Complications Flashcards
(27 cards)
Macrovascular
MI: May be “silent” due to autonomic neuropathy PVD: claudication, foot ulcers CVA
Treatment
Rx: Manage CV risk factors BP (aim <130/80) Smoking Lipids HBA1c
Prevention
Good glycaemic control (e.g. HbA1c <6%) prevents both macro- and micro-vascular complications. Proved by DCCT, EDIC and UKPDS trials Regular screening: fundoscopy, ACR, foot check
Diabetic feet - ischaemia
Critical toes Absent pulses (do ABPI) Ulcers: painful, punched-out, foot margins, pressure points
Diabetic feet - neuropathy
Loss of protective sensation Deformity: Charcot’s joints, pes cavus, claw toes Injury or infection over pressure points Ulcers: painless, punched-out, metatarsal heads, calcaneum
Diabetic feet - Mx conservative
Daily foot inspection (e.g. ̄c mirror) Comfortable / therapeutic shoes Regular chiropody (remove callus)
Diabetic feet - Mx surgical
Abscess or deep infection Spreading cellulitis Gangrene Suppurative arthritis
Mild infection signs
Two or more manifestations of inflammation: Purulence Erythema Pain Tenderness Warmth Induration BUT any cellulitis/erythema extends to 2cm or less around the ulcer and infection is limited to the skin or superficial subcutaneous tissues; no other local complications or systemic illness
Moderate infection signs
Moderate Infection As above in a patient who is systemically well and metabolically stable BUT where there is one or more of the following characteristics: Cellultis extending greater than 2cm Lymphangitic streaking Spread beneath the superficial fascia Deep tissue abscess Involvement of muscle tendon, joint or bone.
Severe infection signs
Infection in a patient with systemic toxicity or metabolic instability
Mild infection Abx and in pen allergy
Flucloxacillin 1g QDS Orally Pen allergy: Doxycycline 200mg OD Orally
Moderate infection Abx and pen allergy
Flucloxacillin Orally 1g QDS and Ciprofloxacin Orally 500mg BD and Metronidazole Orally 400mg TDS (pen allergy: Fluclox switched to doxy 200mg OD Orally)
Severe infection Abx
Tazocin IV 4.5g TDS and Vancomycin IV 1g BD (pen allergy: Taz -> meropenem IV 1g TDS) Vascular surgery referral if necessary
Diabetic retinopathy pathophysiology
Microvascular disease → retinal ischaemia → ↑VEGF ↑ VEGF → new vessel formation
Presentation of retinopathy
Retinopathy and maculopathy Cataracts (sorbitol accumulation) Rubeosis iris: new vessels on iris → glaucoma CN palsies
Diabetic Retinopathy and Maculopathy investigation and treatment
Ix: fluorescein angiography Rx: laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF drugs
Background retinopathy
Dots: microaneurysms Blot haemorrhages Hard exudates: yellow lipid patches

Pre-proliferative retinopathy
Cotton-wool spots (retinal infarcts) Venous beading Haemorrhages
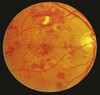
Proliferative retinopathy
New vessels Pre-retinal or vitreous haemorrhage

Maculopathy
↓ acuity may be only sign Hard exudates w/i one disc width of macula
Neuropathy pathophysiology (2)
Metabolic: glycosylation, ROS, sorbitol accumulation Ischaemia: loss of vasa nervorum
Types of neuropathy in diabetes (4)
Symmetric sensory polyneuropathy Mononeuropathy / Mononeuritis Multiplex Femoral Neuropathy / AmyotrophyAutonomic Neuropathy
Signs and symptoms of neuropathy
Glove and stocking: length-dependent ( feet 1st) Loss of all modalities Absent ankle jerks Numbness, tingling, pain (worse @ night)
Treating neuropathy
Paracetamol
Amitriptyline, Gabapentin, SSRI e.g duloxetine
Tramadol
Capsaicin cream
Baclofen


