PCOL Anti arrhythmic Drugs Flashcards
(42 cards)
Which of these tissues generates slow action potentials? (select all)
A. His-Purkinje Fibers
B. AV node
C. Atria
D. Ventricles
E. SA node
B,E
Which of these tissues conducts a fast action potential. (select all)
A. His-Purkinje Fibers
B. AV Node
C. Ventricles
D. SA Node
E. Atria
A, C, E
Which of these tissues can generate this type of action potential? (Select All)
A. His-Purkinje Fibers
B. SA Node
C. Atria
D. AV Node
E. Ventricles

A,C,E
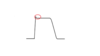
The cart represents a fast action potential (hence the large initial spike in depolarization) and the only tissues that produce fast action potentials such as this include the Atria, Ventricles and His-Purkinje FIbers
What ion channel and ion is responsible for this circled slope?
A. Potassium channel, Potassium
B. Sodium channel, Sodium
C. Calcium channel, Calcium
D. Chloride channel, Chloride

B
What phase does this circled portion represent?
A. Phase 1
B. Phase 2
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 4
E. Phase 0

E
What phase does this cicled portion represent?
A. Phase 1
B. Phase 2
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 4
E. Phase 0

D
What phase does this circled portion of the graph represent?
A. Phase 1
B. Phase 2
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 4
E. Phase 5

A
What phase does this circled portion on the graph represent?
A. Phase 1
B. Phase 2
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 4
E. Phase 0

B
What does the circled portion of this graph represent?
A. Phase 1
B. Phase 2
C. Phase 3
D. Phase 4
E. Phase 0

C
What is the main conformational state of sodium channels in this portion of the graph?
A. Resting (closed)
B. Active
C. Inactive

A
What is the main conformational state of sodium channels on this portion of the graph?
A. Resting (closed)
B. Active
C. Inactive

B
What is the conformational state of the sodium channels on this portion of the graph?
A. Resting (closed)
B. Active
C. Inactive
C
The circled sodium channel represents the _____ conformation and sodium/drug ____ enter the binding sites.
A. Open, Can
B. Resting, Cannot
C. Inactive , Can
D. Inactive Cannot
C
Which of these statements is true?
A. In Phase 4 of a Fast action potential the majority of the sodium channels are in the inactive state
B. In Phase 0 the majority of the sodium channels are in the resting state
C. In Phase 1-2 the majority of the sodium channels are in the inactive state
D. In Phase 3-4 the majority of the sodium channels are in the active state
C
Which of the following statements is true? (select all)
A. In phase 1 and 2 of the fast action potential calcium channels open and calcium enters the cell.
B. In Phase 0 of the fast action potential potassium channels open and potassium flows out of the cell
C. In Phase 3 of the fast action potential calcium channels will close and potassium efflux is still occuring
D. In Phase 1 and 2 of the fast action potential potassium efflux is occuring while calcium influx is occuring.
E. In Phase 1 and 2 of the fast action potential potassium influx is occuring while calcium influx is occuring.
A,C,D
Which of the following statements is true?
A. In phase 1 of the fast action potential the majority of sodium channels are in the inactive state
B. When the majority of the sodium channels are in the inactive state you are more likely to be in the absolute refractory period
C. When the majority of the sodium channels are in the resting state you are more likeley to be in the realtive refractory period.
D. All of the above
D
The image here represents the Q-T interval which is a measure of the____
A. Action Potential Duration (APD)
B. Diastolic fill volume
C. The strength of contraction of the ventrciles
D. The strength of contraction of the atria

A
It is not C because ECGs do not measure contraction strength. They only measure electical activity.
When you increase your QT interval you will ____ your Action Potential Duration (APD)
A. Increase
B. Decrease
A
The QRS interval is a measure of the :
A. Atrial conduction
B. Atrial contraction strength
C. Ventricle conduction
D. Ventricle contraction strength
C
QRS complex is formed how?
A. Electrical impuse spreading into the atria
B. Electrical impulse spreading into the ventricle
B
An elongated QRS interval is a result of a ____ ventricle conduction.
A. Increased (faster)
B. Decreased (slower)

B
It is elongated because the action potential is taking longer to move through the venticle muscle (slow conduction). As a result the QRS complex will look wider.
T/F In an absolute refractory period another action potential can be elicited
F.
In the ABSOLUTE refractory period more action potentials cannot be generated because the sodium channels are in the INACTIVE state.
T/F In the Relative refractory period another action potential can be generated
T.
In the RELAVTIVE refractory period the majority of sodium channels are in the RESTING (closed) state and can become activated again (action potential) with a strong enough stimulus.
Based on this picture which of these statements is true? (select all)
A, The green line is taking a longer period of time to reach threshold in comparison to the red line.
B. The red line is taking a longer period of time to reach the threshold in comparison to the green line.
C. The red line can be a result of PNS activation
D. The Green line can be a result of SNS activation

B,C,D




