ORS03 - Lecture 5 - Spread of Infection Flashcards
(13 cards)
What are the 2 susceptible regions in the body for infection?
Lymphatic Tissue
Tissue spaces (between fascia, organs and tissues)
Descibe the spread of infection through the tooth (7)
1) Caries in the enamel
Signs -> white spot lesion
Test - 3 in 1
Treatmeant = flouride varnish
2) Caries in the dentine (dentine sensitivity)
Symptoms -> sensitivity, short sharp pain, duration = short
Test - 3 in 1
Treatment = restoration
3) Caries in upper 1/3 pulp (acute reversible pulpitis)
Nerve becomes hyperalgesic (sensitive to pain)
Symptoms -> short sharp pain, triggered by hot/cold/sweet, duration = long
Treatment = restoration (GIC/biodentine)
4) Caries in lower 2/3 pulp (acute irreversible pulpitis)
Hard to anaesthetise (acidic environment)
Symptoms -> dull throbbing pain, triggered by hot/cold/sweet
Test = vitality (ethyl chloride) -> enhanced response
Treatment = RCT
5) Pulp dies (Necrotic pulpitis)
If due for extraction - some dentists perscribe antibiotics even though it wont work
They are just waiting for the pulp to die -> pain relieved.
Test = vitality (ethyl chloride) -> no response
Treatment = RCT or exctraction
5) Inflammation of the PDL (acute apical periodontitis)
Bacteria travels through the apex of root -> infecting PDL (containing proprioreceptors)
Signs -> widening of PDL, loss of bone, radiolucency at apex
Test = TTP (tender to percussion) -> pain
6) If left untreated (chronic apical periodontitis)
Signs -> bigger radiolucency, pain upon biting
Test = easy to locate pain (patient can point to it)
7) Pus forms and accumulates (apical abscess)
Collection of pus -> swelling apically
Signs = sinus tract
Treatment = drainage and removing source, give antibiotics if signs of systemic spread (fever, lymphadenopathy, cellulitis)
Describe the spread of infection away from a tooth (4)
1) Pulpal necrosis or Pericoronitis (gum tissue becomes infected and swollen (usually wisdom teeth))
Spreads -> peri-radicualr tissues
2) Acute apical periodontitis/abscess or pericoronal abscess (within the gum)
Draining through the bone into the oral cavity
3) Buccal abscess/sinus or lingual/palaltal abscess/sinus
Fascial spread through anatomical spaces
4) Pus filled fluctuant swelling or cellulitis

What is an abscess? (1)
Localised, well defined collection of pus -> fluctuant swelling
Identify the disease in the picture (3)
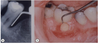
Lateral periodontal abscess
Forms at the base of a deep periodontal pocket
Test = tender to lateral tapping (as opposed to apical), pulp is usually vital (unlike apical abscess where its never vital)
What is cellulitis? (2)
Diffuse, swelling due to fluid exudate in connective tissue
Soft initially but can become firm
Where do upper teeth infections typically spread? (3)
Cheek
Under eye -> eye closure
Primary maxillary space -> orbital cellulitis, cavernous sinus throbosis (backward flowing venous blood can spread infection to area under the brain -> clot formation)

Whata re the signs and symptoms of local and systemic infection? (2)
Local -> inflammation, swelling, red/hot, trisumus, halitosis, TTP
Systemic -> febrile 4, lymphadenopathy, rash, dysphagia, dysartheria, airway obstruction, raised c-reactive protein (CRP) and WBC
Give examples of complications that occur if infection spreads (6)
Airway impingement (Ludwig’s angina)
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Osteomyelitis (of jaw)
Scarring from extra oral sinus
Sepsis or septic shock
Endocarditis
Describe Ludwig’s Angina (5)
Rare skin infection that occurs in the floor of the mouth - mainly caused by L8 infections
Affects -> submandibular, sublingual and submental tissue spaces
Swelling causes -> airway compromise -> lead to death < 24 hours
Symptoms include (7) -> pyrexia, firm swelling (submandibular and submental), raised floor of mouth, tongue up and back, dysphagia (w/ drooling), trismus, change in voice
Management (4) -> intubation (tubes) to protect airways, IV antibiotics/analgesics/fluid, remove source of infection, surgical drainage
What are the 3 steps of managing dental infections?
Remove source of infection (extraction, RCT, periodontal treatment)
Drain pus (incision into swelling, send pus sample for MC&S, extra-oral under GA)
Supportive therapy (antibiotics, analgesia, fluids)
What 3 antibiotics are prescribed for infection in oral surgery?
Metronidazole (200mg / 8 hours for 3 days)
Amoxicillin (250mg / 8 hours for 3 days)
Clindamycin (150mg / 6 hours for 3 days - if allergic to penicillin)
What antibiotics arent recommended for dental infections?
Amoxicillin w/ calvulanic acid
Erythromycin
Penicillin


