Neurology - Misc. Material + Broken Spreadsheets Flashcards
(148 cards)
Ischemic Stroke
(prevelence in stroke, two types and their frequencies)
- 80% of total stroke cases
- Types of ischemic stroke
- Thrombotic (66%)
- Embolic (33%)
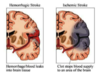
Hemorrhagic Stroke
(prevelence, cause)
- Prevelence - 20% of strokes
- Cause - blood in the brain, usually secondary to uncontrolled HTN
Types of Ischemic Strokes
(list and define 2)
A stroke due to clot in the brain that occludes blowflow
- **Thrombotic - **Stroke due a clot that forms intracranially, it does not migrate
-
Embolic - Stroke due to a clot that forms extracranially and migrates to the brain. Common locations include
- Heart
- Aortic arch
- Cerebral arteries
Carotid Artery Disease
(definition, s/sx, significance)
Definition: progressive blockage of the carotid arteries carotid arteries
S/Sx:
- Amaurosis fugax (sudden unilateral blindness)
- Dysphasia
- Unilateral weakness, paralysis, or numbness in extremities
Significance: highly increases risk of stroke
FAST Exam
(indication, procedure, result interpretation)
(Indication: suspected stroke
Procedure: administer three tests
- Facial movement - smile or show teeth, looking for new lack of symmetry or unilateral movement impairment
- Arm movement - lift patient’s arms together for 90 sec if sitting, 45 sec if supine and ask pt to hold the position for 5 seconds. observe for unilateral arm drift
- Speech - lookfor new speech disturbances, slurring, word-finding difficulties (naming objects)
- (Time - since onset of symptoms, in order to guide treatment algorhythm)
Results: a positive test in any field indicates high liklihood of stroke and warrents immediate hospital transport

Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale
(indication, procedure, results implications)
Indication: suspected stroke
Procedure:
- Facial droop analysis - have pt show teeth or smile
- Arm drift analysis - have pt close eyes with arms extended for 10 seconds
- Speech analysis - have pt repeat a phrase back to you, “the sky is blue in Cincinnati”
Implications: Positive results indicate high liklihood of stroke
- Facial droop - assymetrical face movement
- Arm drift - unilateral action, either 1 arm cannot move for the test or one arm drifts down more than the other
- Speech - noted slurring, incorrect words, or inability to speak

Glascow Coma Scale
(indication, procedure)
Indication: Determination of level of consciousness, specifically in the context of brain injury
Procedure: Evaluate patient for the following qualities and assign the appropriate number (see chart for numbers). Scores vary from 3-15
- Eye opening (4 levels)
- Verbal Response (5 levels)
- Motor response (6 levels)

NIH Stroke Scale
(define)
Neurological exam that assesses severity of neurological impairment. Results are predictive of long term outcome after stroke
higher score = more unfavorable outcome

Function of EKG in Stroke Dx
(3)
May reveal one or all of the following
- A-fib (clot formation that will embolize)
- A-flutter (clot formation that will embolize)
- Recent MI
Exclusion Criteria for T-PA
Goal of screening: avoid serious bleeding associated c drug admin

ICP and Stroke
(relationship, impt time period, significance)
Relationship: increased ICP can lead to cerebral edema, especially in the presence of a large infarction.
Timeframe: cerebral edema peaks b/w 48 and 72 hours
Significance: prolonged ICP associated c massive cerebral infarct can cause secondary coma
Mannitol
(indication, MOA)
Indication: reduce edema in hemorrhagic stroke
MOA: pull fluid from the brain
ABCD2 Score
(indication, components, results)
Indication: administered post TIA to determine risk of ischemic stroke within the next 7 days. also determines 2 day score in combined derivation and validation cohorts.
Components: age, BP, clnical features, duration of s/sx, diabetes
- Age > 60 yo = 1 point
-
BP elevation during intial TIA assessment = 1 point
- Systolic > 140 mmHg
- Diastolic > 90 mmHg
-
Clinical features
- __Unilateral weakness = 2 points
- Isolated speech distrubance = 1 point
- Others = 0 points
-
S/Sx duration
- **> **60 min = 2 points
- 10-59 min = 1 point
- < 10 min = 0 points
- Diabetes = 1 point
**Results **determined by total score
- 6-7 = high 2 day stroke risk (8%)
- 4-5 = moderate 2 day stroke risk (4%)
- 0-3 = low 2 day stroke risk (1%)
aneurysm and burst aneurysm
aquired weakening of vessel wall resulting in a ballooning or dilation in the vessel, bursts under increased arteriol pressure
- suseptability of bursting is proportional to aneurysm diameter
- bleeding is transcient (only a few seconds) but rebleeding is possible
- vasospasm post bleeding is the most dangerous effect of burst aneurysm
- occurs w/i 3 days after hemorrhage
- peaks in severity 1 week post hemorrhage
- due to chemical irritation of BV walls of breakdown prdcts of hemorrhaged bld

HA and Vomiting in Stroke Subtypes
Sentinatl HA = Similar, less severe HA in 2-3 months preceding stroke

Polyneuropathy
Neuropathy c mixed branches:
- Somatic
- motor
- sensory
- Autonomic
- sympathetic
- parasympathetic
Foot Complications in Diabetic Neuropathy
- Denervation of small foot muscles
- Clawing toes
- Altered gait biomechanics
- Increased plantar pressure
- Results in the following
- Calluses
- Ulcerations
Charcot Arthropathy
(definition, 7 step pathophys)
Definition: Complication of diabetic neuropathy.
Pathophys:
- Decreased bloodflow and altered pressure in foot
- Small muscle wasting, decreased sensation, maldistribution while weight bearing
- Collapse of medial longitudinal arch
- Diabetic arthra (abnormal bone structure) in the foot within the food
- Bony callus replaces arch of foot
- Foot wil rock like a rocking chair while attempting ambulation - Rocker Bottom Deformity
- May be painful of painless

Diabetic Neuropathic Pn
(description, 2 txs c 1 MOA)
Description: sharp, stabbing pn due to dysfunctional nerves
Medications: Phenytoin/Dilantin, Carbamezpine/Tegretol.
- Block Na channels
- Dec transmission at NMJ
both of these are anti-seizure meds
Diabetic Deep Aching Pn Tx
(3 c MOAs)
- Amitriptyline/Elavil (tricyclic antidepressant)
- Block serotonin and NE uptake
- Block muscarinic receptors
- Inhibit pn neurotransmission
- Gabapetin/Neurontin - GABA analog that inhibits pn and neurotransmission
- Duloxetine/Cymbalta - Serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
Gludrocortisone or Midrodine
(MOA, indication)
Indication: treat postural hypotension associated c diabetic neuropathy
MOA:
- Mieralcorticoid activates aldosterone receptors
- Inc Na reabsorption
Metochlopramide/Reglan
(indicaiton, MOA)
Indication: treat gastroparesis of diabetic neuropathy
MOA: Dopamine antagonist causing antiemetic and cholinergic activity to facilitate gastric emptying
Labile BP
(definition, associated condition)
**Associated **with Guillain Bare Sydrome
Defined as blood pressure that fluctuates abruptly and repeatedly, often causing symptoms such as headache or ringing in the ears
Elevated PRO in Guillain Barre Syndrome
(explaination, dx study)
Explaination: release of the protein myelin sheaths into the CSF
Dx Study: LP will reveal high protein levels in CSF




