Ophthamology Flashcards
Amblyopia
Lazy eye
Types of chronic conjunctivitis
Vernal keratoconjunctivitis
Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
Features of vernal keratoconjunctivitis
- Children
- Seasonal
- FH of atopy
- Bilateral
- Ulceration and infiltration of upper cornea
Features of atopic keratoconjunctivitis
- Adults
- Associated with atopy
- Bilateral
- Can cause corneal ulceration and scarring
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Usually secondary to N. gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis
Causes of acute red eye
Lids:
- Blepharitis
- Chalazion
- Malposition
Conjunctiva:
- Conjunctivitis
Sclera:
- Episcleritis
- Scleritis
Cornea:
- Keratitis
Uveal tract:
- Uveitis
Trabecular meshwork:
- Acute glaucoma
Periorbital skin:
- Preseptal cellulitis
- Orbital cellulitis
Presentation of Acanthamoeba keratitis
Pain
Red eye
Dendritiform epithelial lesions
Non-suppurative ring
Fungal keratitis presentation
Red eye
Photophobia
Blurred vision
Discharge
Anisocoria
Difference in pupil size > 4mm
Management of fungal keratitis
Topical antifungal
Corneal graft if unresponsive
Topical anti-fungals
Natamycin
Amphotericin

Hyphaema - blood in anterior chamber
Hypopion
Pus in anterior chamber
Orbital cellulitis presentation
Decreased vision
Unwell pt
Unilateral swollen eyelids
Ophthalmoplegia (reduced eye movements)
Proptosis
Orbital cellulitis Mx
Ophthalmological emergency
CT scan
IV antibiotics
Scleritis presentation
Extremely painful - often wakes at night
Cellular infiltration or entire sclera thickness
Red eye
Scleritis complications
Ischaemia and necrosis
Scleral thinning (Scleromalacia perforans)
Globe perforation
Scleritis prognosis
Can be self limiting
Central (/Branch) Retinal Artery Occlusion definition
Commonly embolisation from carotid artery
Central (/Branch) Retinal Artery Occlusion presentation
Painless
Possible RAPD
Retinal pallor
Cherry red spot
RAPD
Relative afferent pupillary defect
Paradoxical dilatation of directly stimulated pupil
Cherry red spot
At macula
Retina thinner - see underlying choroid
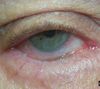
Entropion
Entropion definition
Inward turning of lid margin
Malposition of eye lid
Complication of entropion
Eyelashes cause corneal abrasions

Ectropion
Ectropion definition
Outward turning of lid margin
Almost always lower lid
Ectropion complication
Exposed conjuctiva can become inflammed, scarred and keratinised

Dendritic ulcer on cornea
Bacterial keratitis organisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staph epidermidis
Strep pneumoniae
H. influenzae
Bacterial keratitis presentation
Purulent conjunctivitis
Reduced vision
Corneal ulcer / opacity
Hypopyon

Blepharitis
Blepharitis definition
Infection of lid margins
Overproduction of sebum by lid margin glands
Blepharitis organisms
Staphylococcal bacteria
Sx of blepharitis
Chronic ocular irritation
Watery eye
Red eye
Signs of blepharitis
Crusting and scaling of lash line
Plugs of sebum in meibomian gland orifices

Posterior synechiae
Irregular pupil
Muscles of the eye
Superior, inferior, medial, lateral rectus
Superior, inferior oblique
Levator palpebrae superioris
Management of chronic conjunctivitis
Similar to acute conjunctivitis
Greater use of topical and oral steroids
Uveitis definition
Inflammation of uveal tract
Components of uveal tract
Includes iris, ciliary body and choroids

Iatrogenic / neonatal conjunctivitis
Iatrogenic conjunctivitis definition
Drops prescribed can cause occular irritation and red eye
Management of allergic conjunctivitis
Topical antihistamine
Topical mast cell stabiliser
Combination of antihistamine and mast cell stabiliser
Systemic antihistamines
Topical steroid
Topical antihistamine for allergic conjunctivitis
Levocabastine
Topical mast cell stabiliser for allergic conjunctivitis
Sodium cromoglycate
Combined antihistamine and mast cell stabiliser for allergic conjunctivitis
Olopatadine
Management of bacterial conjunctivitis
Spontaneous resolution
Broad spectrum topical antibiotics
Broad spectrum topical abx for bacterial conjunctivitis
Chloramphenicol
Fucithalmic acid
Conjuctiva definition
Translucent membrane
Lines inside of lids and sclera up to limbus of cornea
Parts of conjunctiva
Palpebral conjunctiva - inside of lids
Bulbar conjunctiva - on sclera
Pupil dilator drugs
Tropicamide +/- Phenylephrine
Hypermetropia
Long sightedness

Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma

Corneal abrasion with fluorescein
Causes of Ectropion
Ageing (involutional)
Conjuctival scarring (cicatricial)
Paralytic (facial nerve palsy)
Mechanical (lower lid tumours)
Complications of Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
Scleritis
Secondary glaucoma
Cranial nerve palsies
Retinitis
Herpes Simplex Virus pathogenesis
Primary infection, then lies dormant in trigeminal ganglion
Causes recurrent epithelial keratitis
Sx of ophthamological HSV infection
Pain
Red eye
Dendritic ulcer
Reduced corneal sensation
Trabecular meshwork pathway
Ciliary bodies produce aqueous humour
Bathes lens
Exits anterior chamber via angle
Allergic conjunctivitis presentation
Rapid onset
Itching
Red eye
Usually bilateral
Signs of allergic conjunctivitis
Giant cobblestone papillae
Conjunctival chemosis (oedema)
Preauricular lymphadenopathy
Myopia
Short sightedness
Causes of keratitis
Bacterial
Viral
Fungal
Acanthamoeba
Fluorescein
Causes yellow staining of epithelial defect
Eg. ulcer, abrasion
More apparent under blue light
Peirorbital cellulitis presentation
Swelling
No decreased vision
No proptosis
Normal eye movements
Mx of periorbital cellulitis
Broad spectrum oral abx
Keratitis risk factors
Contact lens
Trauma
Dry eye / blepharitis
Immunosuppression
Presentation of scleritis
Extreme pain - wakes at night
Epiphora
Red eye
Scleromalacia perforans
Epiphora
Watering of eye
Scleromalacia perforans
Scleral necrosis and thinning
Corneal sensation nerve
Trigeminal nerve
Amaurosis Fugax definition
Embolus from carotid passes through retinal vasculature
Transient loss of vision
Types of uveitis
Anterior uveitis (iritis)
Intermediate uveitis
Posterior uveitis
Anterior uveitis definition
Inflammation of iris and anterior chamber
Intermediate uveitis definition
Inflammation to vitreous and peripheral retina
Posterior uveitis definition
Inflammation of posterior uveal tract and overlying retina
Cause of superior quadrantanopia
Post chiasmal lesion within temporal lobe
Presentation of vial conjunctivitis
Red eye
Watery discharge
Usually bilateral
Conjunctival follicles
Preauricular lymph nodes
Why is viral conjunctivitis usually bilateral
Highly contagious