Pathology of biliary tract Flashcards
Desctribe Cholelithiasis
- Gallstones-
- Hard stone like or gravel like material formed commonly within the gallbladder
- Asymptomatic
What is the normal composition of bile
- Billirubin
- Bile salts
- cholesterol micelles
- Phospholipids
Stored and concentrated in the gallbladder and released by CCK into second part of doudenum
What is the pathogenesis of Cholesterol stones

Formed when there is an imbalance between the ratio of cholesterol and bile salts which distrub micelle formation
What is the appearance of cholesterol stones
Cholesterol excess in bile

What are the risk factors for cholesterol stones
- Female
- obesity
- Genetics
- Diabetes
What is the pathogenesis of pigment stones
Excess bilirubin that cannot be solubalised in bile salts

What do pigment stones look like

Risk factors for pigment stones
Excess bilirubin due to excess breakdown of RBC -> Haemolytic anaemia
What are the causes of gallstone formation
- Acute Cholecystiti and Chronic Cholecystitis
- Mucocoele
- Empyema
- Carcinoma
- Ascending Cholangitis
- Obstructive Jaundice
- Gallstone Ileus
- Acute Pancreatitis and Chronic Pancreatitis
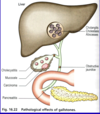
What is choleycysttitis
- Inflammation of the gallbladder
- Commonly associated with gallstone
- can present as acute or chronic
- Common
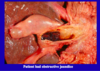
Describe acute choleyscytitis
- Due to gallstones obstructing outflow of bile
- Initially sterile but can become infected
- May lead to empeyma, rupture or peritonitis
- Formation of intense adhesion within 2-3 days - scar tissue that connects it to abdominal wall
What are the complications of acute cholecystitis
- Infection
- Adhesions
- Empyema,
- Peritonitis
- Rupture
What are the histophathological features of acute cholecystitis
- Distended gallbladder

Describe chornic cholecystitis
- Obstruction of gallbladder by gallstones
- Can be insidious or due to repeated acute cholecytitis
- thickening of gallbladder and adhesions
- gallbladder is not distended
What is the histopathologicall appeatance of chronic cholecystitis