Pathology of the Ovary (Gianani) - SRS Flashcards
(38 cards)
Cystic follicles are very common in the ovary, how do they originate? 2 ways
- from unruptured follicles
- in follicles that have ruptured and immediately sealed.
A female patient is brought to the ER by her friend (against her will d/t not having insurance). She appears pasty grey, is having trouble walking and is clearly experiencing severe abdominal pain. On the way back to the exam room the patient passes out in the hallway and hits the deck.
She is taken to surgery and the attached lesion (softball sized) is found. Based on the case, gross sample, and histology, what is your diagnosis?
WHY?

Luteal cyst rupture
These occasionally rupture and cause a peritoneal reaction.
The combination of old hemorrhage and fibrosis may make differentiation from endometriotic cysts tough, but the histology reveals that the cyst is lined by a rim of bright yellow tissue containing luteinized granulosa cells.
(I was the friend in this case, we were supposed to go to the museum and when I picked her up she looked like absolute shit and wouldn’t go to the hospital. So I pretended to give in and told her we would just go to the museum as planned. Then I drove her to the hospital instead. Good times)
In what patient group are luteal cysts common?
Present in the normal ovaries of women of reproductive age.
Identify the attached lesion based on gross, resection and histology.
What is a possible consequence of this?

Endometriotic ovarian cysts: note the hemorrhagic areas on gross, and the clear presence of endometrium on histology.
D/t scarring, infertility can be a consequence.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder characterized by?
5
- hyperandrogenism
- menstrual abnormalities
- polycycstic ovaries
- chronic anovulation
- decreased fertility
This disorder is seen most often in postmenopausal women but can also be seen overlapping with PCOS in younger women. The disorder is characterized by unifrom enlargement of the ovary (up to 7 cm), which has a white to tan appearance on sectioning. The involvement is usually bilateral and microscopically shows hypercellular stroma and luteinization of the stromal cells, which are visible as discrete nests of cells with vacuolated cytoplasm.
What is this disorder?
Stromal hyperthecosis (AKA: cortical stromal hyperplasia)
The WHO classifies ovarian neoplasms into what four categories?
- Surface epithelial-stromal tumors
- Sex cord-Stromal tumors
- Germ cell tumors
- Metastatic carcinoma from non-ovarian primary
What types of serous tumors of the ovary are there that fall into the following categories?
Benign - 2
Borderline - 1
Malignant - 2
- Benign - cystadenoma, cystadenofibroma
- borderline - serous borderline tumor
- malignant - low and high grade serous adenocarcinoma
What are the mucinous (endocervical-like and intestinal type) tumors of the ovary that fit the following categories?
Benign - 2
Borderline - 1
Malignant - 1
- Benign - cystadenoma, cystadenofibroma
- Borderline - mucinous borderline tumor
- Malignant - mucinous adenocarcinoma
What are the types of endometriod tumors of the ovary that meet the following definitions?
Benign - 2
Borderline - 1
Malignant - 1
- Benign - cystadenoma, cystadenofibroma
- Borderline - endometrioid borderline tumor
- Malignant - endometrioid adenocarcinoma
What are the 6 subcategories of surface epithelial-stromal tumors??
- Serous
- Mucinous
- Endometrioid
- Clear cell
- Transitional cell
- Epithelial-stromal
What are the 6 types of sex cord-stromal tumors?
- Granulosa tumors
- Fibromas
- Fibrothecomas
- Thecomas
- Sertoli-leydig cell tumors
- Steroid (lipid) cell tumors
What are the four types of germ cell tumors of the ovary?
- Teratoma
- Dysgerminoma
- Yolk sac tumor
- Mixed germ cell tumor
Ovarian teratomas may fall into what three types?
Immature
Mature (Cystic or solid)
Monodermal (struma ovarii, carcinoid)
What are five common metastatic cancer sources that go to the ovaries?
- Colonic
- appendiceal
- gastric
- pancreaticobiliary
- breast
Abdominal pain and distension, urinary and GI tract symptoms as well as vaginal bleeding occur in ovarian cancers d/t what two possible causes?
Why the bleeding specifically?
Either…
- compression by the tumor
- cancer invasion
Vaginal bleeding d/t increased estrogen leading to endometrial hyperplasia
Can benign tumors kill you?
Yes. I actually did not realize this. huh.
What are the percentages of the following for serous tumors of the ovary?
Benign
Borderline
Malignant
What type of epithelium is it from?
- 60%
- 15%
- 25%
Columnar epithelium
What are the percentages of the following for mucinous tumors of the ovary?
- Benign
- Borderline
- Malignant
What type of epithelium is it from?
- 80%
- 10%
- 10%
Columnar epithelium with apical mucin
What type of epithelium are endometrioid tumors derived from?
Tubular glands resembling endometrium
You see this biopsy of a tumor that shows a lining of tall columnar epithelial cells with apical mucin that lack cilia.
What is this ovarian tumor?
What would the gross specimen be like?
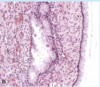
Mucinous ovarian tumor
Tumor would be multilobulated and contain dark brown viscous fluid.
Identify the shown images of ovarian tumors A-D.
Note the salient histological findings.

A. Serous cystadenoma with stromal papillae and columnar epithelium
B. Borderline serous tumor with increased architectural complexity and epithelial cell stratification
C. Low grade “micropapillary” serous carcinoma - complex micropapillary growth
D. High grade serous carcinoma of the ovary with invasion of underlying stroma
You see the attached findings from a patient and note the neoplastic epithelial cells resembling urothelium. You know this is usually a benign tumor because it is a?

Transitional cell tumor (Brenner Tumor)
Brenner tumors are often detected incidentally and even when large behave in benign fashion. Malignant Brenner tumors generally present in stage 1 and for prognostic purposes are considered to be equivalent to?
low-grade (type 1) carcinomas









