Path 3 - Tumors of the large, small bowels, vermiform appendix and peritoneal cavity Flashcards
What does sessile mean?
Flat - though can have villous architecture
What does pedunculated mean?
On a stalk, somewhat resembling a mushroom.
What are three types of non-neoplastic colorectal polyps we covered?
•Hamartomatous polyps
- Inflammatory Polyps
- Hyperplastic Polyps
What are three neoplastic colorectal polyps we discussed?
- Sessile serrated Adenoma
- Adenoma
- Polyposis Syndromes when numerous polyps are present
Hamartomatous Polyps have a haphazard arrangement of normal stromal and epithelial elements. What do they occur mainly as a result of?
Why is it important to recognize these polyps?
- Occur mainly as a component of a polyposis syndrome but can occur as a sporadic hamartomatous polyp
- It is important to recognize these polyps because of associated intestinal and extraintestinal malignancies.
What are two polyp syndromes that give rise to hamartomatous polyps?
–Peutz-Jegher syndrome
–Juvenile polyposis
Is Peutz-Jegher syndrome heritable?
Yes - Autosomal Dominant
What are the physical manifestations of Peutz-Jegher syndrome?
Multiple GI hamartomatous polyps and mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation.
Where do the polyps of Peutz-Jegher syndrome most often appear?
Small intestine
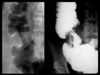
What has this kid got going on?

Peutz Jegher Syndrome
What was the cause of this polyp?
How do you know?

Peutz Jegher Syndrome
Small intestine Peutz Jegher polyps have a smooth muscle core with arborizing branches. Most polyps have a connective tissue core, so this is pretty distinct.
What do you get the pleasure of telling this patient about his disease?

Peutz-Jegher syndrome has a marked increased risk of malignancies.
Ok, so we established that Peutz-Jegher syndrome has a marked increased risk of malignancies. Which ones?
What is the total lifetime % risk?
- Colon
- Pancreas
- Breast
- Lung
- Urinary
- Gynecologic
40% lifetime risk
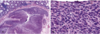
What condition does this person have?
What is being stained in the image on the right?

Peutz-Jegher syndrome
Muscle actin stain - reveals arborizing smooth muscle
The majority of juvenile (retention) polyps occur in children younger than 5 years of age. Describe the malignancy potential of this condition.
If solitary (which is 70% of the time): virtually no malignant potential
Can hovever be associated with dysplasia, and 30 - 50% develop colonic adenocarcinoma by 45.
What is the inheritance pattern of juvenile (retention) polyps?
Autosomal Dominant
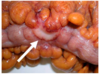
This was removed from the colon of a 5 year old patient, it was the only polyp found. Is it malignant?

Almost certainely not - Juvenile Polyposis
This lesion was removed from the colon area of our patient who has a 3 year history of ulcerative colitis. What is it?
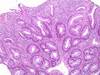
Inflammatory polyp
Inflammatory polyps are found in the regenerative and healing phases of inflammation. What disease states give rise to this?
Severe colitis
chronic inflammatory bowel disease
ameobic colitis
ischemic colitis
bacterial dysentery
Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome
This was obtained from a patient’s left colon/rectum in their 60/70s, This is the most common type of colon polyp.
What is it?
Is it malignant?

Hyperplastic polyp
Benign
(left colon/rectum import for distinguishing from sessile serrated adenoma)
What is the most common type of colonic polyp?
Whe is it typically discovered?
Hyperplastic polyp
6th to 7th decade of life
You find multiple polyps in your patients right colon, some of which are greater than 5mm. What are there?
What is/are the mutations commly in?
How is this patients outlook?
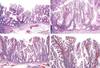
Sessile serrated adenoma (the right colon bit is important)
High rate of BRAF mutations and DNA methylation
Patients with multiple serrated polyps are at an increased risk of colonic adenocarcinoma.
Sessile serrated adenoma are most commonly found in the right colon. What does it typically resemble histologically?
What is one way to distinguish?
Resemble hyperplastic polyp
Hyperplastic polyp - Left colon/rectum
Sessile Serrated adenoma - Right colon
Conventional adenomas are common lesions that are almost always asymptomatic, the clinical importance of these lesions is related to?
Their well established premalignant nature
50% of the the population >50 yo in Western countries such as the United States have adenomas. Size of the lesion is a strong predictor of progression to malignancy. How big do they have to be to have a substantial increase in the risk of malignancy?
Greater than 2 cm
What is the appropriate treatment of colorectal adenomas?
What is the optimal screening tool for this?
Complete removal.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard
At what age do most people need to start colorectal screening?
50 y/o
What is shown here?

Pedunculated tubular adenoma
What does the attached histology depict?

Tubular adenoma - note the sircular formations
Identify the adenomae shown in images A and B.

A. Tubular: The polyps have a dome-shaped surface. The largest polyp in the center also shows subtle lobulations.
B. Villous: The polyp grows as a flat plaque with slightly raised edges. (sessile)
What is this?
Villous adenoma
This image illustrates characteristic findings in a villous adenoma. What are they?
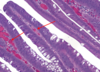
Villous adenomas are characterized by slender papillae containing a fibrovascular (arrows) core and lined by adenomatous epithelium
What are the risks of cancer in a polyp that is the following sizes?
1 - 2 cm
> 2cm
> 4cm
–Between 1-2 cm 5% risk of cancer
–> 2 cm 10-20% risk of cancer
–> 4 cm 40% risk of cancer
Which adenoma is more likely malignant, villous or tubular?
Villous
The severity of epithelial dysplasia increases the odds of a polyp being malignant. Does it increase the risk of carcinoma elsewhere in the colon?
No
What is shown in the circle sign?
How do you treat it?

Cancer in an adenomatous polyp.
Treat by removing the polyp since it is not in the stalk or near the base.
If cancer appears in a polyp close to the margin, how do you treat then?
Either…
Post polyp removal, burn the crap out of the residual mucosa
Or
Remove 10 cm of bowel around the lesion
What is the inheritance pattern of familial adenomatous polyposis?
Autosomal dominant
What is FAP characterized by?
•presence of hundreds to thousands of adenomas in the colorectal mucosa by 20 to 30 years
FAP is the result of an inheriteddefect in what?
One allele of the APC tumor suppressor gene
What does this look like?
What was the inciting event?
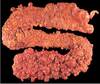
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
APC mutation kicked it off