Obj. 20: CNS infections, encephalopathies Flashcards
What is the most common cause of meningitis in adults?
Strep pneumo
Which meningitis has a rash and which has NO rash?
RASH: meningococcal
NO rash: pneumococcal
Name 3 risk factors for pneumococcal meningitis and 3 risk factors for meningococcal meningitis.
Pneumococcal: recent head trauma, sinusitis, pneumonia
Meningococcal: age (kids), crowded living, travel
As soon as meningitis is suspected, what do you start?
ceftriaxone, vancomycin
What do you expect to find in the CSF of a bacterial meningitis patient?
increased protein
decreased glucose
increased WBCs with PMNs predominant
What will you find on gram stains of pneumococcal and meningococcal meningitis?
pneumococcal: gram-positive cocci
meningococcal: gram-negative intracellular diplococci
What will you find on culture and gram stain of aseptic meningitis?
Viral, so culture and gram stain are negative.
What is a main presenting difference between meningitis and encephalitis?
meningitis: lethargy, pain, but no personality changes
encephalitis: personality or mood changes
What is the difference in CSF findings between bacterial meningitis and encephalitis?
~bacterial meningitis: high protein, low glucose, WBCs elevated with PMNs predominant
~encephalitis: protein & glucose may be normal; WBCs with lymphocytes predominant
Your patient is complaining of HA, confusion, seizures, vomiting, and double vision. Has a hx of recent nose disease. On CT you see an area of contrast enhancement surrounding a low-density core.
What is it?
brain abscess
Your patient is a longtime alcoholic with confusion, ataxia, and nystagmus.
What kind of encephalopathy is this and what causes it?
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
~Wernicke encephalopathy, due to thiamine deficiency
~Diagnosis is confirmed by improvement within 1-2 days of IV thiamine
Your patient is a longtime alcoholic with cirrhosis, asterixis, confusion, and day-night reversal.
What kind of encephalopathy is this and what causes it?
How is it treated?
~hepatic encephalopathy due to inability of liver to detox blood
~lactulose!
~restrict dietary protein when acute
This is the CT of your patient.
What causes it?
What may you find on LP?
What is the treatment?
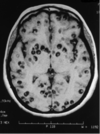
Cysticercosis
T. solium
CSF with increased lymphocytes and eosinophils
albendazole


