Path 3 Flashcards

Acute (short/days, neutrophils, edema, no fibrosis, vasodilation & permeability, fever, leukocytosis)
Chronic (long/weeks-months, lymphocytes & plasma cells, ?edema, fibrosis, neovascularization, granulation tissue, low grade fever, anemia, wt loss)


center w/ caseation necrosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection


epithelioid histiocytes (macrophages) forming multinucleated Langhans Giant cells

normal lung


normal lung


normal lung

bronchopneumonia
- atypical pneumonia
- follows distribution of bronchi & bronchioles (patchy)
- staph aureus, klebsiella (abscess formation),
e. coli, pseudomonas, nosocomial pna



acute bronchopneumonia

acute bronchopneumonia

acute lobar pneumonia
- solid congestion, almost entirety of lung lobe
- less common than bronchopna
- pneumococcus (strep pneumoniae)

acute lobar pneumonia



acute pneumonia


bronchopneumonia

lobar pneumonia


lobar pneumonia
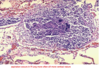
Aspiration pneumonia
- usually occurs in Rt lung d/t more vertical Rt main bronchus
- type of bronchopneumonia


aspiration pna
-foreign bodies/aspirated material found w/in multinucleated giant cells/macrophages


Complications of PNA
- lung abscesses
- Empyema (pus in pleural cavity)
- Organization of exudates w/ pulmonary fibrosis
- Sepsis
- E.g. of lung abscess


lung abscess, cavitation

Lung abscess


Ghon complex, primary TB

secondary TB


miliary TB
-tuberculous bronchopneumonia

miliary TB


miliary TB

miliary TB, multiple granulomas

langhans giant cells in TB, epithelioid cells response to granulomas


caseation necrosis in center of granuloma in TB

AFB stain in TB

Fungi can exist as mole (hyphae) or yeast (rounded)
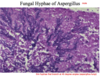

coccidiodes spherules (fungi)


coccidioides (fungi)

histoplasmosis (fungi)



