Gastroenterology Flashcards
Which biomarkers can be used to diagnose and monitor IBD?
Faecal calprotectin and lactoferrin
What is cholelithiasis?
Gallstones
What is cholecystitis?
Inflammation of the gallbladder
What is cholangitis?
Infection of the biliary tree
What are the risk factors for cholelithiasis?
Fat, Female, Fertile (multiple children or pregnant), Forty (or older), Fair-skinned, Family history
6 F’s
What is charcot’s triad for cholangitis?
- Abdominal pain
- High fever
- Jaundice
What is the most common cause of Budd-Chiari syndrome?
Polycythemia vera
What is the pathophysiology of Budd-Chiari syndrome?
Obstruction of hepatic blood outflow → hepatic venous congestion → increased sinusoidal pressure and cellular hypoxia → liver cell damage
What is Murphy’s sign?
Ask the patient to take a deep breath while palpating the right subcostal area
If pain occurs when the inflamed gallbladder comes into contact with the examiner’s hand, Murphy’s sign is positive
Acute cholecystitis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2T0XUQ1M-x0

What is the most important risk factor for AAAs?
Smoking
Also advancing age, atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension
Where is splenic pain referred to?
Left shoulder
What are five clinical signs which suggest appendicitis?
- Blumberg’s sign (rebound tenderness)
- McBurney point tenderness
- Rovsing’s sign
- Psoas sign
- Obturator sign
What is McBurney’s sign?
Point tenderness in the area one-third of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus
Suggests appendicitis

What is Rovsing’s sign
Deep palpation of the LLQ causes RLQ pain
Appendicitis

What is the psoas sign?
RLQ pain with extension of the right leg against resistance
Appendicitis

What is the obturator sign?
RLQ pain with flexion and internal rotation of the right leg
Appendicitis

Which 3 organisms are most commonly responsible for cholecystitis?
- E. coli
- Klebsiella
- Enterococcus
Name 3 of the most common organisms found in abdominal sepsis from the stomach or duodenum
1. Streptococcus
- Candida
- Lactobacilli
- Fungi
* Aerobic species predominate*

Name 3 of the most common organisms found in abdominal sepsis from the bowel and appendix
1. E. coli
2. Bacteroides fragilis
- Clostridium
- Peptostreptococcus
- E. faecalis
Anaerobes predominate

Bowel ischaemia dramatically increases the risk of sepsis from which organism?
Clostridium
What is the empirical treatment for intra-abdominal infections of the lower GI tract e.g. diverticulitis, appendicitis
Gentamicin PLUS amoxicillin/ampicillin PLUS metronidazole
- Metronidazole provides anaerobe cover*
- G + A provide Gram -ve cover*
What is the empirical treatment for intra-abdominal infections originating from the biliary system?
Gentamicin PLUS amoxicillin/ampicillin
G + A provide Gram -ve cover
Anaerobe cover not needed
An increased proportion of immature neutrophils in the blood is known as a right or left shift?
Left shift
What are 4 causes of elevated LFTs in a febrile patient?
- Ascending cholangitis
- Bacteraemia
- Drug reaction
- Viral hepatitis (rare)
What type of nociceptors are most commonly involved in visceral pain and what stimulates them?
Mechanoreceptors
Stimulated by stretch
What type of nociceptors are most commonly involved in somatic pain and what stimulates them?
Chemoreceptors
Stimulated by blood or inflammatory cytokines
List 3 places in the abdomen with somatic chemoreceptors
- Skin
- Muscle (abdominal wall)
- Parietal peritoneum
- Mesenteric attachment
List 2 places in the abdomen with visceral chemoreceptors
- Muscular lumen
- Organ capsules
How do signals from abdominal visceral nociceptors enter the dorsal horn?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic efferent nerves
Via splanchnic nerve
What do Cullen’s and Grey Turner’s signs suggest?
Retroperitoneal bleeding
Non-specific and sensitive sign of haemorrhagic pancreatitis, but associated with a poor prognosis
Also ruptured or leaking AAA

What electrolyte abnormality is found in pancreatitis?
Hypocalcaemia
Lipase breaks down peripancreatic and mesenteric fat → release of free fatty acids that bind calcium →hypocalcaemia
What is the most common cause of acute pancreatitis?
Gallstone
Distal to the ampulla of Vater, impeding the flow of pancreatic secretions
Which organs are retroperitoneal?
SAD PUCKER
S: suprarenal (adrenal) gland
A: aorta/IVC
D: duodenum (second and third part)
P: pancreas (except tail)
U: ureters
C: colon (ascending and descending)
K: kidneys
E: (o)esophagus
R: rectum
What are the pancreatic enzymes?
Lipase
Amylase
What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction?
Adhesions
What is the most common cause of large bowel obstruction?
Colorectal cancer
Where does pain from nephrolithiasis radiate?
Upper ureteral or renal pelvic obstruction: flank pain or tenderness
Lower ureteral obstruction: pain that may radiate to the ipsilateral testicle or labium
What is the most common type of renal calculi?
Calcium oxalate
Which type of renal calculi is radiolucent?
Uric acid
What are the risk factors for uric acid stones?
Gout and hyperuricemia
High purine diet
What causes struvite renal calculi?
Upper urinary tract infections with urease-producing bacteria
(Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Providencia, Enterobacter)
Staghorn stones
What are gallstones characteristically made of?
Cholesterol
What causes black gallstones?
Bilirubin
What type of inguinal hernia herniates lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels?
Indirect

Which type of inguinal hernia involves protrustion of tissue through the internal inguinal ring, external inguinal ring and into the scrotum
Indirect inguinal hernia

What are the boundaries of Hesselbach’s triangle?
Superior: inferior epigastric vessels
Lateral: inguinal ligament
Medial: rectus abdominis

What is the most common cause of lower GI bleeding in adults?
Diverticulosis
What is diverticulosis?
Asymptomatic diverticula
When is the peak incidence of testicular torsion?
First 30 days of life or during puberty
What is Prehn’s sign?
Relief of pain during elevation of the testes and suggests epididymitis rather than torsion
What is the definition of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection?
A bacterial infection that rapidly progresses to fulminant, overwhelming sepsis in the setting of anatomic or functional asplenia
When is the peak incidence of appendicitis?
10-19 years of age
What precipitates appendicitis?
Obstruction of the appendiceal lumen e.g. faecal material, undigested food, enlarged lymphoid follicle
Why do patients with appendicitis initially have diffuse periumbilical pain?
Obstruction of the appendiceal lumen stimulates mechanoreceptors (visceral)
How does an obstruction of the appendiceal lumen cause bacterial overgrowth?
Obstruction → breakdown of mucosal barrier → bacterial invasion
What is the characteristic US sign of appendicitis?
Target sign
Inflammation and oedema of the appendiceal wall causes hyperechoic and hypoechoic layers

What finding on a FBC is classical of appendicitis?
Mild leukocytosis with left shift
(not required for diagnosis)
Which antibody is most strongly associated with coeliac disease?
IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase
What are the x-ray features of a SBO?
- Dilated loops of small or large bowel
- Air-fluid levels proximal to the obstruction
- Distal bowel collapse
- Minimal or no gas in colon
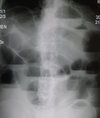
What are the x-ray features of a LBO?
- Air-fluid levels in the colon
- Bowel distention before obstruction
- Kidney bean/coffee-bean appearance of bowel e.g. volvulus

What are the xray features of a paralytic ileus?
- Uniform distribution of gas in the small bowel, colon and rectum
- Obliteration of the psoas muscle outline

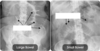
Large: haustra
Small: valvulae conniventes/plicae circulares

Why might a urinalysis be performed when investigating appendicitis? What are the expected findings
Evaluate DDx e.g. acute UTI, nephrolithiasis
Mild pyuria may be present because of the close proximity between the right ureter and appendix
Draw the 9 regions of the abdomen

Where does subdiaphragmatic abdominal pain radiate?
Shoulder
What can cause hyperoxaluria?
Dietary: beets, beans, dark green vegetables
Vitamin C supplements
Bile malabsorption and/or chronic diarrhoea
Low calcium (calcium is required for oxalate absorption, and a decrease in absorption increases renal excretion)
When do people with an ectopic pregnancy present?
4-6 weeks after last period
What is more common, gastric or duodenal ulcers?
Duodenal (3:1)
What is the most common cause of peptic/duodenal ulcers?
H. pylori (80-90% of all ulcers)
What is the history of pain in patients with a perforated peptic ulcer?
Sudden onset, intense, stabbing pain followed by diffuse abdominal pain and distention
Which type of peptic ulcer is associated with weight gain?
Duodenal - pain is worst on an empty stomach
Which type of peptic ulcer is associated with weight loss?
Gastric ulcer
Pain is worst post-prandial
Which bacteria commonly causes mesenteric adenitis, mimicking appendicitis (pseudoappendicitis)?
Yersinia enterocoliticia
How long following the onset of appendicitis does perforation tend to occur?
After 72 hours of symptom onset
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in children?
Lymphoid hyperplasia
What is the most common cause of appendicitis in adults?
Faecalith
Other: fibrosis, neoplasia
What is the classic x-ray finding of gastrointestinal perforation?
Free intraperitoneal air
Image: pneumoperitoneum secondary to PUD

What is Fitzhugh-Curtis syndrome?
Perihepatitis (extension of inflammation to the liver capsule and adjacent peritoneal surfaces)
Seen in PID
Right upper quadrant pain or pleuritic pain, no liver enzyme abnormalities
What findings are found on auscultation of a bowel obstruction?
Hyperactive “tinkling” bowel sounds early in the obstruction
Later bowel sounds are reduced or absent, often in combination with a markedly distended abdomen
Why is serum lactic acid measured in the acute abdomen?
Elevated in mesenteric ischaemia
Which cause of an acute abdomen classically has increased polymorphonucleocytes? (>75%, normal (50-65%)
Appendicitis
Which is a more useful clinical sign of appendicitis, migrating pain or RLQ tenderness/pain?
RLQ pain
Very unlikely if RLQ pain is not present
What is the “pointing sign”?
Patients will point to the spot of pain in peptic ulcer disease
What are the 4 Ds of endometriosis?
- Dysmenorrhoea (unrelieved by NSAIDs)
- Dysuria
- Dyschezia
- Dyspareunia
When does pain from endometriosis occur?
2 days before the onset of menses
Can last for several days
What activities are associated with rupture of an ovarian cyst?
Strenuous physical activities e.g. exercise or intercourse
What is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in patients without a history of abdominal surgery?
Incarcerated hernia
A patient in pain and moving around unable to find a comfortable position is characteristic of which condition?
Renal colic
What imaging is used for diverticular disease?
Contrast enema and colonoscopy
What imaging is used for acute diverticulitis?
CT
What are some complications of diverticular disease?
Haemorrhage
Abscess
Perforation
Peritonitis
Fistula
Stricture
Obstruction
Through which nerve do somatic pain signals travel from the liver capsule/falciform ligament/biliary system/central diaphragmatic peritoneum?
Phrenic nerve
Through which nerve do somatic pain signals travel from the peripheral diaphragmatic peritoneum?
Lower 6 thoracic nerves
Through which nerve do somatic pain signals travel from the parietal peritoneum lining the anterior abdominal wall?
Lower six thoracic and first lumbar nerves
Through which nerve do somatic pain signals travel from the parietal peritoneum?
Obturator nerve (branch of the lumbar plexus)


