Oral hypoglycaemic - Treating Type 2 Flashcards
Treatment algorithm
Lifestyle modification
Metformin when >6.5% after lifestyle interventions
Metformin + SU/ DPP-4i/ TZD e.g pioglitazone if >7.5% 16 weeks later after metformin and lifestyle
Next if >7.5% after 6 months: triple therapy with metformin, SU + pio/DPP-4i or insulin
Try and achieve less than 7% GLP 1 offered with SU and metformin if high BMI of 35 and triple therapy is not effective, not tolerated or contraindicated or insulin is CI due to occupation, weight loss implications in those <35 BMI
Lifestyle: DELAYS
Diet Exercise and education Lipids ABP Aspirin Yearly/ 6 monthly Smoking cessation
Metformin
Increases insulin sensitivity, helps lose weight Not metabolised, renally excreted SE: nausea, diarrhoea, abdo pain, lactic acidosis CI: GFR<30, tissue hypoxia (sepsis, MI), morning before GA and iodinated contrast media 500mg BD after food, ↑ing to 2g max.
Metformin + SU
SU: increases insulin secretion E.g. gliclazide 40mg ̄c breakfast SE: hypoglycaemia, wt. gain (use glipten if high BMI) CI: omit on morning of surgery
Other options to SU
Consider adding a rapid-acting insulin secretagogue (e.g. nateglinide) to metformin instead of a sulfonylurea. May be preferable if erratic lifestyle. Consider adding gliptin to metformin instead of a sulfonylurea if high BMI
6 months later >7.5% on metformin and SU, what’s next? Insulin
eg isophane insulin bd or long-acting analogue Add insulin → insulin + metformin + sulfonylurea Contact DVLA - assess fitness to drive if on insulin/ hypo events
6 months later >7.5% on metformin and SU, what’s next? Glitazone
Or add glitazone ↑ insulin sensitivity SE: hypoglycaemia, fractures, fluid retention, lft↑ (do lft every 8wks for 1yr, stop if alt up >3-fold). CI: past or present ccf; osteoporosis; monitor weight, and stop if ↑ or oedema if insulin unacceptable Employment, social or recreational issues Obesity metformin + sulfonylurea + sitagliptin / pio (can also replaces metformin/SU)
3rd line additional therapy: GLP 1 or DPP-4 inhibitors
GLP 1 analogues: Incretins are gut peptides that work by augmenting insulin release e.g Add exenatide (SC) if insulin unacceptable or BMI>35. Metformin + sulfonylurea + eventide DPP4 inhibitors: prevent 4 breaks down glp-1 sitagliptin: alternative to insulin (if egfr >50), eg if obese (they ↓ appetite)
4th line additional therapy
Consider acarbose if unable to use other glucose- lowering drugs ↓breakdown of starch to sugar se: wind (less if slow dose build-up), abdominal distension/pain
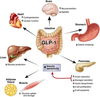
Actions of GLP 1
What are TZD’s?
e.g Rosiglitazone and pio
Pioglitazone is contraindicated by his history of bladder cancer and may contribute to his obesity
PPARγ agonists - transactivation:
Insulin resistance is decreased
Leptin levels decrease (leading to an increased appetite)
TZDs generally decrease triglycerides and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Which oral hypoglycaemic is associated with DKA? What is their action
SGLUT2 e.g Dapagliflozin, canagliflozin & empagliflozin
SGLT2 inhibitors prevent the resorption of glucose from the proximal renal tubule, resulting in more glucose being secreted in the urine.


