Organ by Organ Flashcards
Function of abdominal esophagus:
conduit for food
Function of Stomach and Duodenum:
Digestion
Function of small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum):
Absorption
Function of colon:
resorption of water, storage of stool
Opening through which the aorta reaches the abdomen from the thorax:
- aortic hiatus
- between the diaphragm and vertebral column
Opening through which the IVC reaches the abdomen from the thorax:
- caval hiatus
- opening in the central tendon of the diaphragm
Opening through which the esophagus reaches the abdomen from the thorax:
- esophageal hiatus (around T10)
- opening in muscle of the diaphragm
Label all:
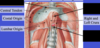

The two types of hiatal hernias:
- sliding type
- paraesophageal type
Sliding type hiatal hernia:
- Abdominal esophagus, cardia, and parts of fundus in thorax
- regurgitation occurs
Paraesophageal type hiatal hernia:
- Cardia in normal position
- Fundus in thorax
- No regurgitation
Which type of hiatal hernia does regurgitation occur?
- sliding type
- diaphragm/esophageal sphincter relationship altered
What type of hiatal hernia is this?
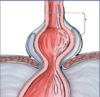
sliding type
What type of hiatal hernia is this?

paraesophageal type
The four parts of the stomach:
- cardia
- fundus
- body
- pyloric part (antrum, canal, pylorus)

Location of stomach cardia:
- surrounds cardial orifice where esophagus enters the stomach
Location of stomach fundus:
- extends from diaphragm to cardial orifice (where esophagus enters)
Location of stomach body:
- between fundus and pyloric antrum
The three parts of the stomach pyloric part:
- Antrum
- Canal
- Pylorus (sphincteric region)
The pyloric canal connects:
stomach to duodenum
The two smooth muscle layers of the digestive system, with the exception of the stomach:
- outer longitudinal
- inner circular
The three smooth muscle layers of the stomach:
- outer longitudinal
- middle circular
- inner oblique
Muscle and function of the pyloric sphincter:
- thickening of middle circular smooth muscle
- controls passage of food from stomach to duodenum
Arterial supply of stomach:
- left gastric and right gastric
- right gastro-omental and left gastro-omental
- short gastrics
Label all:


Arterial supply to lesser curvature of stomach:
right gastric and left gastric anastomosis
Arterial supply to greater curvature of stomach:
- right gastroomental and left gastroomental anastomosis
Arterial supply to fundus of stomach:
short gastric arteries
The poorest collateral blood supply in the stomach is in the area of:
- fundus
- short gastric arteries
Venous drainage of stomach:
portal venous system
The four parts of the duodenum:
- First: superior (L1).
- Second: descending.
- Third: horizontal (L3).
- Fourth – ascending (back to L2).
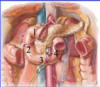
The bile and pancreatic ducts enter the duodenum at what part?
second part
junction of foregut and midgut
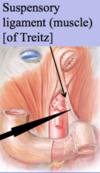
Duodenojejunal flexure:
- sharp turn at the junction of the duodenum and the jejunum
Duodenojejunal flexure is supported by:
suspensory muscle of duodenum (ligament of Treitz)
Label all:


Blood supply to duodenum and head of pancreas:
ANASTOMOSES
- anterior and posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
- branch of Celiac trunk : Gastroduodenal
- anterior and inferior inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
- branch of superior mesenteric artery
What two major arteries of the aorta anastomose in the region of the duodenum and head of the pancreas?
- celiac trunk
- superior mesenteric artery
Label all (pancreas):

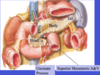
What duct of the pancreas empties into the duodenum with the common bile duct?
major pancreatic duct
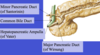
Ampulla of vater:
- point where common bile duct and major duct of pancreas drain into duodenum
- carries both pancreatic secretions and bile into the duodenum
Label all (pancreas):

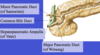
Blood supply to head and neck of pancreas:
- superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
Blood supply to body and tail of pancreas:
splenic artery
Whipple procedure:
- removal of pancreas head (tumor)
- additionally remove duodenum due to same blood supply
- all parts entering dudodenum have to be anastomosed to jejunum
Location of the liver:
- entirely under the right rib cage in a normal patient
- directly under the diaphragm
The region of the area of the liver not surrounded by peritoneum and its border:
- bare area of liver
- border = coronary ligament
What exits the liver in the bare area of the liver?
hepatic veins, which drain into the IVC
What lobes of the liver make up the functional left lobe of the liver?
left lobe, caudate lobe, and quadrate lobe
The portal triad:
- Area of the liver containing:
- Portal Vein
- Proper Hepatic Artery
- Common Hepatic Duct
Biliary duct system from liver to duodenum:
- Right and left hepatic ducts merge to form common hepatic duct.
- Common hepatic duct merges with cystic duct (GB) to form common bile duct.
- Drains into ampulla of Vater into duodenum.
What duct does bile both enter and exit the gallbladder?
cystic duct
Function of gallbladder:
- overflow reservoir for bile produced by liver that cannot enter the duodenum due to closure of the sphincter of oddi.
Sphincter of oddi:
- controls the entry of bile and pancreatic secretions into the duodenum via regulating the ampulla of Vater.
- only open during/following a meal.
Reason for gallbladder stone formation:
- bile is dehydrated and concentrated for storage.
- minerals crystallize and form stones.
How can a gallbladder stone cause jaundice?
- travels through cystic duct
- occludes common bile duct
- bile from liver spills into blood causing jaundice
Label all:
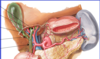
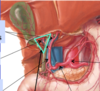
Blood supply to liver:
- Branches of proper hepatic artery:
- right and left hepatic
Blood supply to gallbladder:
- cystic artery
- usually branch of right hepatic artery
Hepatocystic triangle of Calot:
- region where cystic artery crosses to gallbladder
- bounded by liver, cystic duct, and common hepatic duct.
Spleen location:
- Left upper quadrant behind stomach
- under cover of 9th, 10th, 11th left ribs
What attaches the spleen to the left kidney?
- splenorenal ligament
- PASSAGE FOR SPLENIC ARTERY
What attaches the spleen to the stomach?
gastrosplenic ligament
The two parts of the small intestine:
- jejunum (first 2/5)
- ileum (remaining 3/5)
Blood supply to jejunum and ileum:
- superior mesenteric artery
- loops, arcades, vasa recta

In comparison to the ileum, the jejunum is (7):
- thicker walled
- redder
- more vascular
- longer vasa recta
- larger and fewer arcades
- less mesenteric fat
- larger, taller, and more numerous circular folds
Location of jejunum:
- upper left quadrant
- behind greater omentum
Location of ileum:
- lower right quadrant
- behind greater omentum
Label all:


What connects the ileum to the colon/large intestine?
ileocecal valve
Cecum location:
part of the colon inferior to the ileocecal valve
Where does the appendix branch off from?
cecum of the colon
Label all:


Teniae coli:
- 3 longitudinal strips of smooth muscle on the colon
- causes bunching of colon because teniae coli are shorter than colon
Haustra:
- outpocketings of colon formed due to the teniae coli being shorter than the colon
Where is the appendix found in relation to the teniae coli of the colon?
- where the 3 teniae coli converge at the end of the cecum
Name of flexure between the ascending colon and transverse colon:
hepatic flexure

Name of flexure between the transverse colon and the descending colon:
splenic flexure

Which flexure of the colon should be lower: hepatic or splenic?
- hepatic lower due to weight of liver
- splenic flexure equal or lower = enlarged spleen


