most common type of atrial septal defect
secundum ASD
- failure of septum primum and septum secundum to overlap
atrial septal defect is what type of shunt? What changes are made to the heart because of it?
- L to R shunt
- enlarged RA, increased pulmonary flow
symptoms associated with atrial septal defect
- usually asymptomatic, may have fatigue, palpitations, or exercise intolerance
what size of atrial septal defect usually close on thier own
< 8 mm
septation of the atrioventricular canal usually occurs when? How?
end of 4th week
- superior and inferior cushions grow toward each other and eventually fuse seperating AV canal into a right and left channel

what is a complete atrioventricular septal defect
- large VSD and ASD
- common AV valve
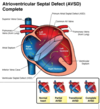
what type of shunt is atrioventricular septal defect
L-R shunt
complete atrioventricular septal defect is repaired in infancy to prevent what
pulmonary vascular obstructive disease
What is a partial atrioventricular septal defect
- Large ASD, no VSD
- two seperate AV valves

repair of partial atrioventricular septal defect is usually delayed until
18-24 months old
patent ductus arteriosus is what type of shunt
- L-R shunt (aorta to pulmonary artery)
medical treatment of patent ductus arteriosus
- indomethacin
- ibuprofen
surgical treatment of patent ductus arteriosus for premies
left thoracotomy: clip
surgical treatment of patent ductus arteriosus for neonates, infants
left thoracotomy, ligate
surgical treatment of patent ductus arteriosus for toddlers and older
left thoracotomy: divide and over sew
catheter based treatment of patent ductus arteriosus
coil closure
what is still’s murmur
- innocent murmur
- vibratory systolic LSB
- decreases with expiration/standing
physiologic peripheral pulmonic stenosis
- innocent murmur
- soft, harsh systolic ejection murmur
- usually disappears by 12 months
the 5T’s that causes cyanotic congenital heart defect
- Truncus arteriosus
- Transposition
- Tricuspid Atresia
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- TAPVR: total anomalous pulmonary venous return
cyanotic CHD are due to R to L shunt. Name the 2 broad categories
- intracardiac defects and obstruction to pulmonary flow
- mixing fo oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
- admixture of pulmonary and system venous return
- single chamber recieves total systemic and pulmonary venous return
Name the three CHD that fall into the intracardiac defects and obstruction to pulmonary flow catagory
- tetralogy of fallot
- tricuspid atresia
- pulmonary atresia
tetralogy of fallot presents with what 4 abnormalities
- right ventricular outflow tract obstruction
- VSD
- overriding aorta
- right ventricular hypertrophy
tet spell hyper-cyanotic spell seen in tetralogy of fallot is precipitated by what 3 factors
- dehydration - decreased heart volume
- anesthesia - vasodilation
- crying
tet spell hyper-cyanotic spell seen in tetralogy of fallot is relieved by
- squatting (baby increases SVR to force more blood flow through pulm artery)
- volume resuscitation
- administer vasoconstrictors
truncus arteriosus
- a single blood vessel (truncus arteriosus) comes out of the right and left ventricles, instead of the normal two vessels (pulmonary artery and aorta
- have large VSD

babies with truncus arteriosus commonly have what gene mutation
22q11 deletion (DiGeorge)
repair for truncus arteriosus
- VSD closure
- RV-PA conduit
- usually operate in first two weeks of life
if baby is blue, what medication should be given
prostaglandins
Transposition of great vessels
- cyanotic
- the aorta and the pulmonary artery are switched
treatment of Transposition of great vessels
- prostaglandins to keep ductus open
- BAS: balloon atrial septostomy
- arterial switch operation
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return: supracardiac
pulmonary vein to Brachiocephalic vein (25-50% can be obstructed)
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
child’s pulmonary veins don’t connect normally to the left atrium. Instead they’re re-directed to the right atrium by way of an abnormal (anomalous) connection
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return: cardiac
- pulmonary vein to coronary sinus
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: infracardiac
- pulmonary vein drains via descending vein into liver
- usually obstructed
- presents: very sick with wet lungs, cyanotic, pulmonary hypertension
- emergency/urgent repair
unexplained HTN in children could be a result of
coarctation of aorta
coarctation of aorta
is a narrowing of the aorta, the large blood vessel that branches off your heart and delivers oxygen-rich blood to your body. When this occurs, your heart must pump harder to force blood through the narrow part of your aorta.
coarctation of aorta is associated with what genetic condition
turners syndrome
CXR findings with coarctation of aorta
- cardiomegaly
- rib-notching- takes several years to develop
gold standard to diagnosis coarctation of aorta
CT-angio or MRA
list acyantoic congential heart defects
- VSD
- ASD
- atrio-ventricular canal
- patent ductus arteriosis
- coarctation of aorta


