Patellar Fracture Flashcards
(16 cards)
Epidemiology of patellar fractures
20-50 year olds
Twice as common in males
Mechanism of injury
Direct trauma to the patella
Can also occur, albeit less common due to rapid eccentric contraction of the quadriceps muscle.
Explain the patella
Largest sesamoid bone in the body formed within the tendon of the quadrices femoris muscle.
It crosses oer the anterior aspect of the knee joint and attaches to the patellar ligament inferiorly.
It serves as a fulcrum for the knee joint as well as protecting the knee joint.
Clinical features
Anterior knee pain following a e.g. hard blow to the patella like dashboard injury in a RTC or strong contraction of the quadriceps.
Pain is made worse with movement
Patient will be unable to straight leg raise
May not be able to bear weight.
Examination findings
Significantly swollen and bruised
Often a visible and palpable patellar defect is present between the bone fragments.
Dx
Tibial plateau fracture
Distal femur fracture
Cruciate or collateral ligament injury
Quadriceps tendon rupture
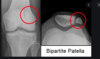
Explain bipartite patella
Congenital condition more common in males.
Failure of patellar fusion leads to two separate bone fragments joined only by fibrocartilaginous tissue.
It is usually asymptomatic and picked up incidentally on imaging.
It can rarely present symptomatically with anterior knee pain, especially after exercise or overuse.
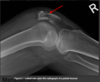
Investigations
Plain film radiographs (AP, lateral and skyline) even if Skyline view is often not possible due to pain inhibiting knee flexion to the necessary 30 degrees
CT is indicated in comminuted fractures or if not seen on x-ray but clinical suspicion is there
Classification of patellar fractures
AO foundation classification
Explain AO Foundation classification of patellar fractures
1 - Extra-articular or avulsion fractures
2 - Partial articular fractures
3 - Complete articular fractures
Indications of conservative management
Non-displaced or minimally displaced patellar fractures
Or vertical fractures where extensor mechanism is still intact
Explain conservative management
Brace or cylinder cast
Early weight bearing in extension should be done.
Do not start flexion early
Indications for surgical intervention
Significant displacement
Compromise to the extensor mechanism
Most common surgical intervention
ORIF with tension band wiring.
Aims to convert the tensile force applied to the patella via the extensor mechanism into a compression force to assist with fracture reduction and healing.
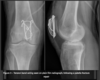
When might ORIF or tension band wiring not be used?
In simple vertical or transverse fractures in healthy bone screw fixation can be used instead of wires.
If ORIF is not possible, partial or total patellectomy may be considered
Complications
Loss of range of motion
Secondary OA at patellofemoral joint


