Path part 2 ho2 Flashcards
(204 cards)
What is the gold standard in investigation of acute lymphadenitis?
culture
What is the most common type of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, especially in children?
follicular lymphoid hyperplasia
The paracortical pattern of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia has…
interfollicular expansion, mainly T cells
What are the three patterns of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia?
follicular pattern
paracortical pattern
sinus pattern
When would you see a sinus pattern of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia?
lymph nodes draining tumors
whipple disease
rosai-dorfman
What is strongly associated as a cause of paracortical lymphoid hyperplasia? What is the description of this?
infectious mononucleosis;
paracortical region expanded, residual follicles are present but obscured
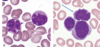
Which one is the non-necrotizing granuloma of sarcoidosis?

the darker purple image
When metastatic tumor cells invade the lymph node, what is the order of locations in which they appear?
first in marginal sinus, then penetrate medually sinuses, then medulla, then cortex
Mets to the L supraclavicular node is probably from a primary tumor of…
abdominal, esp gastric
What is the MC congenital abnormality of the spleen? what is this also called?
accessory spleen
spleniculi
When is a congenital accessory spleen even significant?
in hematologic disorders when splenectomy is a tx
“septic splenitis” is a response to systemic infection by the spleen, seen in ….
follicular (lymphoid) hyperplasia
this can be acute (EBV inf) or chronic
thick white plaques covering the surface of the spleen, common incidental finding at autopsy
perisplenitis
most commonly, cirrhosis will cause splenomegaly due to its…
congestive state
congestive splenomegaly is a direct result of …
venous outflow obstruction
thrombosis of hepatic veins causing splenomegaly
Budd-Chiari syndrome
What are some causes of splenic infarcts?
endocarditis
severe atherosclerosis
massive splenomegaly
thrombosis of splenic vein
splenic infarct appearance
pale, tan, wedge shaped, esp if arterial
subcapsular
What are the MCC of splenic ruptures?
trauma and surgical intervention
What are splenic inplants?
splenosis - little mini spleens appearing after rupture
What could hypersplenism cause? How could you resolve this issue?
any kind of blood cytopenia due to increased functioning (splenic sequestration and destruction)
typically resolve after splenectomy
What are some causes of hypersplenism?
autoimmune diseases
congestive splenomegaly
Gaucher disease
What is the MC primary tumor of the spleen?

hemangioma - usually cavernous type and less than 2 cm in size
What is the morphology of lymphangiomas? Who do they occur in?

subcapsular region of the spleen; multicystic; lumina contain proteinaceous material, not RBCs; endothelium may form small papillary projections
most cases in children