Organisation and Management of the NHS Flashcards
When was the NHS created?
1948
What was the NHS created as part of?
The welfare state
What are the core principles of the NHS?
- Universal
- Comprehensive
- Free at the point of delivery
What is meant by the NHS being universal?
Covers everyone
What is meant by the NHS being comprehensive?
Covers all health needs
What is meant by the NHS being free at the point of delivery?
It is available to everyone based on need, not ability to pay
Who has a duty to provide health services?
Secretary of State for Health
How was the NHS initially run?
Centrally, by the Department for Health
What changes to the NHS happen in the 1950’s and 60’s?
Changes to what consituted a health need
How is there an increasing role for managers in the NHS?
More strategic management roles
Why is there increasing marketisation of provision in the NHS?
Competition between hospitals
What is the aim of competition between hospitals in the NHS?
Aimed at improved choice and quality, and contains cost
What current reforms are happening in the NHS?
- Commissioning
- Health and Social Care Act (2012)
What happens in commissioning in the NHS?
The commissioners act as ‘customers’, choosing between different care providers on patient’s behalf
What do commissioners choose on the basis of?
- Cost
- Patients’ needs
- Quality
What changes were made in the Health and Social Care Act of 2012?
- Devolves power (especially commissioning) to GPs and others in primary care
- Shakes up the NHS’s structure significantly
- Increases use of markets
- Requries efficiency savings of £20bn per annum
How is an increased use of markets achieved?
Opportunities for NHS staff to set up their own care organisations, ‘social enterprises’
What is the budget given in the Health and Social Care Act 2012?
£100bn
What is the result of devolution?
Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland each have differently organised NHS
How is the Scottish NHS organised?
‘Health Boards’, which are integrated regional organisations
How are the Welsh and Northern Irish NHS’s organised?
Have ‘provider-purchaser’ split, similar to England
Draw a diagram illustrating the structure of the NHS
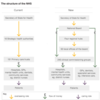
Who has overall accountability for the NHS?
The Secretary of State for Health
What does the Department of Health do?
- Sets overall national standards
- Shapes direction of the NHS and social care services
- Sets national tariff


