Pain Flashcards
Effect of pain on CVS + RS
CVS: tachycardia, HTN, increased O2 demand
RS: reduced VC + FRC, basal atelectasis
Describe the 3 neuron pathway of pain
1st: Site of injury - dorsal root ganglion to spinal cord
2nd: spinal cord to thalamus
3rd: thalamus to somatosensory area

Types of nociceptors + what they respond to
Mechanoreceptors = pinprick + pinch
Silent receptors = inflammation
Polymodal = pressure, heat + allogens
What are allogens?
Bradykinin, histamine, serotonin, H, K + prostaglandins
What happens when there is an injury?
Histamine + bradykinin released
Phospholipase A2 activated
Converts phospholipids to prostaglandins
Action of paracetamol
Inhibits prostaglandin production
COX 3
Action of NSAIDs
COX inhibitors
Blocks prostaglandin + thromboxane production
COX1 vs COX2 inhibitors, names + SE
1 = Ibuprofen, diclofenac
SE = bronchospasm, GI effects, renal + platelet
2 = parecoxib, celecoxib
Less SE
Action of tramadol
MU receptor agonist
Increases inhibitory descending activity (serotonin + noradrenaline)

What is the RAT system?
Recognise Assess Treat
Methods of assessing pain
Verbal rating
Visual analogue scale (VAS)
Faces pain scale (FPS)
Treatments that act on peripheral system
Non-drug: rest, ice, compression, elevation
Anti-inflammatory meds
Treatments that act on spinal cord
Non drug = acupuncture, massage
Opioids, ketamine, local anaesthetics
Drug treatments that act on brain
Paracetamol Opioids Amitryptiline Clonidine
3 layers of spinal cord
Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater

Where is the CSF?
Between pia + arachnoid aka subarachnoid space
Where does a spinal block go?
Subarachnoid space

Where does spinal cord + subarachnoid space end?
Spinal cord = L1
SA space = S1
Where does epidural space end?
Sacrococcygeal hiatus

Where can you do a spinal block?
L4/5, L3/4, L2/3
L3/4 is ideal
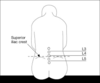
Where can you do an epidural block?
Risk of damage above L1
For labour - done at same level as spinal block
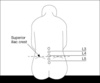
What layers does the needle pass through for an epidural + spinal?
Skin S
C fat
Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
EPIDURAL
Dura + arachnoid mata
SPINAL

What is a spinal block?
Single shot injection of anaesthesia into CSF
Rapid onset, anaesthesia for 2-3 hrs
Small 24G needle

What is an epidural?
LA +- opioid via catheter
Slower onset
Less motor block than spinal T
itratable analgesia for up to 72 hrs
Large 14G needle

A vs C nerve pain
A = sharp pain
C = chronic pain
What is the dose of paracetamol for IV + PO?
15mg/ kg (for >12 y/o + >50kg) every 4 hrs
1g every 4 hrs
Doses of codeine + max dose
8mg 15mg 30mg 60mg
Max 240mg in 24hrs
What to co-prescribe with an opioid?
Nalaxone (opioid receptor antagonist)
Codeine in breastfeeding
Goes into milk so give dihydrocodeine instead
SE of tramadol in elderly
Hallucinations
What is the reverse analgesic ladder?
Start with strong opiates and titrate downwards in severe acute pain
Use of magnesium
Good pain relief intra-operatively
Bronchodilation
How does ketamine work?
NMDA antagonist (used in Alzheimers)

How do neuropathic analgesics work?
Work by neuromodulation


