Part 1: Trilaminar Embryo Flashcards
When does the primitive streak form?
beginning of the third week
Fluid of the primitive node contains:
vesicles containing sonic hedgehog protein
Sonic hedgehog protein vesicles are pushed from the right to the left side of the embryo via the singlar cilia on each cell of the primitive node.
What is the role of sonic hedgehog in this setting?
- induce asymmetric gene expression.
- sets up the “sidedness” of embryo.
What two parts of the embryo do the epiblast cells not invade during gastrulation?
- buccopharyngeal membrane
- cloacal membrane
What layers of the embryo are derived from the epiblast?
- all three (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm)
Initial formation of the notochord process:
- epiblast cells of the primitive node delaminate and establish the midline notochord between the ectoderm and endoderm cranial to the primitive streak
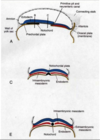
Role of the notochord:
- induces the overlying ectoderm to form the nervous system.
When does elongation of the embryo occur, and what drives it?
- immediately following the formation of the mesoderm.
- mesoderm proliferation drives elongation.
As the embryo elongates, the mesoderm differentiates into what 3 regions?
- paraxial mesoderm
- intermediate mesoderm
- lateral plate mesoderm

Paraxial mesoderm gives rise to:
somites
Intermediate mesoderm gives rise to:
urinary and reproductive systems
Lateral plate mesoderm gives rise to:
limb bones and connective tissue
The three types of folding that occur to the embryo during gastrulation:
- lateral folding
- cranial folding
- caudal folding
Lateral folding of the embryo:
- driven by mesoederm proliferation
- forms gut tube and body cavities
- brings embryo into the amniotic cavitiy

Cranial folding of the embryo:
- driven by developing forebrain
- brings buccopharyngeal membran from dorsal to ventral surface
- brings developing heart into thorax

The two structures moved by cranial folding:
- buccopharyngeal membrane
- dorsal to ventral surface
- heart
- moves into developing thorax
Caudal folding of the embryo:
- brings cloacal membrane from the dorsal surface to the ventral surface
As the embryo begins lateral folding the notochord induces:
- overlying ectoderm to become neural plate.
- neural plate forms neural folds and a neural groove.
The neural plate forms:
- neural folds and a neural groove
- neural folds eventually fuse to form the neural tube

Where do the lateral sides of the neural fold first meet and fuse?
- dorsal midline
- thoracic region

What population of cells originate from the portions of the neural fold that fuse together to form the neural tube?
neural crest cells

What tissue comes together on the dorsal surface to cover the neural tube?
ectoderm
Fusion of the neural tube proceeds in what directions from the initial fusion site in the thoracic region?
cranially and caudally simultaneously
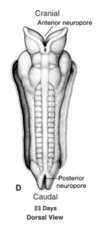
Neuropores are formed by:
- Fusion of the neural tube from the thoracic region in the caudal and cranially directions simultaneously.
- Defects in neuropore closure are termed neural tube defects.

When do the cranial and caudal neuropores close?
end of the fourth week
When is lateral, cranial, and caudal folding complete?
end of the fourth week
Neural tube defects are due to:
failures of fusion/closure at the neuropores
What defect results if the cranial neuropore does not close?
anencephaly (no brain)
What defect results if the caudal neuropore does not close?
- spina bifida
- failure of vertebrae (mesoderm) to cover the spinal cord dorsally
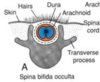
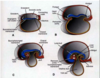
Spina bifida occulta:
- neural tube defect
- caudal neuropore does not close
- spinal cord in place
- lumbar region
- look for tuft of hair
- NO NEUROLOGICAL DEFECTS

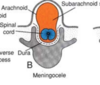
Meningocele:
- neural tube defect
- caudal neuropore does not close
- spinal cord in place
- arachnoid and subarachnoid space protruding
- lumbar region
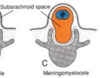
Meningomyelocele:
- neural tube defect
- caudal neuropore does not close
- spinal cord NOT in place
- arachnoid and subarachnoid in spinal canal
- lumbar region
Rachischisis:
- neural tube defect
- caudal neuropore does not close
- neural tissue does not fold properly
- PARALYSIS

What tissue do somites develop from?
mesoderm
Where do the somites develop?
- in pairs, one on each side of the neural tube
There are the same number of somites as:
- vertebrae
- spinal nerves
What happens to the developing neural tube as the somites form?
- nerve fibers/axons from the neural tube grow into the somites, induces the somites to change and migrate, and the somites take the axons with them as they migrate.



