Pathology of the liver 2 Flashcards
Describe Viral hepatitis
- infection of the liver
- May cause acute injury or chronic liver injury
- Causes can be common or rare
What are the common types of hepatitis virus
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis E
What are rare causes of hepatitis
Ebstein-Barr virus, Yellow fever virus, Herpes simplex cirus and cytomegalovirus
Describe hepatitis A
- Transmission: Faecal-oral spread - contaminated food or water
- Short incubation time
- Can be sporadic or endemic (isolated or common)
- Acute - mild ilness with full recovery usuaully
- Directly cytopathis - direct change to host cell
- no carrier state
What are the serological markers in HAV
- IgM = active infection
- IgG = recovery antibody - tells us that there has been recovery from HAV
What are the histological features of HAV
- Periportal inflammation, necrosis and apoptosis

Describe hepatits B virus
- Transmission: blood, blood products, sexually and in utero
- long intubation time
- Liver damage is by antiviral immune response
- Carriers exist
- only 20% become chronic but depends on age - the younger the patient the more likely to become chronic
Describe hepatitis C virus
- Transmission: blood, blood products and sexually
- Short intubation time
- often asymptomatic
- Tends to become chronic
describe the histological features of HCV
- Dense portal chronic inflammation - lymphocytosis
- Interface hepatitis - piecemeal necrosis
- Lobular inflammation
- Council man bodies - intracytoplasmic eosinophillic collection of globulate inside the cell of dying hepatocytes
- Fibrosis and cirrhosis
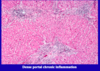
What is piecemeal necrosis
Piecemeal necrosis is defined as the appearance of destroyed hepatocytes and lymphocytic infiltration at the interface between the limiting plate of periportal hepatocyte, parenchymal cells and portal tracts

What does lobular inflammation look like
Describe the outcome of hepatitis B virus
- Fulminant acute infection - death
- Chronic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Asymptomatic - Carrier
What is the outcome of hepatitis C
- Chronic hepatits
- Cirrhosis
What are other causes of chronic hepatits
- Hepatitis B, C
- pirmary biliary cirrhosis
- Autoimmune hepatits
- Drug induced hepatitis
- Primary Sclerosing cholangitis
Describe primary biliary cirrhosis
- Rare autoimmune disease - unknown cause
- Associated with autoantibodies to mitochondria
- Females - 90%
- Biopsy - to stage doisease
- Presence of granulomas and bile duct loss
- Outcome: unpredictable
Descirbe the histological features of primary biliary cirrhosis
- Dese lymphocytic infiltrate in porta tracts
- Inflammation of bile duct
- Granuloma around duct

What does inflammed bile duct look like

What does the duct granuloma look like

What is the complication of primary BC
- Cholestasis
- Liver injury
- inflammation
- fribrosis and cirrhosis

What is autoimmune hepatitis
Chronic self perpetuating inflammatory liver disease of unknown cause mainly occurring in females of all ages and ethnic groups
- Associated with other AI diseases
- Pattern is similar to chronic hepatitis
- Numerous plasma cells
- Autoantibodies to - SM, nuclear, LKM and raised IgG
- Trigger : drugs
Describe chronic drug induced hepatitis
- Similar features to all other types of chornic hepatitis
- May lead to autoimmune hepatits
- loads to causes


