Pathology of Nephrotic Syndrome II Flashcards
Primary criterion for nephrotic syndrome
minor criterion
1) albuminuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, hyperlipidemia
2) malnutrition, thrombosis, incr infection
Causes of proteinuria (2)
1) loss of polyanion
- -> destabilization of foot processes and lose size selectivity and charge selectivity
2) normally basement membrane does not filter large molecules
7 y/o boy over last 2-3 weeks listless,
55% weight –> now 90% weight
4g protein in urine
albumin = 1.9
diagnosis?
nephrotic syndrome
1) hypercellularity ?
2) inflamm cells =?
3) basement membrane thickening?
4) scarring?
diagnosis?

1) hypercellularity = no
2) inflamm cells = open capillary loops so no
3) basement membrane thickening? = look at tubule size
4) scarring? no
diagnosis = normal by light microscopy

fenestrated epithelium
foot process effacement = injury to endo cell = separate and retract—> creates holes
Minimal change nephropathy
1) clinically: ___ syndrome
2) on light microscopy, EM, IF
3) therapy
4) prognosis
1) nephrotic syndrome
2) light = no change
EM = foot process effacement
IF = negative
3) steroids
4) good
RIGHT = hypercellular? inflamm cells? basement membrane? scarring?
LEFT = scarring? focal or segmental or diffuse or global?

RIGHT =
slightly hypercellular
no inflamm cells
basement membrane thickening hard to see
but okay
scarring present
LEFT = too much pink disease = sclerosis
focal @ part of total glomeruli
segmental = @ individual glomerulus
45 y/o male otherwise well
shoes are too tight can’t lace up boot
too lethargic
15 lbs weight gain over 2 weeks
pitting edema
periorbital swelling
albumin = 1.7
cholesterol = 250
protein in uria = 4 (> 3.5g)
diagnosis
FSGS
FSGS
1) __ syndrome
2) on IF
on EM
3) pathogenesis
4) therapy
5) prognosis
1) nephrotic
2) normal on IF
foot process effacement on EM
3) hyperfiltration, hereditary forms
4) steroids = high relapse though
5) ESRD
FSGS most common causes
1) idiopathic/hereditary
2) HIV assoc (Rapid progr form of FSGS
3) heroin
4) secondary - reduced renal mass or initially normal (end stage diabetes)
hypercellular?
inflamm cells?
segmental scars?
basement membrane?
diagnosis?

not hypercellular
no inflamm cells
no segmental scars
thicker and fuzzier basement membrane
—> membranous nephropathy
left = linear or granular
right = basement membrane deposits?
inflamm cells?
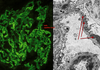
left = granular immune complex deposits
C3, C5a, IgG
right =
capillary loop outlined
with dark immune complex deposits along
basement membrane = subepithelial
no incr in inflamm = on downstream side
washed out inflamm cells in urine
membranous GN
1) ___ syndrome
2) morphology on light microscopy
EM?
IF?
3) therapy
4) prognosis
1) nephrotic
2) GBM thickening = spikes
EM = subepithelial deposits
IF = granular GBM
4) steorids
5) ESRD
Stages of membranous nephropathy
1) injury to glomerular epith cell
2) responds by incr basement membrane to wall off injurious agent
3) overlap of basement membrnae on top
4) agent dissolved away
arrows?
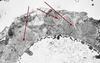
abnormal
membrane
arrows = deposits are blanching
Membranous GN
1) most offen in which patients
2) assoc with …
1) adults
2) bugs = infection, drugs (RA), tumors (malignancy), rheum (SLE)
left = basement membrane?
hypercellular?
endocapillary prolif?
inflamm cells?

left = basement membrane thickening
hypercellular
diffuse endocapillary proliferation
some inflamm cells
right = linear or granular?

left = large deposits
in between layers of double contour
tram tracking
right = globular = not linear or granular

right = subendothelial
deposits , normal basement membr
52 y/o woman
over last 3 weeks = flu-like symptoms
dysuria
can’t sleep
+edema
+rales too many RBC in urine
RBC casts
creatinine = 3.5
albumin = 1.7
4+ proteins in urine
diagnosis?
nephrotic + nephritic syndrome (due to RBC casts = glomerulonephritis and creatinine = 3.5)
hypoalbuminemia, pitting edema, and proteins in urine
MPGN
1) usually __ syndrome
2) on light microscopy
in IF
in EM
3) therapy
4) prognosis
1) nephritic/nephrotic
2) cell prolif, GBM thickening - double countours = tram tracking
EM = subendo deposits
IF = granular GBM
3) steroids, interferon
4) ESRD
Renal amyloidosis
1) 2 light chain types
2) present with ___
3) histology shows
4) congo red stain ___
1) AA vs. AL
2) proteinuria
3) amorphous fluffy pink in glomeruli and vessels
4) apple green birefringence

renal amyloidosis




