Number Properties on the GMAT Flashcards
(21 cards)
Rational Numbers
All of the numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers (all integers and fractions).
Irrational Numbers
All real numbers that are not rational, both positive and negative (e.g., π, -√3)
Properties of Integers
(Added, Subtracted, Multiplied, and Divided)
When an integer is added to, subtracted from, or multiplied by another integer, the result is an integer. An integer divided by an integer may or may not result in an integer.
Rules for Evens and Odds
Odds x Odds =
Even x Even =
Odd x Even =
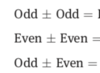
Odd x Odd = Odd
Even x Even = Even
Odd x Even = Even
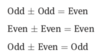
Exponent Rules for Odds and Evens
Oddany positive integer
Evenany positive integer
Oddany positive integer = Odd
Evenany positive integer = Even
Properties of Numbers between -1 and 1
(Getting Reciprocal of a Fraction)
The reciprocal of a number between 0 and 1 is greater than the number itself.
(You can also easily get the reciprocal of a fraction by switching the numerator and denominator. The result will be the same. For example, the reciprocal of 2/3 is 3/2.)
The reciprocal of a number between -1 and 0 is less than the number itself.
Multiplying any positive number by a fraction between 0 and 1 gives a product smaller than the original number.
Multiplying any negative number by a fraction between 0 and 1 gives a product greater than the original number.
Undefined
Division by zero is undefined. When given an algebraic expression, be sure that the denominator is not zero. The fraction 0/0 is likewise undefined.
When multiplying or dividing numbers with the same sign, the result is …
When multiplying or dividing two numbers with different signs, the result is …
When multiplying or dividing numbers with the same sign, the result is always positive. When multiplying or dividing two numbers with different signs, the result is always negative.
When Picking Numbers keep these things in mind
- Every number is a both a factor and a multiple of itself
- 1 is a factor of every number
- 0 is a multiple of every number
Prime Number
- Integer greater than 1 that has only two positive factors, 1 and itself.
- Number 1 is not considered a prime
- Number 2 is only Even prime number
Prime Factorization
Prime factorization of a number is the expression of the number as the product of its prime factors. No matter how you factor a number, its prime factors will always be the same.
The easiest way to determine a number’s prime factorization is to figure out a pair of factors of the number and then determine their factors, continuing the process until you’re lef with only prime numbers.
When is a number divisble by 2
A number is divisible by 2 if its units digit is even.
138 is divisible by 2 because 8 is even.
177 is not divisible by 2 because 7 is not even.
When is a number divisible by 3
A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
4,317 is divisible by 3 because 4 + 3 + 1 + 7 = 15 and 15 is divisible by 3.
32,872 is not divisible by 3 because 3 + 2 + 8 + 7 + 2 = 22 and 22 is not divisible by 3.
When is a number divisble by 4
A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits compose a two-digit number that is itself divisible by 4.
1,732 is divisible by 4 because 32 is divisible by 4.
1,746 is not divisible by 4 because 46 is not divisible by 4.
When is a number divisible by 5
A number is divisible by 5 if its units digit is either a 5 or a 0.
26,985 is divisible by 5.
55,783 is not divisible by 5.
When is a number divisible by 7
A number is divisible by 7 if the difference between its units digit multiplied by 2 and the rest of the number is a multiple of 7.
147 is divisible by 7 because 14 − 7(2) = 0, which is divisible by 7.
682 is not divisible by 7 because 68 − 2(2) = 64, which is not divisible by 7.
When is a number divisible by 8
A number is divisible by 8 if its last three digits compose a three-digit number that is itself divisible by 8.
76,848 is divisible by 8 because 848 is divisible by 8.
65,102 is not divisible by 8 because 102 is not divisible by 8.
When is a number divisible by 9
A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
16,956 is divisible by 9 because 1 + 6 + 9 + 5 + 6 = 27, and 27 is divisible by 9.
4,317 is not divisible by 9 because 4 + 3 + 1 + 7 = 15, and 15 is not divisible by 9.
When is a number divisble by 11
A number is divisible by 11 if the difference between the sum of its odd-placed digits and the sum of its even-placed digits is divisible by 11.
5,181 is divisible by 11 because (5 + 8) − (1 + 1) = 11, which is divisible by 11.
5,577 is a multiple of 11 because (5 + 7) − (5 + 7) = 0, which is divisible by 11.
827 is not divisible by 11 because (8 + 7) − 2 = 13, which is not divisible by 11.
Combining rules of factorizations to figure our divisibility of other numbers
You can combine these rules above with factorization to figure out whether a number is divisible
by other numbers.
To be divisible by 6, a number must pass the divisibility tests for both 2 and 3, since 6 = 2 × 3.
534 is divisible by 6 because 4 is divisible by 2 and 5 + 3 + 4 = 12, which is divisible by 3. To be divisible by 44, a number must pass the divisibility tests for both 4 and 11, since
44 = 4 × 11.
1,848 is divisible by 44 because 48 is divisible by 4 and (1 + 4) − (8 + 8) = −11, which is
divisible by 11.
Note that combining rules to test divisibility only works when the separate numbers you are testing do not have any factors in common (as is the case with 2 and 3 and with 4 and 11 above).
Tricks for Sequences
Sequences can look complicated, and their descriptions can be confusingly worded. Paraphrase, simplify, and stay attuned to the patterns.


