Part 2: Trilaminar Embryo Flashcards
Does the entire spinal cord develop from the neural tube?
- no; the saccral region of the spinal cord develops from the mesoderm
Each somite differentiates into what two structures?
- dorsolateral dermomyotome (low shh)
- ventromedial sclerotome (high shh)

Dermomyotome develops into:
skin and muscle
- derived from somites
Sclerotome develops into:
bone
- derived from somites
- forms the vertebrae around the neural tube
- interference with sclerotome migration leads to spina bifida

The upper limb bud develops adjacent to what somites?
C5-T1
The lower limb bud develops adjacent to what somites?
L2-S3
Mesenchyme is:
- mesoderm that has been invaded by neural crest cells
- mix of mesoderm and neural crest cells
Proximal to distal differential development in the limbs is controlled by:
- interactions between the apical ectodermal ridge and the underlying mesoderm

Medial to lateral asymmetry in the limbs is controlled by:
- factors released from the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) in the caudal limb bud.
- ZPA releases shh
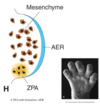
Dorsal to ventral differential development in each limb is controlled by:
- different groups of transcription factors in each region
- controls development of extensors and flexors.

Process of somite dermomyotome division:
- somite dermomyotome divides into dermotome and myotome.
- myotome divides into epimere and hypomere.
- epimere becomes intrinsic back muscles.
- hypomere divides into dorsal and ventral muscle masses in the limbs.
- dorsal mass becomes extensor muscles.
- ventral mass becomes flexor muscles.
The epimere has a relationship with what spinal nerve?
- dorsal primary ramus
- becomes intrinsic back muscles
The hypomere has a relationship with what spinal nerve?
- ventral primary ramus
- divides into dorsal and ventral muscle masses of the limbs.
- dorsal = extensor
- ventral = flexor

What nerve innervates the limbs?
ventral primary ramus
Process of bone development:
- lateral plate mesoderm migrates into the limb to form bones and connnective tissue.
- bone cartilage model formed.
- bone cartilage model becomes ossified at diaphysis.
- bone cartilage model becomes ossified at epiphysis.
- diaphysis and epiphysis separated by epiphyseal (growth) plate.
- diaphysis and epiphysis fuse.

Primary ossification center is called:
- diaphysis
- located in the shaft
Secondary ossification center is called:
- epiphysis
- one at each end of growing bones

The primary (diaphysis) and secondary (epiphysis) ossification centers are separated by:
- epiphyseal (growth) plates.
- primary and secondary centers have different blood supplies.

Relationship between skin overlying limb bud and spinal nerves for sensory innervation:
Linear/nearest dermatome

Effect of lower limb development on the relationship between skin overlying limb bud and spinal nerves for sensory innervation:
- lower limbs rotate 180 degrees medially
- dorsal (extensor) muscle mass becomes ventral
- ventral (flexor) muscle mass becomes dorsal



