Part 1: Structure of Eye Flashcards
1
Q
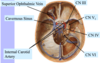
Outer layer of the eye consists of:
A
- sclera
- cornea
2
Q
Sclera:
A
- fibrous outer portion of the eye
- insertion for extraocular muscles
- continuous with the cornea
3
Q
The extraocular eye muscles insert onto the:
A
sclera
4
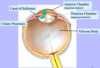
Q
Ciliary body:
A
- continuous with the choroid
- includes the ciliary muscle (for accommodation of the lens)
5
Q
Ciliary processes:
A
- secrete aqueous humor
6
Q
Iris:
A
- pigmented region which contains smooth muscle that controls the size of the pupil
7
Q
Optic disk:
A
- region of the retina from which all of the nerve fibers emerge to form the optic nerve
8
Q
Blind spot of the eye:
A
- at site of optic disk
- region of the retina where there are no photoreceptors
9
Q
The fovea is located where in the eye?
A
- pigmented region on the retina called macula lutea
10
Q
Is the optic nerve part of the CNS or PNS?
A
- CNS
- CNS diseases will affect vision and the optic nerve
- i.e. multiple sclerosis
11
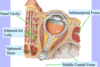
Q
Blood supply to the retina:
A
- central artery of the retina
- central vein of the retina
- surrounded by optic nerve
- no collateral blood supply
12
Q
The optic nerve is surrounded by:
A
- subarachnoid space containing CSF
- dura
13
Q
What structures are medial to the fovea?
A
optic disk and optic nerve
14
Q
Increasing intracranial pressure via CSF may lead to what in the eye?
A
- impingement of the central artery and central vein of the retina.
- CSF surrounds the optic nerve, optic nerve surrounds the artery and vein
15
Q
The region posterior to the lens is the:
A
vitreous body.
16
Q
The region anterior to the lens contains:
A
- anterior chamber and posterior chamber
- both contain aqueous humor

17
Q
Anterior chamber location:
A
- between cornea and iris

18
Q
Posterior chamber location:
A
between iris and lens

19
Q
Structure, location, and function fo vitreous body:
A
- behind lens
- contains vitreous humor
- maintains architecture of eye to prevent the eye from collapsing in on itself