Neurology of the thoracic limb Flashcards
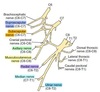
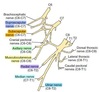
What are the roots of the brachial plexus?
C6, C7, C8, T1 and T2
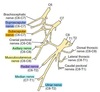
Route and connections of N. suprascapularis
- Enters the intermuscular space between m. supraspinatus ans m. subscapularis.
- Accompanied by the supraspinous artery and vein.

What does N. suprascapularis innervate?
- After passing over the scapular notch, innervates m. supraspinatus.
- Sends a small branck to the lateral part of the shoulder joint.
- Continues across the scapular neck to the end of the spine, where it innervates m. infraspinatus

Origin of Nn. subscapularis
- Usually a single, but occasionally double.
- Arises from the union of a branch from C6 nerve with C7 nerve.
- Divides into cranial and caudal part, before entering the medial surface of m. subscapularis.
- Only 5cm long. Allows extensive sliding movement in the shoulder.
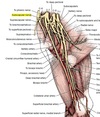
What does Nn. subscapularis innervate?
m. subscapularis
What does N. axillaris innervate?
- The true flexors of the shoulder: m. teres major, m. teres minor and m. deltoideus.
- M. cleidobrachialis (which used to be the clavicular part of the deltoideus).
- Supplies a branch to the shoulder joint capsule.
- Gives off a cutaneus branch: n. cutaneus antebrachii cranialis
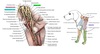
Route and connections of N. musculocutaneus
- From the brachial plexus runs towards the elbow joint on the caudo-medial surface of m. biceps brachii.
- Lies cranial to a. brachialis, n. medianus and n. ulnaris.
- Gives off a small branch at the shoulder joint to m. coracobrachialis.
- Distally to the shoulder, gives off r. muscularis proximalis to m. biceps brachii.
- Proximal to the elbow, gives off r. communicans to n. medianus.
- Distally gives off r. muscularis distalis to m. brachialis and a small branch to the elbow joint.
- Terminates as n. cutaneus antebrachii medialis.
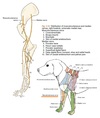
Route and connections of N. radialis
- From the brachial plexus, it runs over the tendinous insertion of m. latissimus dorsi.
- Enters between caput mediale and caput longum of m. triceps brachii.
- Divides into two branches: superficial and deep
- Continues disto-laterally on the caudal and lateral surfaces of m. brachialis.
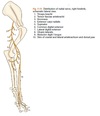
What does N. radialis innervate?
All extensors of the elbow, including the triceps and the anconeus
Route and connections of R. superficialis of N. radialis
- Appears at the cranio-ventral edge of the triceps’ lateral head.
- Divides into two parts: lateralis and medialis
- The lateral branch gives off n. cutaneus antebrachii lateralis.

What does R. superficialis of N. radialis innervate?
The skin on the cranio-lateral, cranial and cranio-medial aspects of the antebrachium

Route and connections of R. profundus of N. radialis
- Runs beneath m. extensor carpi radialis and across the flexor surface of the elbow.
- Reaches the deep lateral aspect of the antebrachium by passing under m. supinator.

What does R. profundus of N. radialis innervate?
- All the extensors of the crpus and digits, including m. extensor carpi ulnaris (which is functionally a flexor)
- M. brachioradialis.
- M. supinator.
- M. abductor digiti I longus.
- Sends a small branch to the elbow joint’s capsule.

Route and connections of N. medianus
- Innitially bound to n. ulnaris by fascia, but separates in the proximal brachium.
- Proximal to the elbow recieves the r. communicans from n. musculocutaneus.
- Distal to the elbow, passes beneath m. pronator teres.
- Runs between the superficial and deep digital flexors, accompanied by a. mediana.
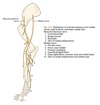
What does N. medianus innervate?
- M. pronator teres.
- M. pronator quadratus.
- M. flexor carpi radialis.
- M. flexor digitorum superficialis.
- Parts of m. flexor digitorum profundus
- The elbow joint’s capsule.