Oral Pathology Flashcards
What is Attrition?
wearing away of the teeth from tooth to tooth contact, malocclusion, grinding, and mastication
What is Bruxism?
excessive grinding - form of attrition *affects masseter muscle*
What is Abrasion?

teeth wear from use of abrasive substances (chewing foreign objects)
What is Abfraction?
angular notch at the gum line caused by bending forces applied to the tooth; non-carious tissue loss

What is Erosion?
loss of tooth structure from a chemical process - chronic vomiting (bulimia), acidic foods (lemons), GERD (gastro-esophageal reflux disease)

What is Supernumerary Teeth (Hyperdontia)?
Cleidocranial Dysostias - excess number of teeth
What is the most common form of supernumerary teeth?
mesiodens - between #8 and #9

What is the second most common form of supernumerary teeth?
maxillary molar area - 4th molars, distomolar (distodens)

What is Anodontia?
complete absence of teeth

What is a type of Anodontia?
Ectodermal Dysplasia - abnormal development of teeth

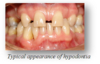
What is Hypodontia?
less than normal number of teeth - partial anodontia: one or several teeth are missing
What is Oligodontia?
congenitally missing 6 teeth or more, excluding the 3rd molars

What is Microdontia?
“peg lateral” - most common (maxillary laterals) small teeth

What is Macrodontia?
large teeth; rare

What is Taurodontism?
“bull tooth” - enlarged pulp chamber, apical displacement of pulpal floor, lack of constriction at the CEJ *more common in Down Syndrome patients*
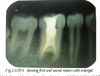
What is Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
hereditary disorder of enamel formation

What is Dentinogenesis Imperfecta?
inherited dentin disorder; teeth are discolored

What is a Diastema?
space between two adjacent teeth - hereditary, frenum attachment or muscle pull
What is Internal Resorption?
enlarged pulp chamber due to possible pulp injury (loss of tooth structure from within the root canal) - tooth may appear pink due to pulp showing through enamel

What is External Resorption?
abnormal dentin condition; resorption of the teeth externally

What is Concrescence?
“stuck together like cement” teeth are joined at cementum
What is Gemination?
two teeth have developed from one single root (teeth in arch are normal count)

What is Fusion?
two teeth are joined together during development resulting in one large tooth (teeth count is one less tooth)

What is Dens in Dente (dens invaginatus)?
“tooth within a tooth” invagination of the crown or root that is lined with enamel *maxillary laterals most common*
What is Dilaceration?
exaggerated curve or bend in a tooth root or crown

What are Enamel Pearls (ectopic enamel)?
disturbance of enamel formation during development *usually present in bifurcations or trifurcations*

What are systemic causes of Hypoplasia?
- Hutchinson’s Incisors and Mulberry Molars - syphilis - Fluorosis

What are local causes of Hypoplasia?
- “Turner’s Tooth” - hypocalcified permanent tooth - enamel is inhibited possibly due to trauma affecting crown development

What is Extrinsic Stain (exogenous)?
staining that occurs from environmental factors; tobacco use, wine, grape juice
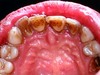
What is Intrinsic Stain (endogenous)?
staining that may occur from enlarged pulp chamber or trauma; darkened dentin
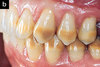
What is Tetracycline Staining?
endogenous gray, yellow, brown staining - caused from mother’s ingestion of tetracycline prenatally

What is Green Staining?
exogenous - may become endogenous over time more serious in children

What is Nicotonic Stomatitis (smoker’s palate)?
- white, hyperkeratotic, coarse, nodular, wrinkled appearance to hard palate in smokers - scattered red “dots” are the orifices of inflamed minor salivary glands (benign but predisposed to malignancy)

What is Leukoplakia?
- white plaque/patches on oral mucosa; CAN NOT WIPE OFF

What is Hairy Leukoplakia?
white patch on lateral border of tongue - associated with HIV clients; caused by EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus)

What is Leukoedema?
milky white lesions of buccal mucosa that disappear when stretched *more prominent in dark skin individuals*

What is Linea Alba?
hyperkeratotic line of buccal mucosa alone plane of occlusion

What is Candida Albicans/Pseudomembranous Candidiasis?
white plaques that WIPE OFF; most common fungal infection
What is Erythematous Candidiasis?
form of candidiasis (thrush) that appears reddened - associated with HIV/AIDS patients

What is a Melanotic Macule?
“Oral Focal Melanosis” flat, brown freckle - found on lip or intraorally *Addison’s Disease - buccal mucosa, gingiva, tongue, & lips (petechiae also on palate)

What is an Amalgam Tattoo?
“Focal Argyrosis” amalgam particles embedded in soft tissue
What are Fordyce Granules?
intraoral sebaceous (oil) glands; yellow nodules of buccal mucosa & vermilion border
What is Angular Cheilitis?
fissured areas at corner of the mouth Treatment: nystatin, clotrimazole (topical); systemic - fluconazole (diflucan)
What are Variscosities?
dilated superficial veins - prominent on ventral tongue (lingual varices)
What is Geographic Tongue?
(Erythema migrans, benign migratory glossitis) areas of erythema (atrophy of filiform papillae) surrounded by raised, white border
What is Ankyloglossia?
(Tongue-tied) short, thick lingual frenum - limitation of tongue movement affecting speech


