Pathology of the urinary tract and kidney Flashcards

- A. Cortex
- B. Medulla/Pyramid
- C. Pelvis


4 arrows


What does this show?

Bowmans capsule
What does this show?
Longitudinal sections of distal tubules and loops of Henle
What is renal function impairment?
- Decreased ability of the kidney to excrete nitrogenous waste and regulation of water and electrolytes
- Acute renal function impairment
- Chronic kidney disease ( CKD) - stages 1- 4 based on the GFR
What do U&E include?
- Urea
- Creatinine
- Na+
- K+
- Cl-
- Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
A. Which two excretory compounds are raised in renal failure?
B. What test will be abnormal when assessing full blood count in chronic renal failure and why?
A. Which two excretory compounds are raised in renal failure? Urea and creatinine
B. What test will be abnormal when assessing full blood count in chronic renal failure and why?
Low haemoglobin due lack of erythropoietin resulting
in normocytic normochromic anaemia
What are the causes of acute renal failure?
»Hypovolaemic shock due to:
»Bleeding from trauma or GIT e.g. varices/ulcers
»Bleeding from a ruptured aortic aneurysm
»Post partum haemorrhage
»Severe burns; diarrhoea and vomiting
»Septic shock due vasodilatation
»Drugs e.g. gentamycin
»Congestive cardiac failure
What are the causes of chronic renal failure?
»Several types of glomerulonephritis
»Chronic use of some drugs such as aspirin
»Chronic pyelonephritis
»Hypertension and diabetes mellitus
»Autoimmune diseases e.g. SLE
»Obstruction of the urinary tract
What does this show?

In some cases of renal failure the glomeruli are scarred ( glomerulosclerosis – thin arrows) and there is associated chronic inflammation – thick arrows
What are the causes of urinary tract obstruction?
- Calculi or stones
- Stricture in the ureter
- Stricture in the urethra
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Cancer of the bladder or prostate
What was the cause of renal failure is this patient?

Renal stones or calculi;
This is termed stag horn calculus.
The kidney is scarred with loss of the cortico-medullary distinction
39 year old man: Haematuria. Weight loss 3 stone. Left loin pain. Raised CRP/ESR/platelets. Abnormal LFTs. Left renal malignancy?

Staghorn calculi with obstruction and severe pyelonephritis abscess formation.
With renal stones always assess calcium levels

- A 51-year-old woman had an incidental finding of abnormal left kidney during investigations for a fibroid uterus for which she underwent hysterectomy
- The CT scan on the next slide shows the left kidney abnormality. What is the diagnosis?
- Her renal function tests were normal.
Why ?
- A 51-year-old woman had an incidental finding of abnormal left kidney during investigations for a fibroid uterus for which she underwent hysterectomy
- The CT scan on the next slide shows the left kidney abnormality. What is the diagnosis? Cystic/dilated kidney due to hydronephrosis
- Her renal function tests were normal.
Why ? Because the right kidney was still functional
What does this show?


What does this show?

Case Report: The histology showed glomerulosclerosis and chronic inflammation
What was the cause of renal failure in this patient?

Autosomal dominant hereditary polycystic kidney – also cysts in the liver and pancreas; not related to polycystic ovaries
What is the common presentation of renal cancer?
- Patients may present with haematuria
- Or as an incidental finding
- Patient may have loin discomfort
- Affects patients in the 60-70 age group
- M>F
patient presented with haematuria


What does this show?


What is Urothelium /transitional cell epithelium?
- Consist of four cells or more
- Acts as a barrier and prevents back diffusion of urine
- Different from squamous epithelium as the cells are more cuboidal than flat
Where does urothelium line?
–Bladder
–Ureters
–Pelvi-calyceal system
What does this show?
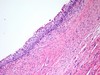
Normal urothelium













