Obs and gynae Flashcards
As a result of the plasma volume changes in pregnancy what happens to Hb?
Hb falls due to dilution
At which age is the vaccine for HPV given for HIV negative females?
11-13 years of age
Can pregnant women with HIV deliver vaginally?
Yes, if viral load is less than 50
Define a missed (delayed) miscarriage
A uterus which contains a dead foetus < 20 weeks
Sac with no foetal pole
Cervical os closed
Define an incomplete miscarriage
Not all products have been expelled
Pain and bleeding, os open
Define an inevitable miscarriage
Heavy bleeding with clots and pain
Cervical os is open
Define polyhydramnios?
2-3L of amniotic fluid
Define recurrent miscarriage
>3 consecutive spontaneous abortions
Define SGA
Less than 10th percentile on USS
During which stage does a chancre develop?
Primary
How are fibroids diagnosed?
Transvaginal USS
How can amenorrhoea be divided?
Primary and secondary
How can fluid in the pouch of douglas be drained?
Via a needle through the posterior fornix of the vagina
How can the lower segment of the uterus be defined?
Below uterovesicalperitoneal fold
Doesn’t contract; passively dilates
7cm above cervix
How can the risk of cleft palate be reduced in pregnant women on phenytoin?
Give vitamin K in the last month of pregnancy
How do the breasts attach to the skin?
Via suspensory ligaments
How do you look at a CTG?
Determine
Risk
Contractions
Baseline
Rate
Variability
Accelerations
Decelerations
Overall
How does depo provera work as contraception?
Inhibits ovulation
Effect on cervical mucus
Effect on endometrium
How does IUS act as contraception?
Renders endometrium unfavourable for implantation
Thickens cervical mucus
Pre-fertilisation effects
How does pregnancy increase the risk of thromboembolism, anatomically?
Uterus presses on IVC causing venous stasis in legs
How does the implant act as contraception?
Inhibition of ovulation
Effect on endometrium
Effect on cervical mucus
How is chlamydia diagnosed?
NAAT - vulvovaginal swab for females, first void urine for males
How is depo given?
IM injection every 13 weeks
How is gonorrhoea diagnosed?
Microscopy
Culture
NAATs
How is placenta praevia diagnosed?
USS
How is POP taken?
Daily at the same time
No break
How is syphilis diagnosed?
Dark ground microscopy
PCR
Serological testing
How is the COCP taken?
Daily for 21 days with 7 days off for a breakthrough bleed
How is the depo started beyond day 5?
Woman must be reasonably certain she is not pregnant and abstain/use condoms for 7 days
How long does the depo provera last?
14 weeks
How long does the implant last?
3 years
How long does the IUD last?
5 years
How long does the mirena last?
5 years
How should amenorrhoea be investigated?
FULL HISTORY
Gonadotrophins (low in hypothalamic, high in ovarian)
TFTs
Prolactin
Oestradiol
In pregnancy women with HIV, which factors reduce vertical transmission?
C section
Bottle feeding
Maternal antiretrovirals
Neonatal antiretrovirals
In what situations is anti-D given to mothers who are rhesus negative?
Women less than 12 weeks: uterine evacuation, ectopic prgenancies
All women with bleeding after 12 weeks
Is the BHCG low or high in Downs?
High
Is the PAPP-A low or high in Downs?
Low
Is thyroxine safe in pregnancy?
Yes
Label this diagram
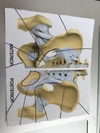

Lable the hormones in this diagram


Name the pathway of the pudendal nerve
Exits pelviz via greater foramen
Passes posterior to sacrospinous ligament
Re-enters pelvis via lesser sciatic foramen
What age group has the highest incidence of cervical cancer?
25 - 29
What antibiotics are given during total abdo hysterectomy?
IV co-amoxiclav
What are complications from hyperemesis gravidarum?
Wernicke’s
Mallory-Weiss tear
What are fibroids?
Benign smooth muscle tumours of uterus
What are follicular cysts due to?
Non-rupture of the dominant follicle
What are hypertensive pregnant women at risk of?
Pre-eclampsia
What are predisposing factors for vaginal candidiasis?
Diabetes
Antibiotic use
Steroids
Pregnancy
HIV
What are risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy?
Damage to tubes
IUCD
POP
IVF
Previous ectopic
Endometriosis
What are risk factors for endometrial cancer?
Obesity
Nulliparity
Unopposed oestrogen
Diabetes
PCOS
What are risk factors for necrotising enterocolitis?
Not breastfeeding
Prematurity
IUGR
Hypoxic ischaemic insult
What are risk factors for PPH?
Previous PPH
Increasing maternal age
Placenta problems
Prolonged labour
Polyhydramnios
Macrosomia
Pre-eclampsia
Emergency C-section
What are risk factors for shoulder dystocia?
DM
Obesity
Macrosomia
What are risk factors from cord prolapse?
Prematurity
Multiparity
Twins
Abnormal presentation
Placenta praevia
High foetal station
What are signs of foetal distress?
Reduced foetal movements
Meconium stained liquor
Increased lactate
What are signs of obstruction in labour?
Moulding
Caput medusa
What are some causes of foetal distress?
Placental abruption
Vasa praevia
Cord collapse
Uterine rupture
Foeto-maternal haemorrhage
Hypoxia
What are some causes of post-coital bleeding?
Infection
Cervical ectropion (COCP!!)
Polyps
Trauma
Cancer
What are some causes of primary amenorrhoea?
Turner’s syndrome
Testicular feminisation
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Imperforate hymen
What are some causes of recurrent miscarriage?
APS
Poorly controlled DM
PCOS
Uterine abnormality
Parental chromosomal abnormalities
Smoking
What are some causes of secondary amenorrhoea?
Hypothalamic
PCOS (increased androgen levels)
Hyperprolactinaemia
Premature ovarian failure
Thyrotoxicosis
Intrasuterine adhesions
What are some of the causes of IMB?
Pregnancy related
Physiological
Vaginitis
Fibroids
Polyps
Tumours
What are the AFP, beta HCG and oestriol levels in Edward’s syndrome?
AFP decreased
BHCG increased
Oestriol decreased
What are the causes of IUGR?
Multiple pregnancy
Malformation
Smoking
DM
Hypertension
Asthma
What are the causes of multiple second trimester miscarriages?
Bicornuate uterus
APS
SLE
Cervical incompetence
What are the causes of polyhydramnios?
Drugs
Diabetes
Rhesus
GI obstruction
Increased urine output
Poor swallowing
What are the common causes of PPH?
Retained placenta
Endometriosis
What are the complications of prematurity?
RDS
PDA
Intraventricular haemorrhage
Sepsis
What are the conditions of use of operative delivery?
Head engaged
Membranes ruptured
Cervix dilated
Empty bladder
What are the features of an amniotic fluid embolism?
Sudden dyspnoea
Hypotension
DIC
Pulmonary oedema
SOB
Chest pain
N&V
Collapse
What are the features of an ectopic pregnancy?
Constant lower abdo pain
Vaginal bleeding: may be dark brown
History of amenorrhoea
Shoulder tip pain/pain on defecation
Cervical excitation
What are the features of baby blues?
Anxious
Tearful
Irritable
What are the features of cervical cancer?
PCB
IMB
PMB
Change in vaginal discharge
What are the features of cervical ectropion?
Change in vaginal discharge
PCB
What are the features of endometrial cancer?
PMB
IMB
What are the features of endometriosis?
Chronic pelvic pain
Deep dyspareunia
Dysmenorrhoea
Subfertility
What are the features of fibroids?
May be asymptomatic
Menorrhagia
Cramping lower abdo pain
Bloating
Urinary symptoms
Subfertility
Bulky uterus
What are the features of PCOS?
Subfertility
Oligomenorrhoea
Acne
Hirsutism
Obesity
Acanthosis nigricans
What are the features of placenta praevia?
Shock in proportion with visible blood loss
Painless blood loss
Can be triggered by sex, usually unprovoked
PP high
Malpresentation common
What are the features of placental abruption?
DIC
Shock inconsistent with blood loss
Constant pain
Tense (woody) uterus
Abnormal CTG
What are the features of PND?
Similar to depression
What are the features of post natal psychosis?
Mood swings
Perception problems
What are the features of uterine rupture?
Pain
Intraperitoneal bleeding
Shock
Cessation of contractions
Foetal distress
What are the features of vaginal candidiasis?
Cottage cheese like discharge
Dysuria
Dyspareunia
Itch
Vulval erythema
What are the features of vulval carcinoma?
Lump/ulcer on labia majora
May be associated with itch/irritation
What are the hormones doing in PCOS?
Increased insulin, increased androgens (testosterone), increased LH, increased oestrogen, low progesterone, normal or low FSH
What are the indications for a c section?
Absolute CPD
Pre-eclampsia
Failure to progress
Cervical cancer
Placenta praevia
Postmaturity
Breech
Vaginal infection
IUGR
Foetal distress
What are the non-contraceptive benefits of the COCP?
Control of heavy, painful periods
Acne control
Endometriosis
Menstrual migraine (NO AURA)
Protection against ovarian and endometrial cancers
What are the oncogenic strains of HPV?
16
18
31
33
45
51
58
What are the risk factors for breech presentation?
Uterine malformations
Placenta praevia
Polyhydramnios
Foetal abnormality
Prematurity
What are the risk factors for cervical cancer?
HPV 16 & 18
Smoking
Early first time
COCP
What are the risk factors for placental abruption?
Hypertension
Trauma
Drugs
Smoking
What are the risk factors for vulval carcinoma?
Age > 65
HPV
Immunosuppression
Lichen sclerosus
What are the side effects of combined hormonal contraception?
Unscheduled bleeding
Mood changes
Weight gain
What are the side effects of depo provera?
Weight gain
Delay in return of fertility
Irregular bleeding
Possible risk of osteoporosis
What are the side effects of IUD?
Heavy, prolonged menses
Pain/infection/PID in first 20 days
Perforation
Expulsion
Low ectopic risk
What are the side effects of the implant?
Irregular bleeding
Weight gain
Acne
Nerve damage
Deep insertion
What are the three layers of the uterus?
Perimetrium
Myometrium
Endometrium
What are the two main types of c section?
Lower segment
Classical (longitudinal incision)
What can be used to stop contractions in prematurity?
Tocolytics - nifedipine, indethemacin
What causes cervical ectropion?
Increased oestrogen levels
What causes Erb’s palsy?
Shoulder dystocia
What changes does oestrogen cause in pregnancy?
Increases breast and nipple growth Increases water retention and protein synthesis
What changes does progesterone cause in pregnancy?
Decreases smooth muscle excitability Increases body temp
What chromosome is Downs?
21
What complications can occur in pregnancy with diabetics?
Polyhydramnios
Preterm labour
Stillbirth
Macrosome
IUGR
What conditions can amniocentesis diagnose?
Neural tube defects (increased AFP) Chromosome disorders Inborn errors of metabolism
What contraception cannot be given with carbamazepine?
No systemic progesterone
What do aminoglycosides cause in pregnancy?
Ototoxicity
What do early decelerations indicate on a CTG?
Increased vagal tone due to head compression
What do fluoroquinolones cause in pregnancy?
Cartilage damage
What do late decelerations indicate on a CTG?
Placental insufficiency –> foetal distress
What do sulphonamides cause in pregnancy?
Kernicterus
What do tetracyclines cause in pregnancy?
Discoloured teeth
What do variable decelerations indicate on a CTG?
Umbilical cord compression/uterine contractions
What is AMH used for?
Assessing ovarian reserve prior to IVF
What does CMV cause?
Jaundice
Hepatosplenomegaly
Microcephaly
What does erythromycin cause in pregnancy?
Acute cholestatic hepatitis
What does metranidazole cause in pregnancy?
Mutagenesis
What does pearl index represent?
Number of contraceptive failures per 100 women per year
What does prolactin cause?
Enlargement of mammary glands
What does ribaviran cause in pregnancy?
Teratogenic

