Off Pump CABG & Mechanical Circulatory Devices - Quiz 7 Flashcards
What are the different approaches for doing a CABG?
Thoracotomy - minimally invasive
&
Full Sternotomy
Other than the Surgeon & Anesthetist, who else is also required to be in the room for a CABG?
Perfusionist w/ a CPB machine ready
An Off-Pump CABG usually takes _____ time than a traditional CPB CABG
An Off-Pump CABG usually takes MORE time than a traditional CPB CABG
What makes a pt. a good candidate for an Off-Pump CABG?
Good LV Function
How does Fluid Management differ from an On-Pump CABG vs an Off-Pump CABG?
Harder to give large amt of fluid Off-Pump unlike the CPB Machine that can give large amounts extremely quickly
Normothermia is absolutely necessary during a CABG. What are ways to maintain normothermia?
Monitor Core Temp
Water Thermoregulation Mattress
Heat Preserving Bouffant
↑Room Temp
What can happen if a pt does not maintain normothermia of 36o C during a CABG?
Will be unable to Extubate
Which Antifibrinolytic is normally given for an On-Pump CABG, but NOT given for an Off-Pump CABG?
Aminocaproic Acid (Amicar) - inhibits Plasminogen binding to Fibrin converting it to Plasmin
What is the dose of Heparin given for an Off-Pump CABG?
Less than it would be for On-Pump CABG
100-200 units/kg w/ a goal ACT > 300
(sometimes full heparin @ 300-400 units/kg)
What is the reversal for Heparin?
Protamine
How is the heart visualized during an Off-Pump CABG?
Surgeon uses Footplate Stabilizers & Retractors that Suction & Lift the Heart
How is the Blood Pressure managed during Verticalization of the Apex to visualize the PDA & Circumflex?
Keep MAP Elevated & Give Volume to counter Extreme Hemodynamic Compromise & Ischemia
At what point during an Off-Pump CABG does the MAP need to be lowered to 60 mmHg?
During the Proximal Graft Aortic Anastomosis
What are the Advantages of an Off-Pump CABG?
Less Bleeding
Less Heparin
Normothermia Maintained –> Potential Extubation
No Aortic Cross-Clamp
Why are Intra-Aortic Ballloon Pumps (IABP) used?
↑Cardiac Perfusion w/ Sync’d Counterpulsation
↑Coronary Blood Flow on Diastole
↓Afterload on Systole
Stabilizes PreOP CABG Pts post MI
What is used as a supplement for an Off-Pump CABG or for patients who have difficulty coming off the CPB machine?
Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
What are contraindications for placing a pt on a IABP?
Sepsis
Descending Aortic Disease
Severe PVD
Severe Aortic Regurg.
What site is the IABP inserted?
Via Femoral Artery
For an Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump, where does the Tip of the Balloon lie?
At the Junction of Aortic Arch & Descending Aorta
&
2 cm distal to the origin of Left Subclavian Artery
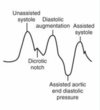
How does the Timing of an IABP work?
Timed w/ Dicrotic Notch & Inflates on Diastole when AV Closes to seal and increase pressure, sending blood to the coronary arteries
When does the IABP deflate?
Deflates right before Systole at the beginning of the R-Wave
What does IABP Deflation do?
Vacuum Effect
↓Aortic Pressure & ↓Afterload
Facilitates Ventricular Ejection
↓O2 Demand
What is happening here?

Premature Deflation during Diastole
Suboptimal Perfusion
Backflow
Angina
↑O2 Demand
What is happening here?
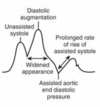
Deflation in Late Diastole as AV Begins to Open
No Afterload Change or ↑Afterload
↑O2 Demand
Prolonged Isovolumetric Contraction
What is happening here?

Inflation before AV Closure
↑LVEDV, ↑LVEDP, & ↑PCWP
↑LV Wall Stress
↑O2 Demand
Aortic Regurg.
What is happening here?
Inflation way after AV Closure
Suboptimal Pefusion
When would it be safe for a pt to be weaned off a IABP?
When pt does ok w/ a 1:4 Ratio on the IABP
What are complications associated w/ an IABP?
Vascular Injury/Ischemia - most common
Thrombus
Infection
Thrombocytopenia
What is Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)?
Closed circuit device that allows heart/lungs to recover while maintaing oxygenation & perfusion
When is ECMO indicated?
Cardiogenic Shock
Failure to Wean off CPB
Rt. Heart Failure
Heart Failure unresponsive to VAD
Post CPR
ARDS
What is the preferred ECMO method for pts. w/ Respiratory Failure & Intact Cardiac Function?
Venovenous ECMO
What are the common cannulation sites for Venovenous ECMO?
Femoral & IJ Veins
How does Venovenous ECMO work?
Blood is drained from SVC & IVC via IJ/Femoral Vein
then Oxygenated
then Returned to the Right Atrium
(can be separate drain & return cannulae or Single double lumen cannula)
Which type of pt is Venoarterial ECMO used on?
Pts who need LV & Pulmonary Support
How is Venoarterial ECMO different from Venovenous ECMO?
Venoarterial ECMO skips the Pulmonary Circulation for Higher Arterial Oxygenation
How does Venoarterial ECMO work?
Centrally placed cannulas drain blood from Right Atrium & Returned to Ascending Aorta
How would Venoarterial ECMO work if there is Peripheral Cannulation?
Blood is drained from Right IJ / Femoral & Returned to Femoral Artery
For Venoarterial ECMO, what happens to the blood once it is drained and before it is returned?
Goes to a roller pump that circulates @ 3-6 L/min thru a Membrane Oxygenator, which removes CO2, Adds O2, then Rewarmed
What are complications of ECMO?
Bleeding
Stroke
Infection
Limb Ischemia
Multiorgan Dysfunction
What are indications for a Ventricular Assist Device?
Cardiogenic Shock post MI
Viral Cardiomyopathies
Post CPB
What are contraindications to a Ventricular Assist Device?
Active Infection
Irreversible Renal/Hepatic Dysfunction
Severe Pulm. HTN
Metastatic Cancer
Major Coagulopathy
How does an LVAD work?
Collects Oxygenated Blood from LA via Inflow Cannula & Pumps blood to the Aorta via the Outflow Cannula
How do various Ventricular Assist Devices differ?
Continuous vs. Pulsatile
Short Term vs Longterm
Pneumatic vs Electric
Location: Intra-, Extra-, Para-Corporeal
What is an Impella?
Small VAD placed percutaneously thru the Femoral Artery that pumps blood from LV to the Aorta @ 2.5 L/min
Why do pts w/ an LVAD have a higher risk for bleeding?
These pts may have Hepatic Congestion from Right HF
What are the Anesthetic Cardiovascular goals for pts w/ an LVAD?
Prevent Bradycardia
&
Maintain Sympathetic Tone
What is the leading cause of death in LVAD patients?
Sepsis - maintain strict sterile technique
Why is Intra-Op TEE used for pts w/ LVAD?
30% of these pts develop RV Dysfunction - use TEE to avoid RV Overfilling
What meds can be given to treat RV Dysfunction?
Epinephrine & Milrinone - ↓RV Afterload
Nitric Oxide - Dilates Pulmonary Vessels
LVAD Flow is highly dependent on Volume. What is the Volume of Choice?
Blood & Blood Products


