Organic Chemistry Flashcards
(224 cards)
What is a functional group?
The part of a molecule where most of its chemical reactions occur. It is the part that effectively determines a compound’s chemical properties in addition to many physical properties.
What is an alkyl group?
A general, non-aromatic, hydrocarbon obtained by removing a hydrocarbon atom from an alkane.

What does R represent?
A general alkyl group
What is the structure of a general primary alcohol?

What is an aryl group?
Aromatic hydrocarbon group from an arene with a H atom removed.

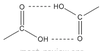
What is a carboxylic acid? (R group is an Aryl group)

What is a phenyl group?

What is an alkanoyl (acyl group) group?
- Alkanoyl (alkyl + carbonyl)

What is an acetyl (ethanoyl) group?

What is a benzoyl group?

What is a nucleophile?
- Nucleophiles are literally “things that love nuclei”. (Nuclei are positively-charged.)
- Nucleophiles are either negatively-charged, or at least have a negatively-polarized part that is reactive.
What is an electrophile?
- Electrophiles “love electrons”.
- They are either positively-charged or have a positively-polarized part.
IR spectrum of C=O shows a strong, sharp band between ____ cm-1.
IR spectrum of C=O shows a strong, sharp band at **1650-1800 **cm-1.
IR spectrum of -OH and -NH groups has bands at ____ cm-1.
-OH and -NH have intermolecular bonding, causing IR bands to be broad, extanding over a wide region (3600-2700 cm-1)
Alkene

Alkane

Alkyne

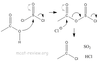
Ammonia
NH3
Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary amine

Amide

Imine

Hydrazone

Oxime

Nitro