Operative Dentistry Flashcards
What is the chemical formula for Hydroxyapatite?
Ca10(PO4)(OH)2

_______ is the main component of enamel and dentin.
carbonate-substitute hydroxyapatite (CHA)

Discuss the shape of an enamel rod or prism in regards to what is the weakest part:
Enamel rods have a head and a tail. The tail tends to be more organic and have less mineral content thus making it more susceptible to decay.
***BOARDS***

How does carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite affect the solubility of enamel?
Carbonate-substitution increases solubility of hydroxyapatite (easier to decay)
On the outer part of enamel has more fluoroapatitite making it more difficult to decay. The closer you go to the DEJ in enamel the more carbonate-substitution their is making it easier to decay.
The deeper the cavity prep the more soluble (easier to decay) the hydroxyapatite . So closer to the DEJ the easier the tooth will decay

Discuss how bacteria demineralizes teeth:

Discuss the Stephan Curve in regards to each of the following:
- What is the pH of the mouth normally?
- What is the critical pH of tooth enamel? (The pH where tooth will begin demineralizing)
***ALWAYS ON BOARDS (Stephen Curve)***
Mouth = pH 7
Critical pt = pH 5.5

What are the 3 benefits of fluoride?
- Remineralization of tooth structure (shifting equilibrium to the left)
- Decreasing enamel solubility (lowering the critical pH)
- Interfering w/ metabolic activity of cariogenic bacteria
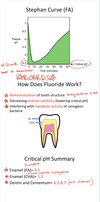
What is the critical pH for each of the following:
- Enamel (FA- Fluoroapatite) = ?
- Enamel (CHA- carbon-substituted hydroxyapatite) = ?
- Dentin and Cementum = ?
Critical pH
Enamel (FA) = 4.5 pH (harder to demineralize)
Enamel (CHA) = 5.5 pH
Dentin and Cementum = 6.2-6.7 pH (more vulnerable)

Discuss Caries in regards to each of the following:
- What is the ADA definition of caries?
- Modified Keyes-Jordan diagram?

Discuss the progress of lesions in regards to each of the following:
- Pit and fissure lesions shape = ?
- Smooth-surface lesions shape (interproximal) = ?
- Root-surface lesions shape = ?
***FORSURE BOARDS Q***

Deeper, dry, leathery, demineralized but not invaded by bacteria describes which of the following:
A. Infected dentin
B. Affected dentin
B. Affected dentin

Superficial, wet, soft mushy and necrotic are all characteristics of which of the following?
A. Infected dentin
B. Affected dentin
A. Infected dentin

Discuss the progression of lesions in regards to each of the following:
- Intact surface?
- Cavitation?
- How long may it take to form an actual enamel cavitation (cavity)?

What is the correct order of the progression of a carious lesion?
- Dentin cavitation
- Enamel cavitation
- Enamel demineralization
- Dentin demineralization
***HE GOT A BOARD Q ON THIS***
Enamel demineralization –> Dentin demineralization –> Enamel cavitation —> Dentin cavitation

Which of the following is on smooth surface, appears opaque white when air-dried and seems to disappear when wet?
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion

________ is characterized as enamel surface is broken (not intact) and usually the lesion has advanced into the dentin.
A. Incipient/Reversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion
B. Cavitation/Irreversible lesion

Which of the following is characterized as: covers three or more surfaces of a tooth (MOD, MODFL)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
C. Complex caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: covers one surface of a tooth (Occlusal)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
A. Simple caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: covers two surfaces of a tooth (MO, DO)?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
B. Compound caries
Simple = one surface
Compound = 2 surfaces
Complex = 3 or more surfaces

Which of the following is characterized as: occurs at junction of tooth and restoration indicating microleakage?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
D. Secondary caries
- Secondary caries = junction of tooth and restoration
- Residual caries = caries that remain in a completed tooth prep

Which of the following is characterized as: caries that remain in a completed tooth prep?
A. Simple caries
B. Compound caries
C. Complex caries
D. Secondary caries
E. Residual caries
E. Residual caries
- Secondary caries = junction of tooth and restoration
- Residual caries = caries that remain in a completed tooth prep

Brown/black, hard, caries-resistant if exposed to fluoride (dentinal lesion has sclerotic dentin) describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
C. Arrested caries

Rapidly damages tooth structure, light-colored, soft, infectious describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
A. Acute/Rampant caries

Demineralized tooth structure that is almost remineralized, discolored and fairly hard describes which of the following?
A. Acute/Rampant caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries
C. Arrested caries
D. Primary caries
B. Chronic/Slow caries

Which of the following is involved in dentinal caries?
A. S. Mutans
B. Lactobacillus
C. Actinomyces
D. S. Pyogenes
B. Lactobacillus
S. mutans = enamel caries
Lactobacillus = dentinal caries
Actinomyces = root caries

Which of the following is associated w/ root caries?
A. S. Mutans
B. Lactobacillus
C. Actinomyces
D. S. Pyogenes
C. Actinomyces
S. mutans = enamel caries
Lactobacillus = dentinal caries
Actinomyces = root caries

Which of the following is associated w/ enamel caries?
A. S. Mutans
B. Lactobacillus
C. Actinomyces
D. S. Pyogenes
A. S. Mutans
S. mutans = enamel caries
Lactobacillus = dentinal caries
Actinomyces = root caries

Discuss Streptococcus mutans in regards to each of the following:
- What part of the tooth does S. Mutans cause caries?
- What type of bacteria is this (gram?)
- ______ is the “glue” that helps this bacteria stick to teeth.
- Acidogenic and aciduric?
- Bacteriocins?

Which of the following components of Saliva are large molecules that agglutiniate (stick) bacteria together to help eliminate them through swallowing?
A. Glycoproteins
B. Lysozyme
C. Lactoferrin
D. Lactoperoxidase
E. sIgA
A. Glycoproteins

Which of the following components of Saliva actively binds iron which is important for bacterial enzymes?
A. Glycoproteins
B. Lysozyme
C. Lactoferrin
D. Lactoperoxidase
E. sIgA
C. Lactoferrin

Which of the following components of Saliva are salivary antibodies against bacteria?
A. Glycoproteins
B. Lysozyme
C. Lactoferrin
D. Lactoperoxidase
E. sIgA
E. sIgA

Which of the following components of Saliva destroys cell walls?
A. Glycoproteins
B. Lysozyme
C. Lactoferrin
D. Lactoperoxidase
E. sIgA
B. Lysozyme

Which of the following components of Saliva inactivates some bacterial enzymes?
A. Glycoproteins
B. Lysozyme
C. Lactoferrin
D. Lactoperoxidase
E. sIgA
D. Lactoperoxidase

What are the different components of saliva that help protect our teeth?

Discuss each of the following clinical exams in regards to caries:
- Visual
- Drying?
- Incipient caries?
- Tactile
- Radiograph
- white spots?
- Enamel cavitation?
- Dentinal cavitation?
- Size of lesions radiographicall?
- PAs are for ? And BW are for?
- Transillumination
- Shine bright light through ________.
- Shadows indicate _____.
- Also used for distinguishing _____ and _______.

All of the following are things that indicate a defective amalgam restoration EXCEPT?
A. Bluish hue
B. Proximal overhang
C. Marginal gap or ditching > 0.5mm
D. Voids
E. Fracture lines
A. Bluish hue

______ is a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces.
A. Erosion
B. Abrasion
C. Attrition
D. Abfraction
E. Hypersensitivity
E. Hypersensitivity
Erosion = caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid
Abrasion = (crown-tooth) loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear
Attrition = (tooth-tooth) occlusal wear from functioning contacts w/ opposing natural teeth
Abfraction = loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure
Hypersensitivity = as a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces
***INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT***

Which of the following is characterized as occlusal wear from function contacts with opposing natural teeth (tooth-tooth)?
A. Erosion
B. Abrasion
C. Attrition
D. Abfraction
E. Hypersensitivity
C. Attrition
Erosion = caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid
Abrasion = (crown-tooth) loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear
Attrition = (tooth-tooth) occlusal wear from functioning contacts w/ opposing natural teeth
Abfraction = loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure
Hypersensitivity = as a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces
***INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT***

Which of the following is a loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear (crown-tooth)?
A. Erosion
B. Abrasion
C. Attrition
D. Abfraction
E. Hypersensitivity
B. Abrasion
Erosion = caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid
Abrasion = (crown-tooth) loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear
Attrition = (tooth-tooth) occlusal wear from functioning contacts w/ opposing natural teeth
Abfraction = loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure
Hypersensitivity = as a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces
***INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT***

Which of the following is characterized as a loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure?
A. Erosion
B. Abrasion
C. Attrition
D. Abfraction
E. Hypersensitivity
D. Abfraction
Erosion = caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid
Abrasion = (crown-tooth) loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear
Attrition = (tooth-tooth) occlusal wear from functioning contacts w/ opposing natural teeth
Abfraction = loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure
Hypersensitivity = as a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces
***INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT***

Which of the following is caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid?
A. Erosion
B. Abrasion
C. Attrition
D. Abfraction
E. Hypersensitivity
A. Erosion
Erosion = caused by acidic foods/beverages or gastric acid
Abrasion = (crown-tooth) loss of tooth structure by mechanical wear
Attrition = (tooth-tooth) occlusal wear from functioning contacts w/ opposing natural teeth
Abfraction = loss of tooth structure in cervical areas due to tooth flexure
Hypersensitivity = as a result of exposure of dentinal tubules in root surfaces
***INCREDIBLY IMPORTANT***

Discuss Root Surface Hypersensitivity in regards to each of the following:
- Hydrodynamic theory?
- GLUMA?

What is the order of the caries Tx plan sequencing?

Discuss the criteria for restoring teeth:

Discuss Preventive Dentistry in regards to each of the following:
- Encourage ______ of incipient smooth-surface lesions)
- Treat caries-prone pits and fissure w/ _______.

Review Dental hand instruments and instrument design:

Review all of the non-cutting instruments:

Which of the following is used for the removal of carious dentin?
A. Scalers
B. Excavators
C. Chisels
B. Excavators

According to the cutting instrument formula, which of the following is known as the blade length?
A. 1st number
B. 2nd number
C. 3rd number
D. 4th number
C. 3rd number
***BOARDS***

According to the cutting instrument formula, which of the following is known as the blade width?
A. 1st number
B. 2nd number
C. 3rd number
D. 4th number
A. 1st number
***BOARDS***

According to the cutting instrument formula, which of the following is known as the blade angle?
A. 1st number
B. 2nd number
C. 3rd number
D. 4th number
D. 4th number
***BOARDS***

According to the cutting instrument formula, which of the following is known as the cutting edge angle?
A. 1st number
B. 2nd number
C. 3rd number
D. 4th number
B. 2nd number
***BOARDS***

Discuss Instrument Grasp in regards to each of the following:
- Pen vs Modified pen grasp?
- All grasps require _____ (fulcrum).
- Use ____ working radius

What is the best way to excavate caries?
***BOARDS****
Low-speed handpiece < 12,000rpm w/ a large round bur

Discuss rotary instruments such as each of the following below:
- Low-speed handpiece
- Medium-speed handpiece
- High-speed handpiece

What is another name for the foot pedal that activates the hand piece?
Rheostat

All of the following are true regarding diamond burs EXCEPT:
A. Better for end-cutting
B. Produce higher heat
C. Greater hardness
D. Better for side-cutting
A. Better for end-cutting
Carbide burs are better for end-cutting

Which of the following is 3mm long and has a 0.8mm diameter?
A. 245 bur
B. 330 bur
C. 169L
D. All of the above
A. 245 bur
***Will show up on BOARDS***

Which of the following is 1.5mm long and has a 0.8mm diameter?
A. 245 bur
B. 330 bur
C. 169L
D. All of the above
B. 330 bur
Note: 330 bur is pear shaped and the smaller size is helpful for pediatric preps
***BOARDS***

Which of the following burs has 6 blades?
A. Cutting burs
B. Finishing burs
C. Fine Finishing burs
D. Ultra fine finishing burs
A. Cutting burs

Which of the following burs has 18-24 blades?
A. Cutting burs
B. Finishing burs
C. Fine Finishing burs
D. Ultra fine finishing burs
C. Fine Finishing burs

Which of the following burs has 12 blades?
A. Cutting burs
B. Finishing burs
C. Fine Finishing burs
D. Ultra fine finishing burs
B. Finishing burs

Which of the following burs has 30-40 blades?
A. Cutting burs
B. Finishing burs
C. Fine Finishing burs
D. Ultra fine finishing burs
D. Ultra fine finishing burs

Discuss the 5 hazards associated with burs:

Which of the following GV Black Classifications involves the cervical third of a tooth?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
F. Class VI
E. Class V
***BOARDS***
Which of the following GV Black Classifications involves pits and fissures (including lingual pits)?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
F. Class VI
A. Class I
***BOARDS***

Which of the following GV Black Classifications involves the proximal surface of anterior teeth without the incisal edge?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
C. Class III
***BOARDS***

Which of the following GV Black Classifications involves the proximal surface of anterior teeth with the incisal edge?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
D. Class IV
***BOARDS***

Which of the following GV Black Classifications ONLY involves incisal edge of anterior teeth or the cusp tip of posterior teeth?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
F. Class VI
F. Class VI
***BOARDS***

Which of the following GV Black Classifications involves the proximal surface of posterior teeth?
A. Class I
B. Class II
C. Class III
D. Class IV
E. Class V
F. Class VI
B. Class II
***BOARDS***

Review cavity preparation:

_______ is where the cavity preparation meets the original tooth surface.
Cavosurface Margin
***BOARDS***
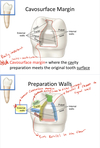
Review the preparation walls of a cavity prep:
Also review:
- Line angle = ?
- Point angle = ?

Discuss Outline Form of initial tooth preparation in regards to each of the following:
- The external outline of the tooth surface to be included in the preparation along the _______.
- Defined by the _____ of the carious lesion.
- Extension to sound tooth structure at an initial depth of ___________mm into ______.
- Extend gingival floor to get _____ always.
- Extend facial and lingual proximal walls to get _____ unless it would require unreasonable removal of sound tooth structure to break the contact.
***BOARDS***

Discuss each of the following:
- Friable enamel = ?
- Unsupported enamel = ?

Discuss Primary Resistance Form of initial tooth preparation in regards to each of the following:
- Resistance = ?
- Pulpal and gingival floor shape?
- If extension of preparation is _____ the distance from primary groove to cusp tip, consider capping the cusp.
- ____ internal line angles.
***BOARDS***

Discuss Primary Retention Form of initial tooth preparation in regards to each of the following:
- Retention = ?
- Convergent walls prevent ____ displacement.
- Dovetail prevents _______ displacement.
- Rely on ______ if using composite.

______ is used to improve access and visibility as needed.
Convenience form

Which of the following is used to improve access and visibility in the initial tooth preparation?
A. Outline form
B. Primary resistance form
C. Primary retention form
D. Convenience form
D. Convenience form

Convergent walls and a dovetail are used to accomplish which of the following?
A. Outline form
B. Primary resistance form
C. Primary retention form
D. Convenience form
C. Primary retention form

Which of the following is implicated in the initial cavity preparation for the prevention of tooth or restoration fracture from occlusal forces?
A. Outline form
B. Primary resistance form
C. Primary retention form
D. Convenience form
B. Primary resistance form

Which of the following is implicated in the initial cavity preparation for the prevention of displacement of restorative material?
A. Outline form
B. Primary resistance form
C. Primary retention form
D. Convenience form
C. Primary retention form

What are the 8 steps in tooth preparation in order from start to finish?
***BOARDS***
- Outline form
- Primary resistance form
- Primary retention form
- Convenience form
- Remaining dentin caries removal
- Pulp protection
- Secondary resistance and retention form
- Finishing external walls
Discuss the 5th step of cavity preparation: Caries Removal

Discuss Pulp Protection in regards to cavity preparation:
- Purpose?
- Deep excavation approximating pulp = ?
- <1mm exposure and asymptomatic = ?
- >1mm exposure and symptomatic = ?

Discuss Sealer/Desensitizer in regards to each of the following:
- Used for _______,
- What do they do?
- GLUMA?

Discuss Liners in regards to cavity preparation:
- What is it used for?
- What do liners provide?
- Electrical insulation
- Thermal protection
- Pulpal tx?
- Materials used as liners?

Discuss using a Base in regards to cavity preparation:
- What are bases used?
- ____ protection?
- Distributio of local stress?
- What are the materials used for bases?

Discuss Secondary Resistance and Retention form in regards to cavity preparation:

Discuss Finishing External Walls in regards to cavity preparation:

Discuss Moisture Control in regards to cavity preparation:

Discuss Amalgam and Gold preparations in regards to each of the following:
- Use a ______ bur for smooth walls
- Retention? (2)
- Resistance for tooth? (6)
- Resistance for amalgam? (2)
***BOARDS***

Discuss Composite preparations in regards to each of the following:
- Use a _____ bur for rough walls.
- Same as amalgam except no need for ____.

Discuss Gold Onlay Preparations in regards to each of the following:
- Collar = ?
- Skirt = ?
- Provide ______.

Discuss Dental Amalgam in regards to each of the following:
- Eame’s Ratio = ?
- What is amalgam composed of?

Discuss Trituration in regards to each of the following:
- What does Trituration do?
- Gamma = ?
- Gamma1 = ?
- Gamma2 = ?

Which of the following phases is unreacted silver-tin?
A. Gamma
B. Gamma1
C. Gamma2
D. Gamma3
A. Gamma

Which of the following phases is a strong silver-mercury matrix?
A. Gamma
B. Gamma1
C. Gamma2
D. Gamma3
B. Gamma1

Which of the following phases is a weak tin-mercury?
A. Gamma
B. Gamma1
C. Gamma2
D. Gamma3
C. Gamma2

Discuss Trituration in regards to each of the following:
- Normal mix = ?
- Over-trituration = ?
- Under-trituration = ?

Discuss the different Alloy Types in regards to each of the following:
- Low-Copper?
- High-Copper?

All of the following are true regarding Spherical alloy particles in amalgam EXCEPT:
A. Microspheres of various sizes
B. Easier to condense
C. Better proximal contacts
D. Sets faster
C. Better proximal contacts
***BOARDS***

All of the following are true regarding Admixed alloy particles EXCEPT:
A. Mixture of irregular and spherical pieces
B. Easier to condense than spherical
C. Better proximal contacts than spherical
D. All of the above are true
B. Easier to condense than spherical
***BOARDS***

All of the following are true regarding Admixed alloy particles EXCEPT:
A. Mixture of irregular and spherical pieces
B. Requires more condensation forces than spherical particles
C. Better proximal contacts than spherical particles
D. All of the above are true
D. All of the above are true
***BOARDS***

All of the following are CONTRAINDICATIONS to amalgam EXCEPT:
A. Very small class VI lesions
B. High esthetic demands
C. Moderate to large lesions
D. Allergic to metals
E. All of the above are true
C. Moderate to large lesions

Discuss amalgam Carving and the instruments used to carve amalgam:

Amalgam marginal ridge fractures are common if ___(5)___.

Discuss Class V amalgam preparation:

Discuss Mercury Toxicity in regards to each of the following:
- ____ is the biggest risk.
- If a spill occurs, use a special ______.
- What are the 4 symptoms of Acute Mercury toxicity?
***BOARDS***

All of the following are Acute mercury toxicity symptoms EXCEPT:
A. Muscle weakness (hypotonia)
B. Loss of hair (alopecia)
C. Weight loss/GI disorders
D. Exhaustion
E. All of the above are acute mercury toxicity symptoms
E. All of the above are acute mercury toxicity symptoms

Discuss the different Mercury Forms:
- Methylmercury = ?
- Elemental = ?
- Mercury salts = ?
***BOARDS***

Discuss Enamel and Dentin bonding:
- Is dentin bonding as strong as enamel bonding?
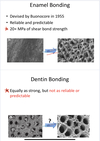
What are the 4 reasons that explain the difficulty of dentin bonding?
***BOARDS***

All of the following are reasons for the difficulty of bonding to dentin EXCEPT:
A. Composition
B. Length
C. Structure
D. Depth
E. Smear layer
B. Length

All of the following are true regarding dental etch EXCEPT:
A. Removes smear layer
B. Etched enamel that makes it chalky or frosty white creates microporosities
C. Etched dentin exposes a layer of collagen, which widens dentinal tubules
D. Can cause allergic dermatitis
E. All of the above are true
D. Can cause allergic dermatitis

Discuss dental Etch in regards to each of the following:
- Etch for _____ seconds
- ___% phosphoric acid
- Removes ______.
- Etched enamel = ?
- Etched dentin = ?
- Rinse for ____seconds and leave moist.

Which of the following can’t cause allergic dermititis?
A. Etch
B. Bond
C. Primer
D. Liner
C. Primer

Which of the following dental materials removes the smear layer?
A. Etch
B. Bond
C. Primer
D. Liner
A. Etch

Which of the following prevents collagen collapse?
A. Etch
B. Bond
C. Primer
D. Liner
C. Primer

Discuss Primer in regards to each of the following:
- HEMA?
- Can cause ______.
- Infiltrates?
- Prevents ____?

Discuss Bond/Adhesive in regards to each of the following:
- Bis-GMA
- Chemically bonds to…

Discuss the hybrid layer in regards to each of the following:
- What is it?
- _____ = adhesive resins lock into the microporosities of etched enamel and intertubular dentin.
- The key to adhesive dentistry is _________.

Discuss the enamel-dentin bonding systems:
- Etch and Rinse System?
- Self Etch systems?
- 4th generation?
- 5th generation?
- 6th generation?
- 7th generation?

Discuss the 3 different components of Composite Resin:
***VERY HIGH YIELD BOARDS***

Which of the following components of the composite resin is the organic component?
A. Bis-GMA
B. Silica
C. Silane
A. Bis-GMA

Discuss the composite types in regards to each of the following:
- Macrofill
- Microfill
- Hybrid
- Nanofill
- Nanohybrid
- Flowable
- Packable
Which of the following composite types uses Camphorquinone as the photoinitiator?
A. Self-Cure
B. Light-Cure
***BOARDS***
B. Light-Cure
Self-Cure = Benzoyl peroxide (initiator)
Light-Cure = Camphorquinone (photoinitiator)

Which of the following composite types uses Benzoyl peroxide as the initiator?
A. Self-Cure
B. Light-Cure
***BOARDS***
A. Self-Cure
Self-Cure = Benzoyl peroxide (initiator)
Light-Cure = Camphorquinone (photoinitiator)

Which of the following composite types uses a Tertiary amine as the activator?
A. Self-Cure composite
B. Light-Cure composite
***BOARDS***
A. Self-Cure composite

Which of the following is needed to initiate polymerization in Light-Cure composites?
A. 375nm light
B. 437nm light
C. 468nm light
D. 528nm light
***BOARDS***
C. 468nm light

Which of the following is the activator for Self-Cure composites?
A. Benzoyl peroxide
B. Camphorquinone
C. Tertiary amine
D. Bis-GMA
C. Tertiary amine

Which of the following is the initiator for Self-Cure composites?
A. Benzoyl peroxide
B. Camphorquinone
C. Tertiary amine
D. Bis-GMA
***BOARDS***
A. Benzoyl peroxide

Which of the following is the initiator for Light-Cure composites?
A. Benzoyl peroxide
B. Camphorquinone
C. Tertiary amine
D. Bis-GMA
***BOARDS***
B. Camphorquinone

Which of the following is set only by a polymerization mechanism buys contain ion-leach able glasses in an attempt to achieve fluoride release?
A. Composite resin
B. Resin-modified Glass Ionomer
C. Compomers (Polyacid-Modified Resin Composites)
D. Ionomer-modified Composites
D. Ionomer-modified Composites

_______nm of light is needed to initiate polymerization of Light-Cure composites.
***BOARDS***
468nm
Which of the following components of Composite Resin is radiopaque, giving the dentist the ability to see the restoration radiographically?
A. Resin matrix
B. Filler particles
C. Coupling agent
B. Filler particles

Which of the following components of Composite Resin is radiopaque, giving the dentist the ability to see the restoration radiographically?
A. Silica
B. Silane
C. Bis-GMA
A. Silica

Discuss Polymerization Shrinkage in regards to each of the following:
- What shrinks and how much of it shrinks?
- Configuration factor (C-factor) is the ratio of ______ to ______ surfaces of composite.
- ______ is inversely related to C-factor (make sure you understand this)
- What does a higher C-factor mean?

Which of the following is composed of an acid and a base?
A. Glass Ionomer
B. Composite resin
C. MTA
D. Bond agent
***BOARDS***
A. Glass Ionomer
Glass ionomer = acid and base
Composite resin = matrix and filler
Which of the following is composed of a matrix and filler?
A. Glass Ionomer
B. Composite resin
C. MTA
D. Bond agent
***BOARDS***
B. Composite resin

What is the acid and base used in glass ionomer?
***BOARDS***
Acid = polyacrylic acid
Base = Fluoroaluminosilicate glass

What is the Matrix and Filler of composite resin made of?
***BOARDS***
Matrix = Bis-GMA
Filler = barium silicate glass

All of the following are true regarding Glass ionomer EXCEPT:
A. Polyacryclic acid is the acid component in glass ionomer
B. Self-adhesion to tooth (bond not required)
C. Exhibits fluoride release
D. Barium silicate glass is the base component in glass ionomer
E. Rely on chemical bond
***BOARDS***
D. Barium silicate glass is the base component in glass ionomer

All of the following are true regarding Composite Resin EXCEPT:
A. Rely on micromechanical bond
B. Light-cure or self-cure
C. Contains a filler and matrix and not an acid or base
D. Barium silicate glass is the matrix component of composite resin
E. No fluoride release
***BOARDS***
D. Barium silicate glass is the matrix component of composite resin

Which of the following is an anhydrous single paste that contains major ingredients of both CR and GI except for water and is used in orthodontics?
A. Composite resin
B. Resin-modified Glass Ionomer
C. Compomers (Polyacid-Modified Resin Composites)
D. Ionomer-modified Composites
C. Compomers (Polyacid-Modified Resin Composites)

Which of the following is set by an acid-base rxn and free-radical addition polymerization (light and/or chemical cure)?
A. Composite resin
B. Resin-modified Glass Ionomer
C. Compomers (Polyacid-Modified Resin Composites)
D. Ionomer-modified Composites
B. Resin-modified Glass Ionomer



