Ophthalmology Flashcards
Which two structures separate during a retinal detachment?
Neural and pigmented retinal layers
List 3 structures in the eye which cause photophobia when affected
- Cornea (abrasion, foreign body, keratitis)
- Iris (iritis)
- Sclera (scleritis)
Not lid or conjunctival entities
What is the difference between an internal hordeolum and a chalazion?
A chalazion is an OBSTRUCTION of the Meibomian gland
An internal hordeolum is an ABSCESS of the Meibomian gland
What is a stye?
External hordeolum
Abscess of the sebaceous gland associated with an eyelash (Moll’s or Zeis)
What is the treatment for an internal hordeolum?
Warm compresses
Oral flu/dicloxacillin
Incision and drainage for persistent or recurrent abscesses
What is the treatment for an external hordeolum?
Warm compresses
Removal or the eyelash often aids resolution
What is the treatment for a chalazion?
Warm compresses
How is bacterial conjunctivitis treated?
Topical chloramphenicol
Hygiene
Regular cleaning with warm water
How is chlamydial conjunctivitis treated?
Oral azithromycin as a single dose
How is gonococcal conjunctivitis treated?
Ceftriaxone/cefotaxime IM or IV as a single dose
Pre-auricular lymphadenopathy is found in which ophthalmological condition?
Viral conjunctivitis
Which antibiotic is used for the treatment of bacterial keratitis?
Ciprofloxacin
What is the treatment for anterior uveitis?
Topical corticosteroids
Dilating drops e.g. cyclopentolate (reduces pain and prevent synechiae)
What is concomitant strabismus?
Ocular deviation is present in all directions of gaze
Non-paralytic
Primarily occurs in childhood
Constant angle of deviation in which the misaligned eye follows the unaffected eye
What is incomitant strabismus?
Ocular deviation present in specific directions of gaze
Paralytic
Functional weakness of individual extraocular muscles
Frequently acquired
What is heterophoria?
(Latent or manifest? And what does that mean?)
Latent strabismus
Only present once binocular vision is interrupted
What is heterotropia?
(Latent or manifest? And what does that mean?)
Manifest
Present during binocular vision
What is stereopsis?
Depth perception
Which tract is damaged in internuclear ophthalmoplegia?
Medial longitudinal fasciculus
What are the findings of internuclear ophthalmoplegia?
Ipsilateral loss of adduction (MR affected)
Contralateral nystagmus
Convergence is not affected (different pathways utilised)
Which type of strabismus does the cover test reveal?
Heterotropia (manifest)

Which type of strabismus does the uncover test reveal?
Heterophoria (latent)

List 4 treatment options for strabismus
- Correction of refractive errors
- Visual training
- Occlusion treatment
- Penalisation therapy (use cyclopentolate to blur vision in the good eye)
- Surgery
What is the definition of amblyopia?
Permanent loss of best corrected visual acuity in a structurally healthy eye
List 3 causes of amblyopia
- Depravation e.g. ptosis, cataract
- Refractive
- Stabismus
List 5 medications used in the treatment of glaucoma
- Pilocarpine
- Dorzolamide/brinzolamide
- Timolol
- Apraclonidine
- Latanoprost
- Mannitol
What is the treatment for anterior uveitis?
Topical corticosteroids
Dilating drop (e.g. cyclopentolate) to reduce pain and prevent synechiae
Which is worse, pre- or post-septal cellulitis?
Post-septal
Where do pathogens causing post-septal cellulitis arise?
Paranasal sinus infection
Orbital trauma
What is papillary conjunctivitis associated with?

Allergic conjunctivitis

What are conjunctival follicles?

Small foci of hyperplastic lymphoid tissue
Associated with viral conjunctivitis
Which condition are conjunctival follicles associated with?
Viral conjunctivitis
When can people with conjunctivitis return to work/school?
Once the discharge has stopped
What are keratic precipitates and when are they found?
Inflammatory deposits on the corneal endothelium
Indicative of inflammatory disease
Seen in anterior uveitis

What are the two components of the uvea?
Anterior - iris and ciliary body
Posterior - choroid
Anterior uveitis = iritis
What is epidemic keratoconjunctivitis?
Complication of some adenovirus conjunctivitis infections
An intense inflammatory response involving the cornea
Pseudomembrane formation (coagulated fibrinous exudate)
Which features distinguish simple adenovirus infection with epidemic keratoconjunctivitis?
Intense redness, irritation, tearing
Blurred vision and photophobia
Follicular conjunctivitis
Preauricular lymphadenopathy
Subconjunctival haemorrhage
Conjunctival oedema
Pseudomembrane formation

What is a pseudomembrane (epidemic keratoconjunctivitis)
Coagulated fibrinous exudate

How is epidemic keratoconjunctivitis treated?
Removal of pseudomembrane
Topical corticosteroids
Urgent ophthalmological referral
How is chlamydia trachomatis treated?
Azithromycin as a single dose
Contact tracing
Facial and hand hygiene
Trichiasis management
What is the likely causative agent of bacterial keratitis/corneal ulcers in a patient who has been swimming with contact lenses?
Acanthamoeba
What is pseudostrabismus?
Part of the nasal sclera is covered, forming an optical illusion of esotropia
Occurs in the first few years of life due to a wide nasal bridge or large epicanthal folds

A foreign body sensation is associated with involvement of which ocular structure?
Cornea
Conjunctivitis is associated with a gritty feeling

Bacterial keratitis
Characteristic white spot on cornea

Anterior uveitis
Irregular pupil shape due to inflammatory adhesions of the iris margin to the anterior lens

Episcleritis

Scleritis
List 2 causes of a red-eye associated with reduced visual acuity
- Infectious keratitis
- Iritis
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma
What are two features which can help distinguish corneal abrasion from iritis?
- Abrasions have a staining defect on fluorescein examination
- Abrasions have a foreign body sensation
How is ciliary flush distinguished from conjunctivitis?
Redness does not extend into the palpebral conjunctiva
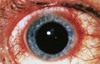
Which condition is most strongly associated with scleritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis
- Scleritis is associated with systemic disease in 50% of cases, the most common of which being RA*
- When scleritis complicates RA, it is a manifestation of rheumatoid vasculitis, indicating the need for an intensification of therapy*
Ocular pain worst at night or early morning is characteristic of which condition?
Scleritis
What complication of adenovirus is associated with fibrous exudates?
Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis
How does trachoma occur?
Chronic/recurring chlamydia in both eyes → conjunctival scarring → progressive conjunctival shrinkage → corneal ulcers and opacities, neurovascularization, entropion, trichiasis (ingrown eyelashes)
What is the major complication of epidemic keratoconjunctitis?
Keratitis
What is sodium cromoglycate?
Mast cell stabiliser
Used for allergic conjunctivitis
What are the adverse effects of topical corticosteroids on the eye?
Ocular hypertension
Ocular infection
Delayed corneal healing
Rebound inflammation upon treatment cessation
Posterior subcapsular cataracts
List 4 causes of bacterial conjunctivitis
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococccus pneumoniae
Haemophilus influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Chlamydia trachomatis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Follicular or papillary?

Follicle
Pale on surface with red base


