Occlusion 1 Flashcards
(27 cards)
What are the different components of the TMJ joint?
- Cranial base
- Mandible
- Muscles of mastication
- Innervation
- Vascular supply
- Articular disk

What type of joint is the TMJ and what is it a joint between?
is a synovial joint between the mandibular fossa on the cranial base and the condylar head
What splits the synovial joint in half?
The articular disc
(splits the joint in 2 each with its own synovial membrane)

What is the articular disk?
The articular disc is a fibrous extension of the joint capsule which surrounds the joint and the movement of the articular disk is mediated by the lateral pterygoid muscle.

What muscles of mastication and suprahyoid musces are involved with the TMJ?
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Mylohyoid
- Stylohyoid
- Geniohyoid
- Digastric
- Muscles of mastication
- Temporalis
- Lateral Pterygoid
- Medial Pterygoid
- Masseter
Describe the action of each of the muscles of mastication.
-
Temporalis (T)
- Elevates and retracts the mandible
- Assists in rotation
-
Lateral Pterygoid
- positions disc in closing (superior - SLP)
- Protrudes and depresses mandible and causes lateral movement (inferior - ILP)
-
Medial Pterygoid (MP)
- Elevates the mandible
- Lateral movement and protrusion
-
Masseter (SMA)
- Elevates and protracts the mandible
- Assists in lateral movement
What are the possible movements of the TMJ/mandible?
Rotation
Translation
Lateral translation
When does rotational movement occur? (also known as hinge movement)
When there is a small amount of mouth opening (up to 20 mm)
Describe the positioning of the condylar head and articular disc during rotational movements of the mandible.
The condyle and disc remain within the articular fossa (There is no downwards or forwards movement)

Describe how the condlyes move during rotational movement.
There rotation of the condylar heads around an imaginary horizontal line which foes through the rotational centres of the condyles

The imaginay line that the condyles rotate around during rotational movement of the TMJ is called what?
The terminal hinge axis
How is the terminal hinge axis measured? What does this measurement allow us to do?
Using a facebow (measures realationship between maxilla and terminal hinge axis)
This relationship allows us to mount maxillary casts on an articulator as close as possible to the patient’s normal occlusion

Describe the changes/movements that happen during translational movement of the mandible.
- The lateral pterygoid contracts
- Articular disc and condyle begin to move
- They travel downwards and forwards along the incline of the articular eminence
- They may also travel laterally (laterotrusive movement)

The border movements of the mandible are represented by what?
Posselts envelope
Describe posselts envelope.
ICP = Intercuspal position
E = Edge to Edge
Pr = Protrusion
T = Maximum opening
R = Retruded Axis Position
RCP = Retruded contact position
There is also a rest position below the intercuspal position

What is the intercuspal position?
- It is the tooth position regardless of the condylar position
- Is the patient’s comfortable bite
- The best fit of the teeth
- Maximum interdigitation of the teeth
Note: it is also known as centric occlusion (CO)
What is edge to edge? Describe it and how the position is reached.
What are the posterior teeth like in this position?
- Is a tooth position again
- The teeth slide forward from ICP on palatal surfaces of anterior teeth
- Incisal edges of upper and lower incisors touch
- There is space between all the posterior teeth – happens with canine guidance
- If has group function then the back teeth would still be touching
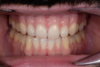
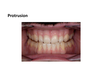
Describe protrusion including what teeth touch and how the condyle moves.
- Condyle moves forwards and downwards on articular eminence
- Only incisors +/- canines touch
- No posterior tooth contacts
- Eventually no tooth contacts
Describe the movements involved in max opening.
- No tooth contacts
- Mouth wide open
- Full translation of the condyle over the articular eminence

Describe the retruded axis position.
- No tooth contacts
- Most superior anterior position of the condylar head in the fossa
- This is where the terminal hinge axis is

Describe the retruded contact position and its relation to ICP.
- First tooth contact when the mandible is in retruded axis position
- ICP is approximately 1mm anterior to RCP in 90% of the population
- RCP and ICP are no coincident so the mandible slides forward to achieve ICP (however it is coincident in some patients)

When talking about lateral translation, what do we term the 2 sides?
A working side and a non-working side
(If the mandible was to be moved laterally to the right then the RHS would be the working side and the LHS would be the non-working side.)

The lateral translation movement is also known as what?
The Bennet movement
What does the Bennet angle show?

the path of the nonworking condyle in the horizontal plane during lateral excursion
When translation movements begin, you get a slight lateral shift (on non-working side?) - this is the Bennet angle



