Glomerular Filtration and Renal Blood Flow Flashcards
where does filtration of plasma into tubule occur?
filtration occurs across what?
arterioles control what
in glomerulus
across the capillary loops into Bowman’s capsule
arterioles on either side of lgomerulus control flow of plasma and lbood through filtration apparatus while regulating GFR
___ cells secrete renin (___)
granular cells = JGA cells = specialized smooth muscle of afferent arteriol
renin = controls AG II production

Describe factors affecting ultrafiltration
what creates the filtration filter
what is molecular size cut-off
smaller proteins are ___ after passing through the filtere
1) molecular size/weight of proteins = up to 60k daltons (smaller, easier to cross, more concentrated in filtrate)
2) slit membranes between podocytes and overlapping podocyte
3) cut off = 60,000 = lower than albumin size
reabsorbed and catabolized to constituent amino acids by tubular epith cells
3 layers of glomerulus
1) endothelium = fenestrated = no slits; exclude circulating RBC
2) basal lamina = secreted by endothelial and podocytes = made of mucoproteins with acidic sugars + protein cores
negatively charged, so more negative charge much lower than expected filterability
3) podocytes = sheet of tubular epith cell = round cells with numeorus “feet” pedicells in endothelial cell
form slit membranes

freely filtered substance has a filterability =
nonfiltered substance, filterability =
1
0
defect in podocyte feet would lead to___
leaky and large proteins easily pass through
3 factors influencing Starling forces
1) Pgc = hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillary –> only force for filtration into tubule
2) back pressure at Bowman’s capsule (Pt) = filtrate only flow in narrow parts of tubule –> backpressure opposing filtration
3) osmotic force that would cause fluid to reverse opposite GFR (pigc)= opposing nnegative relative to glomerular capill pressure
no sosmotic pressure
Starling force for GFR equation
define variables
GFR = K(ΔP) = K(Pgc - Pt— πgc)
Pgc = pressure that drives flow across glomerular capillary endothelium into tubule
Pt = filtrate flow in narrow tubule = back pressure opposing filtration
πgc = net osmotic force across filtration = opposing, negative = oncotic pressure = colloid osmotic pressure = COP
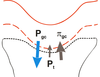
Typical magnitude for each Starling force
Pgc-Pt-πgc= Net filtration pressure (NFP)
● Pgc= 46 mmHg/Torr
● Pt= 10 mmHg/Torr
● πgc = 30 mmHg = colloid osmotic pressure = COP
● NFP=6mm Hg which is<1%of1ATM

Typical magnitude of each Starling force and resultant NFP
How with so little pressure do we filter so much?
Pgc =46mm
Pt =10mm
πgc= 30mm
NFP = 6mm
_____
Low resistance + large surface area for filtration (1 m^2) = large constant K (how much fluid flow across glomerulus per unit time for each unit pressure= more efficient)
What if when you are sleeping your BP drops to 85 from 100
What if when exercising BP goes from 100 –> 115?
How does Pgc change?
Pgc and GFR stays constant
Process of autoregulation of GFR and RBF
Autoregulation is mediated by ____
if you have a short term drop in MAP, what happens to arteriole?
if you have incr in MAP, what happens to arteriole
changes in afferent arteriolar ton–> myogenic so intrinsic to smooth muslce
afferent dilate to restore Pgc, GFR, and RBF to normal values
afferent constricts

Range over which autoregulation occurs?
MAP 75-150

What is the renal solution to hypovolemia?
GFR maintained by ____
1) decr MAP
2) incr total peripheral resistance (TPR) to shunt blood flow to vital organs
3) decr Renal blood flow
4) afferent arteriole constricts, decr RBF, decr Pgc, decr GFR (good for CV bad for kidney b/c GFR changing)
5) efferent arteriole constricts (divertor), incr Pgc back to normal incr GFR, incr renal vascular resistance, decr RBF even more for diverting perfusion to other organs
GFR maintained coordinated constriction of afferent and efferent arterioles

GFR is regulated to be relatively ___ in normal physiology
But in real life, GFR decr depend on severity of hypovolemia, but compared to RBF?
constant

GFR will decr somewhat but not as much as RBF;
RPF decr and RBF decr
filtration fraction, and πgc incr
Mechanism of hemorrhage (decr MAP)
1) decr MAP
2) incr stim of arterial baroreceptor reflex
3) incr firing of renal symp nerve
4) incr constriction of afferent and efferent arterioles
5) decr RBF, GFR constant
Renal prostaglandins produced by ____
Secreted in response to? and have what effect on renal arterioles?
renal interstitial cells located in kidney medulla between pyramids
angiotensin II and have LOCAL DILATORY EFFECT ON RENAL ARTERIOLES
2 effects of dilatory renal prostaglandins
1) maintain adequate renal blood flow by blunting effect of Angiotensin II (vasoconstrictor) on renal arteriole (so RBF and GFR reductions not as severe as with pure vasoconstrictive baroreceptor and AGII)
2) PROTECT AGAINST ACUTE RENAL FAILURE IN HYPOVOLEMIA
3) selective for afferent arteriole for vasodilation to restore GFR to normal
compare autoregulatory vs. baroreceptor response

complete mechanism of renal response to hypovolemia
1) hypovolemia, decr MAP
2)
a) stim of arterial baroreceptor reflex –> incr firing rate of renal symp nerve
b) (HORMONAL = incr JGA baroreceptor stim –> incr JGA renin secretion –> incr AGII)
c) intrarenal baroreceptors on granular cells
4) constriction of afferent/efferent arterioles (and incr TPR to restore MAP). decr RBF
5) Pgc constant and (decr renal blood flow –> incr filtration fraction –> incr πgc)
6) modest to moderate decr GFR
JGA cells on afferent arteriole stim by renal symp nerve –> secrete renin

podocyte feet slit membranes and basal lamina CONTRIUBTE to
molecular sieving properties in glomerulus
glomerular capillaries covered by ___
mesangial cells contact, decreasing
mesangial cells
area and decr K and decr GFR
GFR is regulated to be relatively ___
tubular handling of each regulated substance is __
what happens when GFR constant but rate of water reabsorption decr
constant in normal physiology
varied
incr urine output
capillary blood pressures are low compared to ___
if MAP incr by 15% will cause what changes in NFP and GFR
changes in MAP ___ proportionate changes in glomerular capillary pressure
MAP because blood has to flow thru major arteries before reaching capillaries
NFP double, GFR to 0
DO NOT CAUSE




