Local Anaesthetic Flashcards
What is LA?
Reversibly prevents transmission of nerve impulse in region to which it is applied
What are the types of LA?
Esters + amides

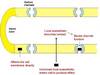
How is LA composed?
Lipid soluble hydrophobic aromatic group + charged hydrophilic amide group
Joined by ester or amide bond

What are the differences in esters + amides?
Esters - less stable + more likely to cause allergic reaction due to para-aminobenzoate (PABA)
Amides can be stored for longer
What are the short, medium + long duration ester LA?
Short = procaine, benzocaine, cocaine
Medium = prilocaine
Long = amethocaine
What are the medium + long duration amide LA?
Medium = lidocaine, mepivacaine
Long = bupivacaine, ropivacaine
Mechanism of action of LA + benefits
Inhibition of voltage sensitive sodium channel in axon, preventing action potential
Prevents pain by causing reversible block of conduction
Have membrane stabilisation effect

Mechanism of action of LA toxicity
Block Na+ channels found in brain + heart
S+S of LA toxicity
Tongue paraesthesia, metallic taste, dizziness
Slurred speech, tinnitus, confusion, restlessness, convulsions
Resp + cardiac arrest
Treatment of LA toxicity
A - maintain + secure with tracheal tube
B - give 100% O2
C - confirm IV access
D - control seizures with benzo, thiopental or propofol
Give IV intralipid 15ml/kg bolus followed by infusion 1.5ml/kg/hour
Max doses of LA
Lidocaine: 3 mg/kg
With adrenaline: 7mg/kg
Bupivacaine / levobupivacaine: 2 mg/kg
With adrenaline: 2 mg/kg
Prilocaine: 6 mg/kg
With adrenaline: 9 mg/kg
Chloroprocaine: 11mg/kg
With adrenaline: 14mg/kg
Ropivacaine: 2.5mg/kg
With adrenaline: 3mg/kg
How to work out ml of LA?
Multiply % with 10 and you get mg/ml i.e.
1% means 1X10= 10 mg/ml 2
% means 2X10= 20mg/ml
0.25% means 0.25X10 = 2.5 mg/ml
When to not give adrenaline with LC?
Areas with end arteries
Ears, penis, nose, tongue, fingers
How to work out how much ml to give a pt of LA?
Work out max dose (mg/kg)
Divide by ml of LA (% x 10)
What is the difference between levobupivacaine + bupivacaine?
Levo = left stereo-isomer - less cardiac toxicity
Bupivacaine = 50-50 racemic (50% levo 50% dextro)
What is local infiltration?
Injection of tissue with LA
What is a fracture haematoma block?
Hematoma created by fracture is infiltrated with LA
What is EMLA cream?
2.5% lidocaine + prilocaine
Topical anesthetic


