Osteoarthritis & Joint Replacement Flashcards
Define osteoarthritis [1]
A degenerative disease of weight bearing joints which occurs as a result of a disorder of articular cartilage
Describe the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis [5]
- Proteolytic breakdown of the cartilage matrix from an increased production of enzymes, such as metalloproteinases
- The proteoglycan and collagen fragments released into the synovial fluid as the disease progresses
- Erosion to the cartilage roughens the surface of the joint
- Fibrillation narrows the joint space, osteophytes may form and subchondral changes happen
- Increased production of synovial metalloproteinases, cytokines and TNF can diffuse back into the cartilage to destroy soft tissue around the knee (so the capsule, ligaments, tendons and muscles may get affected)
What are the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis? [8]
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Clicks/crepitus
- Deformity
- Mobility
- Walking/support/instability
- Night sleep disturbances
What are the clinical features of secondary osteoarthritis? [9]
- Other joint problems
- Nearby joint problems
- Systemic problems
- Back problems
- Long-term medicines
- Allergies - metals
- Family history
- Treatment history/previous surgeries
- Social history/personal habits
What examinations and investigations should you carry out on a patient with suspected osteoarthritis? [9]
- Examination
- General examination - including gait
- Systemic examination
- Specific joint examination
- Look/feel/move/special tests
- Neurovascular status distally
- Investigations
- Imaging
- Blood
- Urine
- Aspirate
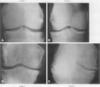
Describe the features of each CXR stage of osteoarthritis
- grade 0? [1]
- grade 1? [2]
- grade 2? [2]
- grade 3? [4]
- grade 4? [4]
- Grade 0
- No radiographic features of OA are present
- Grade 1
- Doubtful joint space narrowing (JSN)
- Possible osteophytic lipping
- Grade 2
- Definite osteophytes
- Possible JSN on anteroposterior weight-bearing radiograph
- Grade 3
- Multiple osteophytes
- Definite JSN
- Sclerosis
- Possible bony deformity
- Grade 4
- Large osteophytes
- Marked JSN
- Severe sclerosis
- Definite bony deformity
What are the management options for stage 1 (minor) osteoarthritis? [3]
- No therapeutic treatment as symptoms are minimal if any
- Lifestyle considerations
- Regular exercise
- Weight loss
What are the management options for stage 2 (mild) osteoarthritis? [4]
- Physiotherapy
- Strict exercise regimen and strength training
- for increased joint stability and weight loss
- Braces, knee supports or shoe inserts
- to protect the knee from stress
- Analgesia
What are the management options for stage 3 (moderate) osteoarthritis? [10]
- Over-the-counter NSAIDs or pain-relief therapies
- if not effective, give stronger pain medicine, such as codeine and oxycodone etc.
- If does not respond to physical therapy:
- weight loss
- brace
- acupuncture
- heat/cold therapy
- massage
- local anti-inflammatory gels
- May require intra-articular infections of steroid/hyaluronic acid into the joint
- not curative - symptom relief
- Risk of infection
- Some may consider prophylactic realignment surgery
What are the management options for stage 4 (severe) osteoarthritis? [11]
- If does not respond to analgesia:
- physical therapy
- weight loss
- brace
- acupuncture
- heat/cold therapy
- massage
- local anti-inflammatory gels
- Surgery
- Realignment
- Replacement
- Excision
- Fusion
What are the 3 types of knee joint replacements? [3]
- Total knee replacement
- Unicompartmental replacement
- Patellofemoral replacement
What are the potential complications of both knee and hip joint replacement surgery? [11]
- DVT/PE
- Infection
- Neurovascular damage
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- No or partial relief
- Recurrence
- Anaesthetic problems
- Renal, gastric, respiratory, cardiac, cerebral compromise
- Death
- Failure of procedure
What are the potential complications of hip replacement surgery? [5]
- Dislocation
- Fracture
- Leg length discrepancy
- Hip noise
- Implant breakage/failure
What are the potential complications of knee replacement surgery? [5]
- Stiffness
- Fracture
- Ligament or tendon damage
- Kneeling difficulty
- Failure


